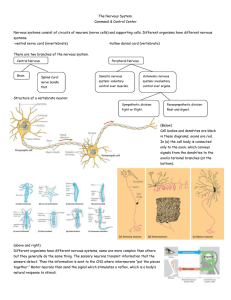
Biology 211 Anatomy & Physiology I
... Endoneurium Perineurium in peripheral nervous system Epineurium Epithelium found only in blood vessels of PNS Muscle (smooth) ...
... Endoneurium Perineurium in peripheral nervous system Epineurium Epithelium found only in blood vessels of PNS Muscle (smooth) ...
Functional Classification of the Peripheral Nervous System
... Nodes of Ranvier – gaps in the myelin sheath along the axon ...
... Nodes of Ranvier – gaps in the myelin sheath along the axon ...
Nervous System Outline 1
... 1. This is the interpretation of the energy by the Central Nervous System (CNS). (Basically “thinking” about the stimulus.) 2. This interpretation of the stimulus leads to a determination of the appropriate response. C. Motor Output – Sending out of impulses from the brain or spinal cord to glands o ...
... 1. This is the interpretation of the energy by the Central Nervous System (CNS). (Basically “thinking” about the stimulus.) 2. This interpretation of the stimulus leads to a determination of the appropriate response. C. Motor Output – Sending out of impulses from the brain or spinal cord to glands o ...
Med Term Chapter 10
... from nerve cells. In multiple sclerosis, the immune system's T cells and B cells attack oligodendrocytes, ultimately damaging the myelin sheath to the point that the electrical signals transmitted by the axons beneath it are disrupted. (David Rowitch, et al. University of California - San Francisco. ...
... from nerve cells. In multiple sclerosis, the immune system's T cells and B cells attack oligodendrocytes, ultimately damaging the myelin sheath to the point that the electrical signals transmitted by the axons beneath it are disrupted. (David Rowitch, et al. University of California - San Francisco. ...
15-1 Section Summary
... he nervous system receives information about what is happening both inside and outside your body. It also directs the way in which your body responds to this information. In addition, the nervous system helps in maintaining stable internal conditions. A stimulus is any change or signal in the enviro ...
... he nervous system receives information about what is happening both inside and outside your body. It also directs the way in which your body responds to this information. In addition, the nervous system helps in maintaining stable internal conditions. A stimulus is any change or signal in the enviro ...
1. The diagram below is of a nerve cell or neuron. i. Add the following
... 3. The connection between adjacent neurons. ...
... 3. The connection between adjacent neurons. ...
Nervous System
... the sensory receptors toward the CNS • Motor (efferent) - delivers messages from the CNS to organs – Somatic nervous system - messages sent to muscles – Autonomic nervous system - messages sent to smooth muscle, cardiac muscles, and glands. – Which would be considered the involuntary nervous system? ...
... the sensory receptors toward the CNS • Motor (efferent) - delivers messages from the CNS to organs – Somatic nervous system - messages sent to muscles – Autonomic nervous system - messages sent to smooth muscle, cardiac muscles, and glands. – Which would be considered the involuntary nervous system? ...
Nervous
... Modern brain–imaging techniques suggest that consciousness may be an emergent property of the brain based on activity in many areas of the cortex. Nerve Cell Development Signal molecules direct an axon′s growth by binding to receptors on the plasma membrane of the growth cone. The genes and basic ev ...
... Modern brain–imaging techniques suggest that consciousness may be an emergent property of the brain based on activity in many areas of the cortex. Nerve Cell Development Signal molecules direct an axon′s growth by binding to receptors on the plasma membrane of the growth cone. The genes and basic ev ...
Nervous System - Phoenix Union High School District
... Divisions of the PNS I. Sensory (afferent) division A) Somatic sensory afferent fibers – carry impulses from skin, skeletal muscles, and joints to the brain B) Visceral afferent fibers – transmit impulses from visceral organs to the brain ...
... Divisions of the PNS I. Sensory (afferent) division A) Somatic sensory afferent fibers – carry impulses from skin, skeletal muscles, and joints to the brain B) Visceral afferent fibers – transmit impulses from visceral organs to the brain ...
1 - mrnicholsscience
... 3. What is the main pathway between the brain and the PNS? 9. Name the layers of the meninges from outside to inside. 4. What does CSF flow through between the third and fourth ventricles? Where does CSF go when it leaves the brain? ...
