Chapter 3
... Chapter 2 Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses Module 2.1 The Cells of the Nervous System 1. Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. 2. Know the main types of glia and their functions. 3. Be able to describe the advantages and disadvantages of the blood-brain barr ...
... Chapter 2 Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses Module 2.1 The Cells of the Nervous System 1. Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. 2. Know the main types of glia and their functions. 3. Be able to describe the advantages and disadvantages of the blood-brain barr ...
Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses Quiz Answers
... a) one dendrite and many axons covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier b) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier c) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by the synapse d) one dendrite and many axon ...
... a) one dendrite and many axons covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier b) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier c) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by the synapse d) one dendrite and many axon ...
Name
... 1. What is homeostasis? Give examples. 2. What are the functions of the nervous system? 3. What is the structure of a neuron and what kinds of neurons are found in the body? 4. How do nerve impulses travel from one neuron to another? 5. What are the structure and functions of the central nervous sys ...
... 1. What is homeostasis? Give examples. 2. What are the functions of the nervous system? 3. What is the structure of a neuron and what kinds of neurons are found in the body? 4. How do nerve impulses travel from one neuron to another? 5. What are the structure and functions of the central nervous sys ...
Vocabulary: Chapter 1 Body Control Systems Neuron
... Motor neuron- nerve cell in the peripheral nervous system that carries information from the CNS to the muscles and organs. Retina- an area at the back of the eye that contains sensory receptors for light. Dendrite- part of a neuron that collects information from other neurons. Nerve impulse- message ...
... Motor neuron- nerve cell in the peripheral nervous system that carries information from the CNS to the muscles and organs. Retina- an area at the back of the eye that contains sensory receptors for light. Dendrite- part of a neuron that collects information from other neurons. Nerve impulse- message ...
Powerpoint
... • Neurons in brain and spinal cord= Central Nervous System (CNS) • Nerves that connect CNS to rest of body= Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) ...
... • Neurons in brain and spinal cord= Central Nervous System (CNS) • Nerves that connect CNS to rest of body= Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) ...
Nervous System Test Review After you accidentally touch a hot pan
... 1. After you accidentally touch a hot pan, you immediately jerk your hand away without thinking about your action, and before you even feel the pain of the burn. What type of response is the known as? a. Reflex 2. In order for a nerve impulse to pass from an axon tip to the next structure, it must c ...
... 1. After you accidentally touch a hot pan, you immediately jerk your hand away without thinking about your action, and before you even feel the pain of the burn. What type of response is the known as? a. Reflex 2. In order for a nerve impulse to pass from an axon tip to the next structure, it must c ...
013368718X_CH31_483
... Chapter 31 Vocabulary Review For Questions 1–10, match the term with its description. ...
... Chapter 31 Vocabulary Review For Questions 1–10, match the term with its description. ...
The nerve A nerve is an enclosed, cable
... In the central nervous system, the analogous structures are known as tracts Neurons are sometimes called nerve cells, though this term is potentially misleading since many neurons do not form nerves, and nerves also include nonneuronal Schwann cells that coat the axons in myelin. ...
... In the central nervous system, the analogous structures are known as tracts Neurons are sometimes called nerve cells, though this term is potentially misleading since many neurons do not form nerves, and nerves also include nonneuronal Schwann cells that coat the axons in myelin. ...
Spinal cord worksheet
... 7.A complete pathway through the nervous system from stimulus to response____________________ ...
... 7.A complete pathway through the nervous system from stimulus to response____________________ ...
Lesson 1 | The Nervous System
... 7. The central nervous system consists of the brain and (sensory system/spinal cord). 8. Thought processes are carried out in the (cerebrum/cerebellum). 9. The peripheral nervous system consists of the somatic and (central/autonomic) systems. 10. The most common cause of damage to the nervous system ...
... 7. The central nervous system consists of the brain and (sensory system/spinal cord). 8. Thought processes are carried out in the (cerebrum/cerebellum). 9. The peripheral nervous system consists of the somatic and (central/autonomic) systems. 10. The most common cause of damage to the nervous system ...
N1 - Kůra mozku HE
... • extracellular material is extremely reduced replaced by glial branched process • neurons receive stimuli and conduct nerve impulse via their processes • action potential transmission to the next cell through synapses (= intercellular contacts) • extensive vasculature with variable amount of connec ...
... • extracellular material is extremely reduced replaced by glial branched process • neurons receive stimuli and conduct nerve impulse via their processes • action potential transmission to the next cell through synapses (= intercellular contacts) • extensive vasculature with variable amount of connec ...
Ch 11 Part 1 - Groch Biology
... Supporting cells found in the CNS are called neuroglia. ___ _______________ Neurons are mitotic. ___ ____________________ Schwann cells and satellite cells are found only in the CNS. ___ ________________ Ependymal cells show irritability and conductivity. ___ ____________________ Almost 50% of the v ...
... Supporting cells found in the CNS are called neuroglia. ___ _______________ Neurons are mitotic. ___ ____________________ Schwann cells and satellite cells are found only in the CNS. ___ ________________ Ependymal cells show irritability and conductivity. ___ ____________________ Almost 50% of the v ...
