Lecture_1
... Ideal Voltage sources supply a fixed voltage V independent of the resistance of the load. (i.e., they have zero internal resistance.) However, real voltage sources have an internal non-zero resistance and the voltage delivered depends upon the resistance of the load. Ideal Current sources supply a f ...
... Ideal Voltage sources supply a fixed voltage V independent of the resistance of the load. (i.e., they have zero internal resistance.) However, real voltage sources have an internal non-zero resistance and the voltage delivered depends upon the resistance of the load. Ideal Current sources supply a f ...
“Fuzzy Logic Speed Controllers Using FPGA Technique
... Beyond the peak point, current increases as voltage decreases in the negative resistance region. The voltage reaches a minimum at the valley point. The resistance of RB1, the saturation resistance is lowest at the valley point. ...
... Beyond the peak point, current increases as voltage decreases in the negative resistance region. The voltage reaches a minimum at the valley point. The resistance of RB1, the saturation resistance is lowest at the valley point. ...
Design and Analysis of 4x1 MUX and 2x4 Decoder Circuits using
... Single Electron Transistor is an attractive candidate for future ultra low power VLSI and ULSI systems. However, practical SET circuit applications are likely not feasible with a pure Single Electronics approach, mainly due to its low current drive. And also it is unlikely that SET can replace the C ...
... Single Electron Transistor is an attractive candidate for future ultra low power VLSI and ULSI systems. However, practical SET circuit applications are likely not feasible with a pure Single Electronics approach, mainly due to its low current drive. And also it is unlikely that SET can replace the C ...
Non-isolated Constant Current Linear LED Driver BL8312
... *Stress beyond above listed “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may lead permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operations of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications are not implied. Exposure to absolute m ...
... *Stress beyond above listed “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may lead permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operations of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications are not implied. Exposure to absolute m ...
Manual for Power Supply 3630.00 9 8 7
... under normal use (high temperature combined with high loading for a long period of time), the power supply will automatically shut down when a given ...
... under normal use (high temperature combined with high loading for a long period of time), the power supply will automatically shut down when a given ...
Session 25 Answers - Iowa State University
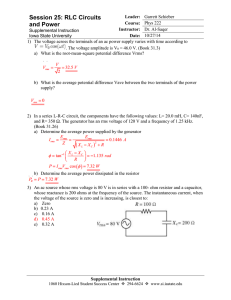
... b) Determine the average power dissipated in the resistor 3) An ac source whose rms voltage is 80 V is in series with a 100- ohm resistor and a capacitor, whose reactance is 200 ohms at the frequency of the source. The instantaneous current, when the voltage of the source is zero and is increasing, ...
... b) Determine the average power dissipated in the resistor 3) An ac source whose rms voltage is 80 V is in series with a 100- ohm resistor and a capacitor, whose reactance is 200 ohms at the frequency of the source. The instantaneous current, when the voltage of the source is zero and is increasing, ...
Fundamentals of Linear Electronics Integrated & Discrete
... • The base-emitter and base-collector junctions in a transistor can be checked for opens and shorts by measuring resistance with a DMM or VOM. • You can usually distinguish the base-emitter from the base-collector because the resistance will read lower from base to collector. Actually, what your met ...
... • The base-emitter and base-collector junctions in a transistor can be checked for opens and shorts by measuring resistance with a DMM or VOM. • You can usually distinguish the base-emitter from the base-collector because the resistance will read lower from base to collector. Actually, what your met ...
View - Toshiba America Electronic Components
... design to prevent device malfunction or breakdown caused by the current resulting from the inrush current at power ON or the negative current resulting from the back electromotive force at power OFF. IC breakdown may cause injury, smoke or ignition. Use a stable power supply with ICs with built-in p ...
... design to prevent device malfunction or breakdown caused by the current resulting from the inrush current at power ON or the negative current resulting from the back electromotive force at power OFF. IC breakdown may cause injury, smoke or ignition. Use a stable power supply with ICs with built-in p ...
Vout Vdd Vss 50 ohms - + 2 pF 500 ohms 500 ohms
... You are asked to design a wideband gain amplifier that drives a sample and hold circuit, modeled as a 50Ω resistor in series with 2 pF sampling capacitor, shown in Figure 1. The available circuit components are NMOS transistors, PMOS transistors or resistors. Ideal sources can only be used to genera ...
... You are asked to design a wideband gain amplifier that drives a sample and hold circuit, modeled as a 50Ω resistor in series with 2 pF sampling capacitor, shown in Figure 1. The available circuit components are NMOS transistors, PMOS transistors or resistors. Ideal sources can only be used to genera ...
VLSI Iterative Decoder Design
... Fujio Ishihara, Farhana Sheikh, Borivoje Nikolic, “Level Conversion for Dual –Supply Systems,” IEEE Transactions on VLSI Systems, Vol. 12, No. 2, February 2004. ...
... Fujio Ishihara, Farhana Sheikh, Borivoje Nikolic, “Level Conversion for Dual –Supply Systems,” IEEE Transactions on VLSI Systems, Vol. 12, No. 2, February 2004. ...
Design Guidelines for JFET Audio Preamplifier Circuits By Mike
... When designing a JFET circuit, it is highly recommended to prevent the absolute maximum current from being exceeded under any conditions. In design calculations. never use more than 75% of the maximum drain current as specified by the manufacturer. JFET Design Example 1 For the first design example, ...
... When designing a JFET circuit, it is highly recommended to prevent the absolute maximum current from being exceeded under any conditions. In design calculations. never use more than 75% of the maximum drain current as specified by the manufacturer. JFET Design Example 1 For the first design example, ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.