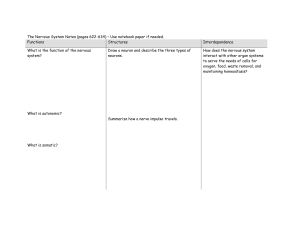
Neuron Structure
... – longest cytoplasmic extension from cell body – 100 axons could fit into typical human hair ...
... – longest cytoplasmic extension from cell body – 100 axons could fit into typical human hair ...
Nervous - Lamont High
... – longest cytoplasmic extension from cell body – 100 axons could fit into typical human hair ...
... – longest cytoplasmic extension from cell body – 100 axons could fit into typical human hair ...
2222222222222222222 System • Responsible for coordinating the
... _________ neurons- sends information from the CNS to the muscle cells or the glands __________ Neurons- Nerve cells transmits information about the internal and external environment changes to the CNS ...
... _________ neurons- sends information from the CNS to the muscle cells or the glands __________ Neurons- Nerve cells transmits information about the internal and external environment changes to the CNS ...
The Nervous System
... Myelin is the fatty substance that wraps around axons and protects/insulates them Formed by Schwann Cells in the PNS, gaps called Nodes of Ranvier are left between the myelin Myelination and the Nodes of Ranvier increase the speed that the electrical signal moves down the axon. ...
... Myelin is the fatty substance that wraps around axons and protects/insulates them Formed by Schwann Cells in the PNS, gaps called Nodes of Ranvier are left between the myelin Myelination and the Nodes of Ranvier increase the speed that the electrical signal moves down the axon. ...
nervous07
... •Soma producing: Free ribosomes, protein, RNA and other molecules. •The axon and myelin sheath distal to the lesion degenerates as far as the axon collateral •sprouting of the axon into endoneurium •guiding by proliferating Schwann cells toward the target •regeneration in the presence of macrophages ...
... •Soma producing: Free ribosomes, protein, RNA and other molecules. •The axon and myelin sheath distal to the lesion degenerates as far as the axon collateral •sprouting of the axon into endoneurium •guiding by proliferating Schwann cells toward the target •regeneration in the presence of macrophages ...
File - Mr. Haan`s Science
... change in and out of body b. Integration – processes and interprets data to see what to do c. Motor output – causes response of effector organs ...
... change in and out of body b. Integration – processes and interprets data to see what to do c. Motor output – causes response of effector organs ...
6.1 Overview of the Nervous System
... 3. axons – transmit impulses away from the cell body b. myelin sheaths cover axons and increase the rate of impulse transmission, appear white (White matter); Gray matter is non-myelinated nerve fibers c. insulated gaps between Schwann Cells are call nodes of Ranvier ...
... 3. axons – transmit impulses away from the cell body b. myelin sheaths cover axons and increase the rate of impulse transmission, appear white (White matter); Gray matter is non-myelinated nerve fibers c. insulated gaps between Schwann Cells are call nodes of Ranvier ...
Nervous System
... 31. List the four types of glial cells in the CNS. 32. How does the cytoplasm of CNS glial cells appear with routine histological techniques? 33. What type of glial cell facilitates neuronal migration during the development of the CNS? ...
... 31. List the four types of glial cells in the CNS. 32. How does the cytoplasm of CNS glial cells appear with routine histological techniques? 33. What type of glial cell facilitates neuronal migration during the development of the CNS? ...
Nervous System
... of the physical movement of the body as well as responding to the action of all the senses of hearing, sight, smell, taste, and touch Enables animals to react to the internal and external stimuli in their environment ...
... of the physical movement of the body as well as responding to the action of all the senses of hearing, sight, smell, taste, and touch Enables animals to react to the internal and external stimuli in their environment ...
BIO 2310 - MSU Denver
... Junction between adjacent neurons [Telodendria – ends of axon] Neurotransmitters – chemicals bridging the synapse ...
... Junction between adjacent neurons [Telodendria – ends of axon] Neurotransmitters – chemicals bridging the synapse ...
