High Performance VLSI Design Using Body Biasing in Domino
... energy-efficient ultra-low voltage domino circuits to be realized. In addition, forward biasing the NMOS transistors in the evaluation tree can reduce both delay and PDP. Minimum energy in the sub threshold region then depends not only on supply voltage but also on the sub threshold bias voltage. ...
... energy-efficient ultra-low voltage domino circuits to be realized. In addition, forward biasing the NMOS transistors in the evaluation tree can reduce both delay and PDP. Minimum energy in the sub threshold region then depends not only on supply voltage but also on the sub threshold bias voltage. ...
MS Word
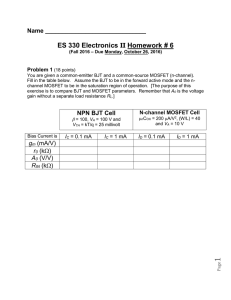
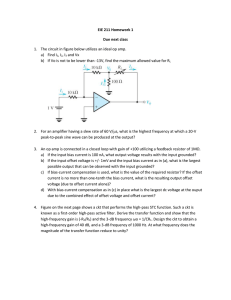
... You are given the circuit drawn below. It is fabricated in a CMOS process for which nCOX = 2pCOX = 200 A/V2, V’An = |V’Ap| = 20 V/m, Vtn = -Vtp = 0.5 volt and VDD = 2.5 volts. The two transitor types have L = 0.5 m and are to be operated at |VOV | = 0.3 volt. Find the required gate node voltage ...
... You are given the circuit drawn below. It is fabricated in a CMOS process for which nCOX = 2pCOX = 200 A/V2, V’An = |V’Ap| = 20 V/m, Vtn = -Vtp = 0.5 volt and VDD = 2.5 volts. The two transitor types have L = 0.5 m and are to be operated at |VOV | = 0.3 volt. Find the required gate node voltage ...
1-Bit Sub Threshold Full Adder in 65nm CMOS Technology
... Authorized licensed use limited to: San Francisco State Univ. Downloaded on March 06,2010 at 15:07:36 EST from IEEE Xplore. Restrictions apply. ...
... Authorized licensed use limited to: San Francisco State Univ. Downloaded on March 06,2010 at 15:07:36 EST from IEEE Xplore. Restrictions apply. ...
Slic-dc
... The ringing SLIC-DC with integrated DC/DC converter, is the latest addition to Infineon’s family of SLIC products. The SLIC-DC provides cost optimized solutions for CPE applications and requires only a single power supply voltage. All POTS supply voltages are generated by the onchip DC/DC converter ...
... The ringing SLIC-DC with integrated DC/DC converter, is the latest addition to Infineon’s family of SLIC products. The SLIC-DC provides cost optimized solutions for CPE applications and requires only a single power supply voltage. All POTS supply voltages are generated by the onchip DC/DC converter ...
Design of Operational Amplifier in 45nm Technology
... analog to digital converter. It compares the two analog signals and based upon the different conditions produce a binary value either logic 0 or logic 1. Comparator is the most important design for various applications like image and signal processing, general purpose processor, embedded processor; ...
... analog to digital converter. It compares the two analog signals and based upon the different conditions produce a binary value either logic 0 or logic 1. Comparator is the most important design for various applications like image and signal processing, general purpose processor, embedded processor; ...
Circuit Timing
... A timing diagram illustrates the logical behavior of signals as a function of time. Causality: which input transitions cause which output transitions. Different through a circuit paths may have different delays. A signal timing diagram may contain many different delay specifications. Delay depends o ...
... A timing diagram illustrates the logical behavior of signals as a function of time. Causality: which input transitions cause which output transitions. Different through a circuit paths may have different delays. A signal timing diagram may contain many different delay specifications. Delay depends o ...
Distributed Integrated Circuits: Wideband Communications for the
... namely, bandwidth, signal power, and noise, are the most important parameters in determining the performance of any given communications system. One of the more common methods of increasing the bandwidth, and hence the bit rate, of any given system is to migrate to higher operating frequencies. The ...
... namely, bandwidth, signal power, and noise, are the most important parameters in determining the performance of any given communications system. One of the more common methods of increasing the bandwidth, and hence the bit rate, of any given system is to migrate to higher operating frequencies. The ...
Digital Systems: Combinational Logic Circuits
... Short between two pins (other than ground or Vcc): whenever two signals that are supposed to be different show the same logic-level ...
... Short between two pins (other than ground or Vcc): whenever two signals that are supposed to be different show the same logic-level ...
Oscillators & Components
... Low power consumption is an advantage of CMOS integrated circuits compared to TTL integrated circuits. (G6C03) • CMOS is the most commonly used digital logic family of integrated circuits. ...
... Low power consumption is an advantage of CMOS integrated circuits compared to TTL integrated circuits. (G6C03) • CMOS is the most commonly used digital logic family of integrated circuits. ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.