... 3. What is the main pathway between the brain and the PNS? 9. Name the layers of the meninges from outside to inside. 4. What does CSF flow through between the third and fourth ventricles? Where does CSF go when it leaves the brain? ...
11 - Karmayog .org
... Nerve Impulse Chemicals - ions and electric charge This impulse is brought about by the movement of chemical ions either into or out of a neuron. - These ions have an electric charge this causes the flow of an electric current. - When it reaches a junction between two neurons (synapse). It causes ...
... Nerve Impulse Chemicals - ions and electric charge This impulse is brought about by the movement of chemical ions either into or out of a neuron. - These ions have an electric charge this causes the flow of an electric current. - When it reaches a junction between two neurons (synapse). It causes ...
Nervous Sys Learning targets
... 1. List the basic functions of the nervous system 2. draw a concept map to show the structural and functional divisions of the nervous system 3. List the types of neuroglia and cite their functions ...
... 1. List the basic functions of the nervous system 2. draw a concept map to show the structural and functional divisions of the nervous system 3. List the types of neuroglia and cite their functions ...
Development of the central nervous system
... Origin of the nerve cell and the various types of glial cells. Neuroblasts, fibrillar and protoplasmic astrocytes, and ependymal cells originate from neuroepithelial cells. Microglia develop from mesenchyme cells. The origin of the oligodendroglia is not clear. ...
... Origin of the nerve cell and the various types of glial cells. Neuroblasts, fibrillar and protoplasmic astrocytes, and ependymal cells originate from neuroepithelial cells. Microglia develop from mesenchyme cells. The origin of the oligodendroglia is not clear. ...
The nervous system
... DENDRITES OF A NEURON RECEIVE MESSAGES OR STIMULI AND TRANSFORM THEM INTO NERVE IMPULSES THE NERVE IMPULSES ARE THEN TRANSMITTED ALONG AXONS TO THE AXON TERMINALS NERVE IMPULSES TRAVEL FROM ONE NEURON TO ANOTHER VIA NEUROTRANSMITTERS SECRETED BY AXON TERMINALS ACROSS A NARROW SPACE OR TRANSMISSION Z ...
... DENDRITES OF A NEURON RECEIVE MESSAGES OR STIMULI AND TRANSFORM THEM INTO NERVE IMPULSES THE NERVE IMPULSES ARE THEN TRANSMITTED ALONG AXONS TO THE AXON TERMINALS NERVE IMPULSES TRAVEL FROM ONE NEURON TO ANOTHER VIA NEUROTRANSMITTERS SECRETED BY AXON TERMINALS ACROSS A NARROW SPACE OR TRANSMISSION Z ...
Name: Date: Grade / Section: _____ Neurons Questions Notes 1
... them to move in response Explain what each neuron does in the picture when the person puts her hand near the flame: Sensory Interneuron Motor - ...
... them to move in response Explain what each neuron does in the picture when the person puts her hand near the flame: Sensory Interneuron Motor - ...
Central nervous system
... Process, transfer, and store information Neuroglia – (also called “glial cells”) Support and protect neurons ...
... Process, transfer, and store information Neuroglia – (also called “glial cells”) Support and protect neurons ...
Unit 10 Chapter 36 The Nervous System
... to the spinal cord & brain Motor neurons carry impulses from the spinal cord & brain to the body Interneurons are found within the spinal cord & brain, pass response impulses between sensory & motor ...
... to the spinal cord & brain Motor neurons carry impulses from the spinal cord & brain to the body Interneurons are found within the spinal cord & brain, pass response impulses between sensory & motor ...
Bowman`s capsule movie
... • Oligodendrocytes: glial cells of CNS which performs function similar to Schwann cells • Astrocytes: Star-shaped glial cells that create blood-brain barrier – Surround the smallest, most permeable blood vessels in the brain and protect brain from damage by chemical toxins; protection of brain is cr ...
... • Oligodendrocytes: glial cells of CNS which performs function similar to Schwann cells • Astrocytes: Star-shaped glial cells that create blood-brain barrier – Surround the smallest, most permeable blood vessels in the brain and protect brain from damage by chemical toxins; protection of brain is cr ...