Lab 8: Muscle and Nervous Tissue
... images for the microscope work. Go to the HistoWeb Nerve site. (link from “Project Info” on PhysioWeb) 4. Obtain a prepared slide of spinal cord smear. Using low power magnification, search the slide and locate the large, deeply stained cell bodies of motor neurons (multipolar neurons) ...
... images for the microscope work. Go to the HistoWeb Nerve site. (link from “Project Info” on PhysioWeb) 4. Obtain a prepared slide of spinal cord smear. Using low power magnification, search the slide and locate the large, deeply stained cell bodies of motor neurons (multipolar neurons) ...
Nervous System - EMTStudyCenter.com
... 5. All of the following are functions of the nervous system EXCEPT senses changes. analyzes changes. ...
... 5. All of the following are functions of the nervous system EXCEPT senses changes. analyzes changes. ...
The Nervous System
... collides against skull • Can cause headache, dizziness, confusion, memory loss, brain damage ...
... collides against skull • Can cause headache, dizziness, confusion, memory loss, brain damage ...
The Nervous System
... of K, the outer environment has a high Na concentration. The neuron’s cell membrane has active Na/K gates. When an impulse comes in contact with the membrane, it turns off the gate.[polarized] Na rushes in, K leaves and the electrical impulse passes through the cell body. [wave of depolarization] Af ...
... of K, the outer environment has a high Na concentration. The neuron’s cell membrane has active Na/K gates. When an impulse comes in contact with the membrane, it turns off the gate.[polarized] Na rushes in, K leaves and the electrical impulse passes through the cell body. [wave of depolarization] Af ...
The Brain and Behavior
... from the body's sense receptors (eyes, ears, etc.) to the CNS. • Motoneurons or Multipolar neurons carry signals from the CNS muscles and glands. • Interneurons or Pseudopolare (Spelling) cells form all the neural wiring within the CNS. These have two axons (instead of an axon and a dendrite). One a ...
... from the body's sense receptors (eyes, ears, etc.) to the CNS. • Motoneurons or Multipolar neurons carry signals from the CNS muscles and glands. • Interneurons or Pseudopolare (Spelling) cells form all the neural wiring within the CNS. These have two axons (instead of an axon and a dendrite). One a ...
Chapter 8 Study Guide: The Nervous System
... • Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – Cranial Nerves – Spinal Nerves – Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): Involuntary • Sympathetic • Parasympathetic ...
... • Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – Cranial Nerves – Spinal Nerves – Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): Involuntary • Sympathetic • Parasympathetic ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... Most abundant cells in the nervous system CNS production and circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) 2 types (PNS) Satellite Cells Schwann Cells ...
... Most abundant cells in the nervous system CNS production and circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) 2 types (PNS) Satellite Cells Schwann Cells ...
Introduction to the Nervous System and Nerve Tissue
... impulses toward cell body. Receive stimuli from synapses or sensory receptors. Cell Body: Contains nucleus and nissl bodies, a form of rough endoplasmic reticulum. Axon: Carry nerve Impulses away from the cell bodies. Axons interact with muscle, glands, or other neurons. ...
... impulses toward cell body. Receive stimuli from synapses or sensory receptors. Cell Body: Contains nucleus and nissl bodies, a form of rough endoplasmic reticulum. Axon: Carry nerve Impulses away from the cell bodies. Axons interact with muscle, glands, or other neurons. ...
File
... Answer: Cell body- control center (nucleus & cytoplasm). Axons- extends from cell body & produces nerve terminals. Dendrite- receives messages from other neurons. ...
... Answer: Cell body- control center (nucleus & cytoplasm). Axons- extends from cell body & produces nerve terminals. Dendrite- receives messages from other neurons. ...
The Nervous System – Use notebook paper if
... How does the nervous system interact with other organ systems to serve the needs of cells for oxygen, food, waste removal, and maintaining homeostasis? ...
... How does the nervous system interact with other organ systems to serve the needs of cells for oxygen, food, waste removal, and maintaining homeostasis? ...