gunadarma.ac.id
... function onto the same single chip as a high performance image sensor[4]. CMOS image sensors with integrated signal processing have been implemented for a number of applications[5]. Most current CMOS imaging arrays have been designed for video applications, and digital photography. Improvement conti ...
... function onto the same single chip as a high performance image sensor[4]. CMOS image sensors with integrated signal processing have been implemented for a number of applications[5]. Most current CMOS imaging arrays have been designed for video applications, and digital photography. Improvement conti ...
III B.Tech II Semester STUDENT HANDBOOK for VLSI Design
... Gates, Scaling of MOS circuits, Limitations of Scaling. Objectives: To understand the VLSI Design Flow. To understand the Design Rules and Layout. To discuss Stick Diagrams and Transistors Layout Diagrams for NMOS and CMOS Inverters and Gates. To discuss Scaling of MOS circuits. ...
... Gates, Scaling of MOS circuits, Limitations of Scaling. Objectives: To understand the VLSI Design Flow. To understand the Design Rules and Layout. To discuss Stick Diagrams and Transistors Layout Diagrams for NMOS and CMOS Inverters and Gates. To discuss Scaling of MOS circuits. ...
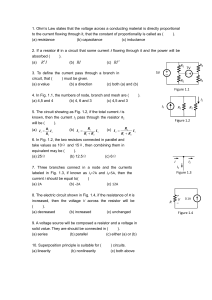
1. Ohm`s Law states that the voltage across a conducting material is
... 1. Ohm’s Law states that the voltage across a conducting material is directly proportional to the current flowing through it, that the constant of proportionality is called as ( ...
... 1. Ohm’s Law states that the voltage across a conducting material is directly proportional to the current flowing through it, that the constant of proportionality is called as ( ...
CN-0115
... by Analog Devices for their use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from their use. Analog Devices reserves the right to change any "Circuits from the Lab" at any time without notice, but is under no obligation to do so. Trademarks and registered tr ...
... by Analog Devices for their use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from their use. Analog Devices reserves the right to change any "Circuits from the Lab" at any time without notice, but is under no obligation to do so. Trademarks and registered tr ...
Outline - UMT Admin Panel
... Sweep generators. Saturating and non-saturating logic families (DTL, TTL, ECL, I2L, CMOS). Transfer characteristics, Speed, Power consumption, Detailed study of timer ICs and their applications, Analogue and digital circuit interface with applications, Oscillators. Pulse Modulation and multiplexing. ...
... Sweep generators. Saturating and non-saturating logic families (DTL, TTL, ECL, I2L, CMOS). Transfer characteristics, Speed, Power consumption, Detailed study of timer ICs and their applications, Analogue and digital circuit interface with applications, Oscillators. Pulse Modulation and multiplexing. ...
ABSTRACT
... • Consider a reasonable lifetime of five years with cutoff resistance of 10kΩ. • Use Synopsys Custom Designer for schematic design and HSPICE for running simulations. ...
... • Consider a reasonable lifetime of five years with cutoff resistance of 10kΩ. • Use Synopsys Custom Designer for schematic design and HSPICE for running simulations. ...
PHYSICS 100 CIRCUITS
... A circuit is a closed loop where current flows continuously from high voltage to low voltage. A battery or power supply is needed to supply the potential energy difference. For conductors, Ohm’s Law states that the voltage difference across a circuit element is proportional to the current that flows ...
... A circuit is a closed loop where current flows continuously from high voltage to low voltage. A battery or power supply is needed to supply the potential energy difference. For conductors, Ohm’s Law states that the voltage difference across a circuit element is proportional to the current that flows ...
0 - 30 v Adjustable voltage, current stabilized voltage supply
... This is a a A high quality product which can continue to adjust Voltage supply.Adjust Voltage is 0-30V, It contains Output current limiting circuit, which can effectively control the output current from 2mA to 3A(Continuous adjustable). This feature makes the stabilized voltage supply as an indispen ...
... This is a a A high quality product which can continue to adjust Voltage supply.Adjust Voltage is 0-30V, It contains Output current limiting circuit, which can effectively control the output current from 2mA to 3A(Continuous adjustable). This feature makes the stabilized voltage supply as an indispen ...
Low-Power and High Speed High-to-Low Level Shifter
... multi-voltage signals, level shifters are used which have simple function to convert the signal from one voltage level to another. Another use of level shifters is the data signal connection between core circuits and I/O circuitry. Hence, they can have dual functionality to provide both high-to-low ...
... multi-voltage signals, level shifters are used which have simple function to convert the signal from one voltage level to another. Another use of level shifters is the data signal connection between core circuits and I/O circuitry. Hence, they can have dual functionality to provide both high-to-low ...
MOS Transistors Outline
... • MOS transistors are conceptually simple devices • Both NMOS and PMOS transistors can be made, and effectively combined in CMOS circuits • Transistor scaling leads to great benefits, and has driven Moore’s law during the last three decades • Transistor down-scaling leads to some problems, which hav ...
... • MOS transistors are conceptually simple devices • Both NMOS and PMOS transistors can be made, and effectively combined in CMOS circuits • Transistor scaling leads to great benefits, and has driven Moore’s law during the last three decades • Transistor down-scaling leads to some problems, which hav ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.