Word - University of California, Berkeley
... Attach an ammeter in series between the power supply and the Vdd pin, power up, measure the average current draw from the supply. Assuming that the short circuit current is negligible, determine the average power dissipation. iii. Using the calculated power dissipation, it is now possible to determi ...
... Attach an ammeter in series between the power supply and the Vdd pin, power up, measure the average current draw from the supply. Assuming that the short circuit current is negligible, determine the average power dissipation. iii. Using the calculated power dissipation, it is now possible to determi ...
Growth and magnetic properties of epitaxitial MnAs thin films grown
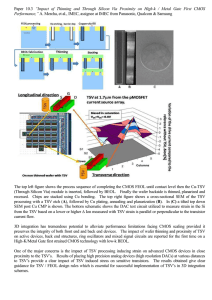
... (Through Silicon Via) module is inserted, followed by BEOL. Finally the wafer backside is thinned, planarized and recessed. Chips are stacked using Cu bonding. The top right figure shows a cross-sectional SEM of the TSV processing with a TSV etch (A), followed by Cu plating, annealing and planarizat ...
... (Through Silicon Via) module is inserted, followed by BEOL. Finally the wafer backside is thinned, planarized and recessed. Chips are stacked using Cu bonding. The top right figure shows a cross-sectional SEM of the TSV processing with a TSV etch (A), followed by Cu plating, annealing and planarizat ...
lecture13 - Brown University
... • Leakage depends exponentially on Vth. How to control Vth? – Remember: Vth also controls your saturation current delay ...
... • Leakage depends exponentially on Vth. How to control Vth? – Remember: Vth also controls your saturation current delay ...
Part 2 – Operational Transconductance Amplifier
... To understand the operation of differential pairs and how they are used to construct operational transconductance amplifiers. Simulation Models As will be standard with all projects involving circuit simulations, we will be using the 0.5μm EKV model for MOSFETs because it correctly handles both subt ...
... To understand the operation of differential pairs and how they are used to construct operational transconductance amplifiers. Simulation Models As will be standard with all projects involving circuit simulations, we will be using the 0.5μm EKV model for MOSFETs because it correctly handles both subt ...
Basic Electricity Study Guide
... Current is the actual number or amount of electrons that are moving at any given time. 4. How did we define resistance in terms of electron movement? Resistance is the slowing down or hindrance to the movement of electrons. This is not a bad thing since resistance results in a transfer of energy to ...
... Current is the actual number or amount of electrons that are moving at any given time. 4. How did we define resistance in terms of electron movement? Resistance is the slowing down or hindrance to the movement of electrons. This is not a bad thing since resistance results in a transfer of energy to ...
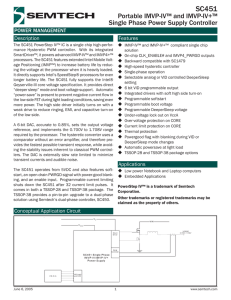
SC451 - Semtech
... “deeper sleep” mode and boot voltage support. Automatic “power-save” is present to prevent negative current flow in the low-side FET during light loading conditions, saving even more power. The high side driver initially turns on with a weak drive to reduce ringing, EMI, and capacitive turn-on of th ...
... “deeper sleep” mode and boot voltage support. Automatic “power-save” is present to prevent negative current flow in the low-side FET during light loading conditions, saving even more power. The high side driver initially turns on with a weak drive to reduce ringing, EMI, and capacitive turn-on of th ...
What Is Digital?
... inside a fixed interval of time between two clock pulses, called a clock cycle As long as this condition is met (ignoring certain details), the circuit is guaranteed to be reliable Only care about value of combinational circuits just before rising edge of clock Change saved state after noise-inducin ...
... inside a fixed interval of time between two clock pulses, called a clock cycle As long as this condition is met (ignoring certain details), the circuit is guaranteed to be reliable Only care about value of combinational circuits just before rising edge of clock Change saved state after noise-inducin ...
Semiconductor Devices II
... subsequent collisions quickly become an avalanche. When this process is taking place, very small changes in voltage can cause very large changes in current. The breakdown process depends upon the applied electric field, so by changing the thickness of the layer to which the voltage is applied, zener ...
... subsequent collisions quickly become an avalanche. When this process is taking place, very small changes in voltage can cause very large changes in current. The breakdown process depends upon the applied electric field, so by changing the thickness of the layer to which the voltage is applied, zener ...
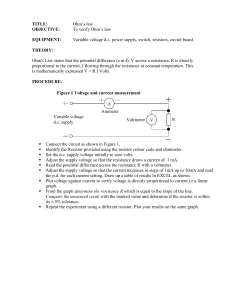
L3 Ohms_law
... Identify the Resistor provided using the resistor colour code and ohmmeter. Set the d.c. supply voltage initially to zero volts. Adjust the supply voltage so that the resistance draws a current of 1 mA. Read the potential difference across the resistance R with a voltmeter. Adjust the supply voltage ...
... Identify the Resistor provided using the resistor colour code and ohmmeter. Set the d.c. supply voltage initially to zero volts. Adjust the supply voltage so that the resistance draws a current of 1 mA. Read the potential difference across the resistance R with a voltmeter. Adjust the supply voltage ...
Equations and Key Concepts (Excellence Project)
... Voltage is the potential or difference. It is the energy or pressure in a circuit. In S.I. units it is 1 joule/coulomb. (See p. 4). Current is the flow of electrons in a circuit. It is measured in amperes. 1 ampere = 6.24 x 1018/sec. Resistance is the tendency of a material to resist the flow of ele ...
... Voltage is the potential or difference. It is the energy or pressure in a circuit. In S.I. units it is 1 joule/coulomb. (See p. 4). Current is the flow of electrons in a circuit. It is measured in amperes. 1 ampere = 6.24 x 1018/sec. Resistance is the tendency of a material to resist the flow of ele ...
RF and A&M Signal Technologies for Wireless Communications
... 2) Analog precision MOS device scaling but with relatively high voltages to achieve high signal to noise ratios and low signal distortion 3) Capacitors, and resistors; all devices are optimized for precision, matching performance, 1/f noise, low nonlinearity, and low temperature gradients. ...
... 2) Analog precision MOS device scaling but with relatively high voltages to achieve high signal to noise ratios and low signal distortion 3) Capacitors, and resistors; all devices are optimized for precision, matching performance, 1/f noise, low nonlinearity, and low temperature gradients. ...
1 - University of California, Berkeley
... b) Cascade the output of the circuit into a second stage to implement F=[((A+B)C)’+D]’ Shown above in Figure 2 c) ...
... b) Cascade the output of the circuit into a second stage to implement F=[((A+B)C)’+D]’ Shown above in Figure 2 c) ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.