NeuroReview3
... • If Schwann cell myelin sheaths remain intact, regenerating neurons grow through them to original targets • If nerve is severed and cut ends are separated by a small space regrowth can be directed to incorrect targets • If severed ends are far apart or long section of nerve is damaged functional re ...
... • If Schwann cell myelin sheaths remain intact, regenerating neurons grow through them to original targets • If nerve is severed and cut ends are separated by a small space regrowth can be directed to incorrect targets • If severed ends are far apart or long section of nerve is damaged functional re ...
nervous system study guide
... SOMATIC VS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM What does each do? Which is involuntary? ...
... SOMATIC VS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM What does each do? Which is involuntary? ...
Nervous Tissue [PPT]
... Much smaller than the neurons 10 times more numerous than neurons 4 types: Astrocytes(Fibrous and ...
... Much smaller than the neurons 10 times more numerous than neurons 4 types: Astrocytes(Fibrous and ...
1. Intro to Nervous System WEB
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) = brain & spinal cord The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) = all neural tissue not included in CNS ...
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) = brain & spinal cord The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) = all neural tissue not included in CNS ...
PPt #2 Human Body Nervous system
... Axon: long extension that carries electrical messages away from the body to the terminal axons Terminal Axons: passes the signal to the next cell. Myelin sheath: Protective covering for axon ...
... Axon: long extension that carries electrical messages away from the body to the terminal axons Terminal Axons: passes the signal to the next cell. Myelin sheath: Protective covering for axon ...
Nerve Tissue - Coach Frei Science
... 23. ____ A neuron that conducts impulses away from the brain and the spinal cord to the muscles or glands. 24. ____ Some change that occurs within or outside the body, that cause signals to be sent via the nervous System, for example: a change in temperature. 25. ____ A neuron that conducts impulses ...
... 23. ____ A neuron that conducts impulses away from the brain and the spinal cord to the muscles or glands. 24. ____ Some change that occurs within or outside the body, that cause signals to be sent via the nervous System, for example: a change in temperature. 25. ____ A neuron that conducts impulses ...
Nervous System
... Long axons are called nerve fibers Usually there is only one unbranched axon per neuron Rare branches, if present, are called axon collaterals Axonal terminal – branched terminus of an axon ...
... Long axons are called nerve fibers Usually there is only one unbranched axon per neuron Rare branches, if present, are called axon collaterals Axonal terminal – branched terminus of an axon ...
The Nervous System
... Axons: single, long “fiber” which conducts impulse away from the cell body, sends information (Action Potentials) ...
... Axons: single, long “fiber” which conducts impulse away from the cell body, sends information (Action Potentials) ...
Nervous System Project
... is responsible for making sure that all the automatic things that your body needs to do to keep you going, like breathing, digesting etc continue working smoothly without your having to think about them. (How hard would it be to have to keep thinking, "Breathe in, breathe out," or "Start digesting t ...
... is responsible for making sure that all the automatic things that your body needs to do to keep you going, like breathing, digesting etc continue working smoothly without your having to think about them. (How hard would it be to have to keep thinking, "Breathe in, breathe out," or "Start digesting t ...
The Nervous System - chemistrywithmrsmorton
... Cell body – contains nucleus; metabolic center Dendrite – fiber that conveys messages toward cell body Axon – conduct nerve impulses away from the cell body Axon terminals – end of axon; contain neurotransmitters & release them Synaptic cleft/synapse – gap between neurons ...
... Cell body – contains nucleus; metabolic center Dendrite – fiber that conveys messages toward cell body Axon – conduct nerve impulses away from the cell body Axon terminals – end of axon; contain neurotransmitters & release them Synaptic cleft/synapse – gap between neurons ...
Slide ()
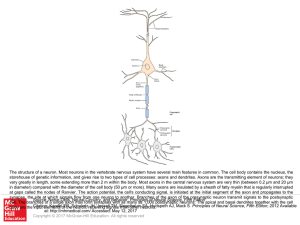
... storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; they vary greatly in length, some extending more than 2 m within the body. Most axons in the central nervous system are very thin (between 0.2 μm and ...
... storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; they vary greatly in length, some extending more than 2 m within the body. Most axons in the central nervous system are very thin (between 0.2 μm and ...
The Nervous System - FW Johnson Collegiate
... - Central Nervous System – contains the brain and spinal cord - Peripheral Nervous System – carries information between the organs of the body and the central nervous system 2 Divisions of the Peripheral Nervous System: - Somatic Nerves – control the skeletal muscle, bones, skin, and sensory organs ...
