Minimum Operating Supply Voltage of MCML Circuits
... Streszczenie. W artykule przedstawiono schemat obwodu logicznego typu MCML niskiej mocy. Struktura zawiera tranzystory NMOS pull-down ...
... Streszczenie. W artykule przedstawiono schemat obwodu logicznego typu MCML niskiej mocy. Struktura zawiera tranzystory NMOS pull-down ...
Lecture 37: CMOS Digital Logic Inverter.
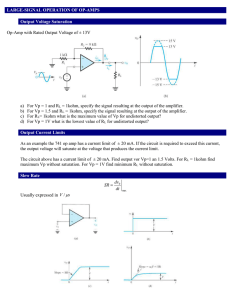
... (Gives rise to the so-called noise margins.) 2. The static power dissipation is nearly zero (a fraction of a W) in both states. The dynamic power dissipation is not zero as the gates are changing states. 3. Low output resistance in either state: low resistance to ground in the “low” output state, a ...
... (Gives rise to the so-called noise margins.) 2. The static power dissipation is nearly zero (a fraction of a W) in both states. The dynamic power dissipation is not zero as the gates are changing states. 3. Low output resistance in either state: low resistance to ground in the “low” output state, a ...
V in - WSU EECS - Washington State University
... Two zero gain regions and one infinite gain region ...
... Two zero gain regions and one infinite gain region ...
IEEE NANO 2007 Paper
... resistance between its two states (low resistance in parallel P state and high resistance in anti-parallel AP state). The ratio between these two resistance values, named Tunnel MagnetoResistance (TMR) [2] is an important factor for design of the reading circuit. TMR as high as 230% has been obtaine ...
... resistance between its two states (low resistance in parallel P state and high resistance in anti-parallel AP state). The ratio between these two resistance values, named Tunnel MagnetoResistance (TMR) [2] is an important factor for design of the reading circuit. TMR as high as 230% has been obtaine ...
14.1 Series Circuits
... • The total of all voltage drops must add up to the battery’s voltage. • This is known as Kirchhoff’s voltage law (named after German physicist Gustav Robert Kirchhoff ...
... • The total of all voltage drops must add up to the battery’s voltage. • This is known as Kirchhoff’s voltage law (named after German physicist Gustav Robert Kirchhoff ...
Midterm 1 - University of California, Berkeley
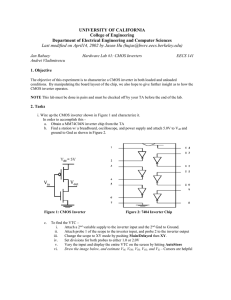
... a) (8pts) If the width of the NMOS transistor in the second stage is Wn = 1, find the size of the PMOS transistor, such that the second inverter exhibits the same LH and HL ...
... a) (8pts) If the width of the NMOS transistor in the second stage is Wn = 1, find the size of the PMOS transistor, such that the second inverter exhibits the same LH and HL ...
2 The TTL Inverter
... The logical functioning of the circuit can be established by determining the state of conduction of each transistor in turn from input to output for all possible combinations of input states. Transistors can be taken as either ON or OFF. Note that the input transistor, T1, may conduct in either forw ...
... The logical functioning of the circuit can be established by determining the state of conduction of each transistor in turn from input to output for all possible combinations of input states. Transistors can be taken as either ON or OFF. Note that the input transistor, T1, may conduct in either forw ...
Inverter Design Report
... The nmos transistor was drawn first. An active region layer of size 15Lx5L was defined, situated horizontally. Next a 2Lx9L polysilicon layer was drawn, bisecting and overlapping the active region. Two contact-to-active points of 2Lx2L were then drawn on either side of the active region. The left c ...
... The nmos transistor was drawn first. An active region layer of size 15Lx5L was defined, situated horizontally. Next a 2Lx9L polysilicon layer was drawn, bisecting and overlapping the active region. Two contact-to-active points of 2Lx2L were then drawn on either side of the active region. The left c ...
A Forward-Body-Bias Tuned 450MHz Gm-C 3rd-Order Low
... percent. In this paper, we show that by exploiting body biasing in an Ultra-Thin BOX and Body, Fully-Depleted SOI (UTBB FDSOI) CMOS technology, we overcome the requirement for a tunable V DD in inverter-based Gm-C filters, while achieving a high linearity over a wide supply voltage range. ...
... percent. In this paper, we show that by exploiting body biasing in an Ultra-Thin BOX and Body, Fully-Depleted SOI (UTBB FDSOI) CMOS technology, we overcome the requirement for a tunable V DD in inverter-based Gm-C filters, while achieving a high linearity over a wide supply voltage range. ...
EEL 6935: HW#2
... but not equal to one and derive your answer. Show all of your work and explicitly state all assumptions, e.g. which transistors are in saturation, subthreshold operation, matching of devices, etc. You will have to think a little bit more about this circuit than those in HW#1. ...
... but not equal to one and derive your answer. Show all of your work and explicitly state all assumptions, e.g. which transistors are in saturation, subthreshold operation, matching of devices, etc. You will have to think a little bit more about this circuit than those in HW#1. ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.