Signal Types and Terminations
... Low Voltage PECL (LVPECL) refers to PECL circuits designed for use with 3.3V or 2.5V supply, the same supply voltages as for low voltage CMOS devices. LVPECL forms the basis of a number of protocols including Gigabit Ethernet and Fibre Channel. The LVPECL electrical specification is similar to LVDS, ...
... Low Voltage PECL (LVPECL) refers to PECL circuits designed for use with 3.3V or 2.5V supply, the same supply voltages as for low voltage CMOS devices. LVPECL forms the basis of a number of protocols including Gigabit Ethernet and Fibre Channel. The LVPECL electrical specification is similar to LVDS, ...
Digital IC Family
... • Before ICs, every circuit connection was from one discrete component to another. ...
... • Before ICs, every circuit connection was from one discrete component to another. ...
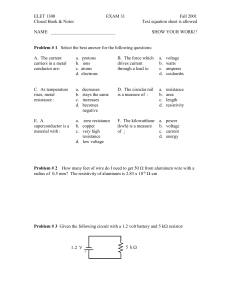
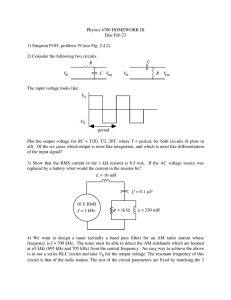
Physics 4700 HOMEWORK III Due Feb 23
... 3) Show that the RMS current in the 1 kΩ resistor is 6.5 mA. If the AC voltage source was replaced by a battery what would the current in the resistor be? ...
... 3) Show that the RMS current in the 1 kΩ resistor is 6.5 mA. If the AC voltage source was replaced by a battery what would the current in the resistor be? ...
Lecture-3: Transistors - Dr. Imtiaz Hussain
... three doped semiconductor regions separated by two pn junctions • Regions are called emitter, base and collector ...
... three doped semiconductor regions separated by two pn junctions • Regions are called emitter, base and collector ...
You Thought You Knew Analog-----------------------------------
... Achieves full swing input/output operation at a supply voltage of 1.7V. Designed for applications used in conjunction with low-voltage digital devices such as DRAM. Also ideal for applications with a bias current of 1pA (typ.) and extremely small sensor amps. Conventional full-swing CMOS opamps swit ...
... Achieves full swing input/output operation at a supply voltage of 1.7V. Designed for applications used in conjunction with low-voltage digital devices such as DRAM. Also ideal for applications with a bias current of 1pA (typ.) and extremely small sensor amps. Conventional full-swing CMOS opamps swit ...
Comparative Study of 4-Bit ALU using CMOS and BiCMOS for
... An Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) is the heart of all microprocessors. It is a combinational logic unit that performs its logical or arithmetic operations. ALU is getting smaller and more complex nowadays to enable the development of a more powerful but smaller computer. However there are a few limitin ...
... An Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) is the heart of all microprocessors. It is a combinational logic unit that performs its logical or arithmetic operations. ALU is getting smaller and more complex nowadays to enable the development of a more powerful but smaller computer. However there are a few limitin ...
ISSCC 2007 / SESSION 30 / BUILDING BLOCKS FOR HIGH
... force for the telecommunication industry to expand the optical networks closer to customers’ home and businesses. Developing low-cost optical transceivers accelerates the deployment of alloptical networks by reducing the overall cost of the optical networks. Deep submicron CMOS technology has a lowe ...
... force for the telecommunication industry to expand the optical networks closer to customers’ home and businesses. Developing low-cost optical transceivers accelerates the deployment of alloptical networks by reducing the overall cost of the optical networks. Deep submicron CMOS technology has a lowe ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.