![NMEA GPS Module - main [gps.0xdc.ru]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006332431_1-f6d741b7c1fd26623b37b5b0b457162e-300x300.png)
NMEA GPS Module - main [gps.0xdc.ru]
... Port B Serial Receive Data. VCC CMOS levels. Differential GPS messages. ...
... Port B Serial Receive Data. VCC CMOS levels. Differential GPS messages. ...
Dharmendra Dongardiye et al Int. Journal of Engineering Research and... ISSN : 2248-9622, Vol. 4, Issue 5( Version 1), May...
... Sample-and-hold (S/H) circuits play an important role in the design of data-converter systems. They can greatly minimize errors due to slightly different delay times. However, when designing S/H circuit for low supply voltage operation, quite quickly we encounter a severe difficulty: the switch-driv ...
... Sample-and-hold (S/H) circuits play an important role in the design of data-converter systems. They can greatly minimize errors due to slightly different delay times. However, when designing S/H circuit for low supply voltage operation, quite quickly we encounter a severe difficulty: the switch-driv ...
A CMOS Current-Mode Full-Adder Cell for Multi Valued Logic VLSI
... conforms to MOSIS design rules. When originally designed, this module could be run on ISIS graphics workstations or a Y AX. Currently, there is no operating version of this tool available for use on any modern graphical workstation available at NPS. However, the individual cells can still be assembl ...
... conforms to MOSIS design rules. When originally designed, this module could be run on ISIS graphics workstations or a Y AX. Currently, there is no operating version of this tool available for use on any modern graphical workstation available at NPS. However, the individual cells can still be assembl ...
Minimization of Charge Sharing ~ Problems in Dynamic BiCMOS
... Figure 2: Dynamic BiCMOS logic circuit with PMOS predischarge However, as the input chain is long, many precharge PMOS devices are required with their gates connected to 'Clk'; hence the area requirement is also increased, which may suppress the basic advantage of BiCMOS. In addition to this, a volt ...
... Figure 2: Dynamic BiCMOS logic circuit with PMOS predischarge However, as the input chain is long, many precharge PMOS devices are required with their gates connected to 'Clk'; hence the area requirement is also increased, which may suppress the basic advantage of BiCMOS. In addition to this, a volt ...
ET 4
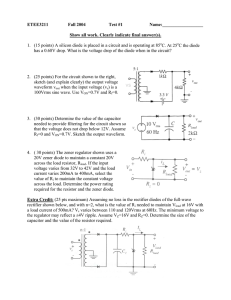
... 5. Explain the advantages of high power factor. A coil of 10 resistance and 0.2 H inductance is connected in parallel with a variable condenser across a 200 V, 50 Hz supply. Determine the capacitance of the condenser so that the current drawn may be in phase with the supply voltage. 6. A rudder mo ...
... 5. Explain the advantages of high power factor. A coil of 10 resistance and 0.2 H inductance is connected in parallel with a variable condenser across a 200 V, 50 Hz supply. Determine the capacitance of the condenser so that the current drawn may be in phase with the supply voltage. 6. A rudder mo ...
Chapter 4.10 - Other Analog Circuits
... Multipliers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Linear Four-Quadrant Multipliers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Smoke Detectors (CMOS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Package Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
... Multipliers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Linear Four-Quadrant Multipliers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Smoke Detectors (CMOS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Package Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Muddiest Points Week 8 2016
... Question: The most confusing concept this week was that of input resistance and output resistance. I had a hard time differentiating between the two. I understand why they matter, but I didn't understand how to find them when just looking at parts of circuits. I also didn't understand the difference ...
... Question: The most confusing concept this week was that of input resistance and output resistance. I had a hard time differentiating between the two. I understand why they matter, but I didn't understand how to find them when just looking at parts of circuits. I also didn't understand the difference ...
Issues in ATM Network Control - Engineering School Class Web Sites
... Manual synthesis is infeasible due to large numbers of gates ...
... Manual synthesis is infeasible due to large numbers of gates ...
Hardware Security Challenges Beyond CMOS: Attacks
... possible functionalities whereas fully programmable logic can implement any possible function with a fixed number of inputs. For instance, [14] presented gates that can change their functionality based on the supply voltage level. In this work we discuss how basic logic blocks implemented using polar ...
... possible functionalities whereas fully programmable logic can implement any possible function with a fixed number of inputs. For instance, [14] presented gates that can change their functionality based on the supply voltage level. In this work we discuss how basic logic blocks implemented using polar ...
Series and Parallel Circuits
... • The total load (resistance) in a series circuit with “n” loads is the sum of the resistance of the “n” objects. Rtot = R1 + R2 + … + Rn. ...
... • The total load (resistance) in a series circuit with “n” loads is the sum of the resistance of the “n” objects. Rtot = R1 + R2 + … + Rn. ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.