NAME: AP Biology/ Ms. Gaynor (Unit #10: Animal Physiology
... 9. How is polarization maintained across a neuron’s membrane? ...
... 9. How is polarization maintained across a neuron’s membrane? ...
Slide 1 - Cloudfront.net
... 23.Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by endoneurium, a delicate layer of loose connective tissue that also encloses the fiber’s associated myelin or neurilemma sheath. Groups of fibers are bound into bundles called: ...
... 23.Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by endoneurium, a delicate layer of loose connective tissue that also encloses the fiber’s associated myelin or neurilemma sheath. Groups of fibers are bound into bundles called: ...
Neuron Labeling WS
... The connection between adjacent neurons. The chemical secreted into the gap between neurons at a synapse. A rapid automatic response to a stimulus. The covering of fatty material that speeds up the passage of nerve impulses. The structure at the end of an axon that produces neurotransmitters to tran ...
... The connection between adjacent neurons. The chemical secreted into the gap between neurons at a synapse. A rapid automatic response to a stimulus. The covering of fatty material that speeds up the passage of nerve impulses. The structure at the end of an axon that produces neurotransmitters to tran ...
Exercise 17 - Harford Community College
... – maintain blood-brain barrier – provide structural framework for brain due to extensive cytoskeleton – repair damaged neural tissue – guide neuronal development – regulating interstitial environment ...
... – maintain blood-brain barrier – provide structural framework for brain due to extensive cytoskeleton – repair damaged neural tissue – guide neuronal development – regulating interstitial environment ...
summing-up - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... from one nerve cell to another, or from one nerve cell to a muscle cell, across the synapse. ...
... from one nerve cell to another, or from one nerve cell to a muscle cell, across the synapse. ...
Nervous System - Crossword Labs
... 11. The small gap that separates the presynaptic membrane and the postsynaptic membrane 14. detect or respond to stimuli 15. Carries motor commands 16. All neural tissue outside CNS 20. cytoplasm of axon 21. Cell that receives message 22. carries action potential to target 24. Cells with highly bran ...
... 11. The small gap that separates the presynaptic membrane and the postsynaptic membrane 14. detect or respond to stimuli 15. Carries motor commands 16. All neural tissue outside CNS 20. cytoplasm of axon 21. Cell that receives message 22. carries action potential to target 24. Cells with highly bran ...
The Nervous System
... (Figure 8-1). The nervous system is divided into two subsystems: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). A nerve cell or neuron is the basic element of the nervous system. All neurons have three parts: 1. The cell body, which has branches or fibers that reach out to ...
... (Figure 8-1). The nervous system is divided into two subsystems: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). A nerve cell or neuron is the basic element of the nervous system. All neurons have three parts: 1. The cell body, which has branches or fibers that reach out to ...
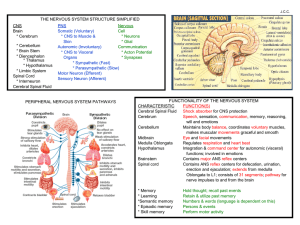
CNS Brain * Cerebrum * Cerebellum * Brain Stem * Diencephalon
... Speech, sensation, communication, memory, reasoning, will and emotions Cerebellum Maintains body balance, coordinates voluntary muscles, makes muscular movements graceful and smooth Midbrain Eye and facial movements Medulla Oblongata Regulates respiration and heart beat Hypothalamus Integration & co ...
... Speech, sensation, communication, memory, reasoning, will and emotions Cerebellum Maintains body balance, coordinates voluntary muscles, makes muscular movements graceful and smooth Midbrain Eye and facial movements Medulla Oblongata Regulates respiration and heart beat Hypothalamus Integration & co ...
Guided notes 2 Histology - Liberty Union High School District
... These supporting cells serve many functions: ____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ...
... These supporting cells serve many functions: ____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ...
Slide 1
... Each branch of this arborization terminates on the next cell in dilatations called end bulbs (boutons), which interact with other neurons or nonnerve cells, forming structures called synapses. ...
... Each branch of this arborization terminates on the next cell in dilatations called end bulbs (boutons), which interact with other neurons or nonnerve cells, forming structures called synapses. ...
Nerve Tissue
... 1. Somatic (voluntary) nervous system-this is were our control of voluntary functions or conscious actions occur. 2. Autonomic (involuntary) nervous system-this you do not control but it happens (heart beating/digestion) ...
... 1. Somatic (voluntary) nervous system-this is were our control of voluntary functions or conscious actions occur. 2. Autonomic (involuntary) nervous system-this you do not control but it happens (heart beating/digestion) ...
neuron
... Nerve tissue - morphology cells : 1.neurons and 2.glial cells • extracellular material is extremely reduced replaced by glial branched process • neuropil – high amount of synapses, dendrite´s arborisation, non-myelinated axons • extensive vasculature with variable amount of connective tissue both i ...
... Nerve tissue - morphology cells : 1.neurons and 2.glial cells • extracellular material is extremely reduced replaced by glial branched process • neuropil – high amount of synapses, dendrite´s arborisation, non-myelinated axons • extensive vasculature with variable amount of connective tissue both i ...