... - Central Nervous System – contains the brain and spinal cord - Peripheral Nervous System – carries information between the organs of the body and the central nervous system 2 Divisions of the Peripheral Nervous System: - Somatic Nerves – control the skeletal muscle, bones, skin, and sensory organs ...
The Nervous System
... • - The junction where one neuron meets another and an impulse is transferred is called a synapse. For a nerve impulse to be carried along at a synapse, it must cross the gap between the axon and the next structure. The axon tips release chemicals that carry the impulse across the gap. ...
... • - The junction where one neuron meets another and an impulse is transferred is called a synapse. For a nerve impulse to be carried along at a synapse, it must cross the gap between the axon and the next structure. The axon tips release chemicals that carry the impulse across the gap. ...
Nervous System Exam.tst
... 10) The three major parts of the brain stem are the: A) dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater B) basal nuclei, pineal body, and choroid plexus C) cerebrum, cerebellum, and diencephalon D) thalamus, epithalamus, and hypothalamus E) midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata ...
... 10) The three major parts of the brain stem are the: A) dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater B) basal nuclei, pineal body, and choroid plexus C) cerebrum, cerebellum, and diencephalon D) thalamus, epithalamus, and hypothalamus E) midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata ...
Slide ()
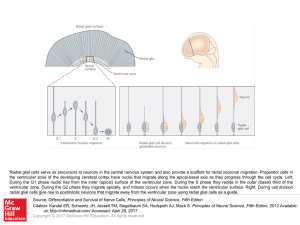
... Radial glial cells serve as precursors to neurons in the central nervous system and also provide a scaffold for radial neuronal migration. Progenitor cells in the ventricular zone of the developing cerebral cortex have nuclei that migrate along the apical-basal axis as they progress through the cell ...
... Radial glial cells serve as precursors to neurons in the central nervous system and also provide a scaffold for radial neuronal migration. Progenitor cells in the ventricular zone of the developing cerebral cortex have nuclei that migrate along the apical-basal axis as they progress through the cell ...
Nerve tissue for stu..
... C. Myelinated axons in the central nervous system (CNS) – myelin sheath is formed by processes of oligodendrocytes. One inetrnodal segment is formed by one process of oligodendrocyte. One oligodendrocyte can form more internodal segments by its processes. D. Non-myelinated axons in the CNS – axons a ...
... C. Myelinated axons in the central nervous system (CNS) – myelin sheath is formed by processes of oligodendrocytes. One inetrnodal segment is formed by one process of oligodendrocyte. One oligodendrocyte can form more internodal segments by its processes. D. Non-myelinated axons in the CNS – axons a ...
Notes - The Nervous System
... 4. The interneurons interpret the nerve impulses and decide on a response, you should answer the phone. 5. Impulses travel along motor neurons to the ...
... 4. The interneurons interpret the nerve impulses and decide on a response, you should answer the phone. 5. Impulses travel along motor neurons to the ...
Organization of the Nervous System and the Neuron
... Until the neuron repolarizes it cannot conduct another impulse= absolute refractory period There also exists a relative refractory period when a stronger than usual stimulus is required ...
... Until the neuron repolarizes it cannot conduct another impulse= absolute refractory period There also exists a relative refractory period when a stronger than usual stimulus is required ...
Nervous System Notes - Mrs. Franco's Biology & Anatomy Page
... Astrocytes – star shaped cells ...
... Astrocytes – star shaped cells ...
Nerve Chips
... M.D./Ph.D. Program, University of Pittsburgh 2 years med school 3+ years grad school 2 more years med school And then residency… ...
... M.D./Ph.D. Program, University of Pittsburgh 2 years med school 3+ years grad school 2 more years med school And then residency… ...
File
... STRUCTURE OF A NEURONE Receptors are special nerve endings found within our skin and include: touch, pain, pressure and temperature receptors. It is their job to detect changes in the environment. These changes, known as stimuli may include temperature changes, pain or pressure, are carried in the f ...
... STRUCTURE OF A NEURONE Receptors are special nerve endings found within our skin and include: touch, pain, pressure and temperature receptors. It is their job to detect changes in the environment. These changes, known as stimuli may include temperature changes, pain or pressure, are carried in the f ...

![Nervous Tissue [PPT]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000313628_1-63044c543d97a5d91f1cbdf37558ffd7-300x300.png)