An 8-bit 50-MS/s CMOS DIGITAL-ANALOG CONVERTER
... In this paper a new 8-bit CMOS DAC has been presented. The presented DAC is constructed using only active elements, which makes it suitable for integration. The performance of the DAC is tested using SPICE simulation program. The conversion rate of the proposed DAC is 50 Msample/s with settling time ...
... In this paper a new 8-bit CMOS DAC has been presented. The presented DAC is constructed using only active elements, which makes it suitable for integration. The performance of the DAC is tested using SPICE simulation program. The conversion rate of the proposed DAC is 50 Msample/s with settling time ...
CMP1202 Electronics II
... i-v characteristics Regions of operation, models, and limitation Transfer characteristic of BJT with load resistor Biasing for logic and amplifier applications Logic level definitions The differential pair as a current switch Transistor-transistor logic – inverters, NAND, other functio ...
... i-v characteristics Regions of operation, models, and limitation Transfer characteristic of BJT with load resistor Biasing for logic and amplifier applications Logic level definitions The differential pair as a current switch Transistor-transistor logic – inverters, NAND, other functio ...
Bds96 - Instituto de Ingeniería Eléctrica
... and weak inversion in the subthreshold region, together with the low saturation voltages allow to satisfy condition (1) even for VT0 of 1.0V. The next section describes the methodology followed to size the transistors to achieve the performance desired and to satisfy condition (1). A digitally progr ...
... and weak inversion in the subthreshold region, together with the low saturation voltages allow to satisfy condition (1) even for VT0 of 1.0V. The next section describes the methodology followed to size the transistors to achieve the performance desired and to satisfy condition (1). A digitally progr ...
Lab1
... 1. Review the logic gates that are widely used in electronic systems 2. Review the operation of some common logic gates. B. Introduction A logic gate is a device that performs a logical operation on one or more logical inputs, and produces a single logical output. Logic gates are used in most electr ...
... 1. Review the logic gates that are widely used in electronic systems 2. Review the operation of some common logic gates. B. Introduction A logic gate is a device that performs a logical operation on one or more logical inputs, and produces a single logical output. Logic gates are used in most electr ...
Slide 1
... Length – short wires have less resistance Area- thick wires have less resistance Material- different materials have different conductivity of charge Temperature- heat slows the flow of charge. ...
... Length – short wires have less resistance Area- thick wires have less resistance Material- different materials have different conductivity of charge Temperature- heat slows the flow of charge. ...
Analog Electronics
... a lab exercise on building and designing voltage and current regulated power supplies for test fixtures. It shows the basics of what is inside linear regulators, covers most of the popular voltage regulators found in the gaming industry, and briefly covers switching regulators. Knowledge up through ...
... a lab exercise on building and designing voltage and current regulated power supplies for test fixtures. It shows the basics of what is inside linear regulators, covers most of the popular voltage regulators found in the gaming industry, and briefly covers switching regulators. Knowledge up through ...
Notes18
... through which electric current flows (p374). There must of source of electrical potential difference (voltage)—such as a battery—in order to produce a current flow. Other components in the circuit dissipate this change in potential energy (caused by the battery), by doing work or dissipating the ene ...
... through which electric current flows (p374). There must of source of electrical potential difference (voltage)—such as a battery—in order to produce a current flow. Other components in the circuit dissipate this change in potential energy (caused by the battery), by doing work or dissipating the ene ...
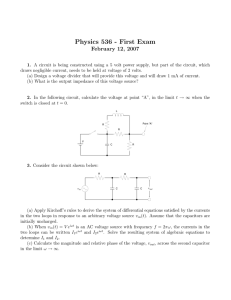
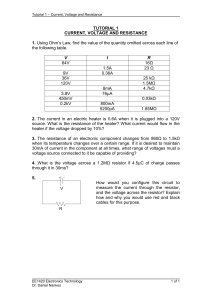
Tutorial 1
... heater if the voltage dropped by 10%? 3. The resistance of an electronic component changes from 860Ω to 1.5kΩ when its temperature changes over a certain range. If it is desired to maintain 30mA of current in the component at all times, what range of voltages must a voltage source connected to it be ...
... heater if the voltage dropped by 10%? 3. The resistance of an electronic component changes from 860Ω to 1.5kΩ when its temperature changes over a certain range. If it is desired to maintain 30mA of current in the component at all times, what range of voltages must a voltage source connected to it be ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.