Mata Kuliah Tehnik Digital Jurusan Fisika FMIPA Univ. Jember
... Logic probe (kalau ada, if gak ada ya buat…) ...
... Logic probe (kalau ada, if gak ada ya buat…) ...
... forward biased unless the P-substrate is pulled up to 0.6V. Therefore, cautious layout, with multiple P+ contacts on the P-substrate, is required in order to avoid its voltage from building up. For 1.8V devices, the voltages IV,l, lvdsl and lvbsl must always be kept below 1.8V in order to prevent th ...
Mar 2008 - Tiny, Fast and Efficient Comparator Regenerates Clock Signals up to 3MHz
... The LTC6702’s push-pull output stage and its ability to operate with either input above the positive supply rail simplifies logic level translation. Many comparators use an open collector or open drain type output stage to enable ...
... The LTC6702’s push-pull output stage and its ability to operate with either input above the positive supply rail simplifies logic level translation. Many comparators use an open collector or open drain type output stage to enable ...
**** 1
... Reports on this design project should include the followings : 1. A schematic circuit that satisfies the specification. 2. PSpice simulation results that show the meets the design specification. 3. Detailed explanations on how the values of circuit elements are derived. ...
... Reports on this design project should include the followings : 1. A schematic circuit that satisfies the specification. 2. PSpice simulation results that show the meets the design specification. 3. Detailed explanations on how the values of circuit elements are derived. ...
Design 3 - godinweb
... Resistance on a ground conductor affects signals due to resistive voltage drops. In copper conductors the length and cross-sectional area affect resistance. ...
... Resistance on a ground conductor affects signals due to resistive voltage drops. In copper conductors the length and cross-sectional area affect resistance. ...
Electrical 2
... • CMOS uses very little power in the static state (in the order of W). • As switching increases (more dynamic), so does power consumption. This is primarily due to capacitance. • Power requirements also increase with ambient temperature. As temperature increases, so does power consumption. • Static ...
... • CMOS uses very little power in the static state (in the order of W). • As switching increases (more dynamic), so does power consumption. This is primarily due to capacitance. • Power requirements also increase with ambient temperature. As temperature increases, so does power consumption. • Static ...
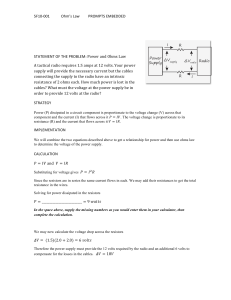
Voltage: Current: Resistance: Ohm`s Law:
... Explain the difference between the money and the hula hoop analogies and what that has to do with electric circuits. ...
... Explain the difference between the money and the hula hoop analogies and what that has to do with electric circuits. ...
Optical Encoders SERIES 61C
... CIRCUITRY, TRUTH TABLE, AND WAVEFORM: Standard Quadrature 2-Bit Code Clockwise Rotation Position Output A Output B ...
... CIRCUITRY, TRUTH TABLE, AND WAVEFORM: Standard Quadrature 2-Bit Code Clockwise Rotation Position Output A Output B ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.