DN126 - The LT1166: Power Output Stage Automatic Bias System Control IC
... Class AB amplifiers are popular because of their “near Class A” performance and their ability to operate on considerably less quiescent power than Class A. Class AB amplifiers are easy to construct, rugged and reliable. However, there is an aspect of these amplifiers that can cause perplexity, const ...
... Class AB amplifiers are popular because of their “near Class A” performance and their ability to operate on considerably less quiescent power than Class A. Class AB amplifiers are easy to construct, rugged and reliable. However, there is an aspect of these amplifiers that can cause perplexity, const ...
CMOS
... Low-Power Schottky TTL, 74LS series Advanced Schottky TTL, 74AS Series Advanced Low-Power Schottky TTL, 74ALS ...
... Low-Power Schottky TTL, 74LS series Advanced Schottky TTL, 74AS Series Advanced Low-Power Schottky TTL, 74ALS ...
Homework 5
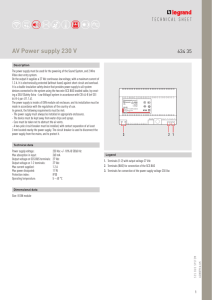
... Label the voltage V = 25.0 V and the resistances (clockwise from b) R1 = 20.0Ω, R2 = 5.00Ω, R3 = 10.0Ω, R4 = 10.0Ω, and R5 = 5.00Ω. Computing some equivalent resistance of R1 and R2 in series we have Rs = R1 + R2 = 25.0Ω Computing the equivalent resistance of Rs , R4 , and R5 in parallel we have ...
... Label the voltage V = 25.0 V and the resistances (clockwise from b) R1 = 20.0Ω, R2 = 5.00Ω, R3 = 10.0Ω, R4 = 10.0Ω, and R5 = 5.00Ω. Computing some equivalent resistance of R1 and R2 in series we have Rs = R1 + R2 = 25.0Ω Computing the equivalent resistance of Rs , R4 , and R5 in parallel we have ...
References
... NDR device is composed of metal-oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOS) devices. The discrete-time cellular neural ...
... NDR device is composed of metal-oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOS) devices. The discrete-time cellular neural ...
AV Power supply 230 V
... Video door entry system. On the output it supplies a 27 Vdc continuous low voltage, with a maximum current of 1.2 A. It is electronically protected (without fuses) against short circuit and overload. It is a double insulation safety device that provides power supply to all system devices connected t ...
... Video door entry system. On the output it supplies a 27 Vdc continuous low voltage, with a maximum current of 1.2 A. It is electronically protected (without fuses) against short circuit and overload. It is a double insulation safety device that provides power supply to all system devices connected t ...
Datasheet - DE-SW0XX
... For input voltages above 25V, an output current of at least 40mA is needed to maintain the regulated output voltage. This can be accomplished by adding a 1kΩ load resistor, or by simply connecting the load you wanted to use anyway. Absolute Maximum ratings Operation beyond these parameters may perma ...
... For input voltages above 25V, an output current of at least 40mA is needed to maintain the regulated output voltage. This can be accomplished by adding a 1kΩ load resistor, or by simply connecting the load you wanted to use anyway. Absolute Maximum ratings Operation beyond these parameters may perma ...
A CMOS Scheme for 0.5V Supply Voltage with Pico
... designs. Since the power consumption of CMOS VLSIs quadratically depends on the supply voltage, low-voltage circuits have been exploited. If a VLSI is operated in 0.5V~0.8V VDD range for lowpower consumption, the threshold voltage of MOSFETs, VTH, should be well below 0.5V to turn the MOSFETs on. VT ...
... designs. Since the power consumption of CMOS VLSIs quadratically depends on the supply voltage, low-voltage circuits have been exploited. If a VLSI is operated in 0.5V~0.8V VDD range for lowpower consumption, the threshold voltage of MOSFETs, VTH, should be well below 0.5V to turn the MOSFETs on. VT ...
IC Logic Families
... Low-Power Schottky TTL, 74LS series Advanced Schottky TTL, 74AS Series Advanced Low-Power Schottky TTL, 74ALS ...
... Low-Power Schottky TTL, 74LS series Advanced Schottky TTL, 74AS Series Advanced Low-Power Schottky TTL, 74ALS ...
The smart AC solution
... Input / Output Radio Frequency Interference compliant to FCC Complete supervision possibility Parallel operation in True Redundant System Large DC input voltage range Patented technology This new family of design-improved modular inverters can be supplied from any DC source in voltage range from 180 ...
... Input / Output Radio Frequency Interference compliant to FCC Complete supervision possibility Parallel operation in True Redundant System Large DC input voltage range Patented technology This new family of design-improved modular inverters can be supplied from any DC source in voltage range from 180 ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.