The peripheral nerves
... *nerve fiber regeneration starts by growing of proximal neurilemma tube till its cut ends. Then, it sprouts into several branches , at the same time the distal part grows towards sprouting neurofibrils by chemotaxis secreted by schwann cells. *The myelin sheath is regenerated by neurilemmal cells *s ...
... *nerve fiber regeneration starts by growing of proximal neurilemma tube till its cut ends. Then, it sprouts into several branches , at the same time the distal part grows towards sprouting neurofibrils by chemotaxis secreted by schwann cells. *The myelin sheath is regenerated by neurilemmal cells *s ...
HUMAN ANATOMY
... • Secretion – nerve endings secret neurotransmitters, that stimulates other cells. ...
... • Secretion – nerve endings secret neurotransmitters, that stimulates other cells. ...
4-Nervous system I: Structure and organization
... Q: What is the nervous system? A network of billions of nerve cells linked together in a highly organized fashion to form the rapid control center of the body In the brain, roughly 100 billion (1011) neurons and 100 trillion (1014) synapses (connections between nerve cells) ...
... Q: What is the nervous system? A network of billions of nerve cells linked together in a highly organized fashion to form the rapid control center of the body In the brain, roughly 100 billion (1011) neurons and 100 trillion (1014) synapses (connections between nerve cells) ...
Introduction_to_nerv..
... 3 To act upon the information, usually by coordinating the organism’s activities. ...
... 3 To act upon the information, usually by coordinating the organism’s activities. ...
How the Nervous System Works
... The nervous system receives information about what is happening both inside and outside your body. It also directs the way in which your body responds to this information. In addition, the nervous system helps maintain homeostasis. A stimulus is any change or signal in the environment that can make ...
... The nervous system receives information about what is happening both inside and outside your body. It also directs the way in which your body responds to this information. In addition, the nervous system helps maintain homeostasis. A stimulus is any change or signal in the environment that can make ...
The NERVOUS System
... decides on response based on past experience, reflexes, and current conditions. ...
... decides on response based on past experience, reflexes, and current conditions. ...
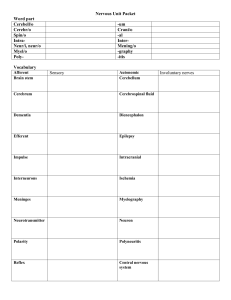
Nervous System Vocab1 - Everglades High School
... integrating and command center of the nervous system. 5. Peripheral Nervous System: The part of the nervous system outside the CNS, nerves that extend from the brain and spinal cord, serve as communication lines. 6. Afferent: Convey impulses to the CNS 7. Efferent: Carries impulses from the CNS 8. S ...
... integrating and command center of the nervous system. 5. Peripheral Nervous System: The part of the nervous system outside the CNS, nerves that extend from the brain and spinal cord, serve as communication lines. 6. Afferent: Convey impulses to the CNS 7. Efferent: Carries impulses from the CNS 8. S ...
chapter the nervous system and the effects of drugs
... The nervous system is like a very complicated computer. As in a computer, electrical signals travel throughout the system. Instead of the wires you would see in a computer, the nervous system is made up of nerve cells, or neurons. The neurons have gaps between them, called synapses, which an electri ...
... The nervous system is like a very complicated computer. As in a computer, electrical signals travel throughout the system. Instead of the wires you would see in a computer, the nervous system is made up of nerve cells, or neurons. The neurons have gaps between them, called synapses, which an electri ...
PsychSim 5 neural messages
... This activity explains the way that neurons communicate with each other. ...
... This activity explains the way that neurons communicate with each other. ...
The nervous system
... leaves the skull through the foramen magnum extending to the level of the second lumbar vertebra. At this point, it gives rise to numerous individual nerve roots, called the cauda equina. A ...
... leaves the skull through the foramen magnum extending to the level of the second lumbar vertebra. At this point, it gives rise to numerous individual nerve roots, called the cauda equina. A ...
The Nervous System crossword
... 10. The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. 11. Neurotransmitters are stored and packaged into a vesicle before being released into the synaptic cleft. 12. A neurone is a type of nerve cell. 13. The myelin sheath is an insulating layer, surrounding peripheral nerve cells. 1 ...
... 10. The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. 11. Neurotransmitters are stored and packaged into a vesicle before being released into the synaptic cleft. 12. A neurone is a type of nerve cell. 13. The myelin sheath is an insulating layer, surrounding peripheral nerve cells. 1 ...
1-nervous_system
... around axons Holds neurons in place Speeds up transmission Can repair if damaged Keeps messages from being scrambled ...
... around axons Holds neurons in place Speeds up transmission Can repair if damaged Keeps messages from being scrambled ...
The Nervous System The master and
... It has several cell _________________ that wrap themselves around many _________________ neurons. ...
... It has several cell _________________ that wrap themselves around many _________________ neurons. ...
The Nervous System
... Ears, mouth, nose, muscles, and skin Other receptors are sensitive to pressure, temperature, and pain and make us aware of our balance, position and motion ...
... Ears, mouth, nose, muscles, and skin Other receptors are sensitive to pressure, temperature, and pain and make us aware of our balance, position and motion ...
Nerve cord
... Stimulus: a signal that causes an animal to react Example: touch, sound, smells, tastes Response: an animal’s reaction to a stimulus ...
... Stimulus: a signal that causes an animal to react Example: touch, sound, smells, tastes Response: an animal’s reaction to a stimulus ...
13.1- neurons
... - Axons are covered with a glistening white coat of a fatty protein called myelin sheath, which acts as insulation for the axons. - The myelin sheath acts as insulation by preventing the loss of charged ions from the nerve cell. ...
... - Axons are covered with a glistening white coat of a fatty protein called myelin sheath, which acts as insulation for the axons. - The myelin sheath acts as insulation by preventing the loss of charged ions from the nerve cell. ...
Nervous System functions
... 2.Explain differences in the function of the peripheral nervous system and the central nervous system. ...
... 2.Explain differences in the function of the peripheral nervous system and the central nervous system. ...
Nervous System
... Central Nervous System Communication and coordination system of the body Seat of intellect and reasoning Consists of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. ...
... Central Nervous System Communication and coordination system of the body Seat of intellect and reasoning Consists of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. ...
A1984SR69800001
... It had been expected that peripheral transmitters, such as acetyicholine and noradrenaline, would have a prominent role in the central nervous system (CNS). Amino acids, with well-identified roles in cellular metabolism, protein synthesis, etc.—and found abundantly throughout the brain—did not fit t ...
... It had been expected that peripheral transmitters, such as acetyicholine and noradrenaline, would have a prominent role in the central nervous system (CNS). Amino acids, with well-identified roles in cellular metabolism, protein synthesis, etc.—and found abundantly throughout the brain—did not fit t ...