three basic functions of the nervous system
... •Longevity – can live and function for a lifetime •Do not divide (Amitotic) – fetal neurons lose their ability to undergo mitosis; neural stem cells are an exception ...
... •Longevity – can live and function for a lifetime •Do not divide (Amitotic) – fetal neurons lose their ability to undergo mitosis; neural stem cells are an exception ...
An Herbalist`s View of the Nervous System
... Resting membrane potential (RMP) Summation Threshold ...
... Resting membrane potential (RMP) Summation Threshold ...
Histology05-NerveTissue
... Connective tissue layers in a peripheral nerve. Tight junctions between perineurium cells form a important isolating barrier. ...
... Connective tissue layers in a peripheral nerve. Tight junctions between perineurium cells form a important isolating barrier. ...
The Nervous System
... electrical signals to communicate with other cells • An impulse is: an electrical signal travelling through a neuron • A nerve is: a bundle of neurons • Sensory neurons: carry impulses from receptors (e.g. in skin) to the central nervous system (brain/spinal cord) • Motor neurons: carry impulses fro ...
... electrical signals to communicate with other cells • An impulse is: an electrical signal travelling through a neuron • A nerve is: a bundle of neurons • Sensory neurons: carry impulses from receptors (e.g. in skin) to the central nervous system (brain/spinal cord) • Motor neurons: carry impulses fro ...
The Brain
... • White Matter- Fat coated nerve tissue. Helps neurons work better. Myelin wraps the neurons to protect them and make them work faster (like an insulator). • Gray Matter- Nerve tissue found wrapped inside white matter. Not coated by myelin. More fragile and slow. ...
... • White Matter- Fat coated nerve tissue. Helps neurons work better. Myelin wraps the neurons to protect them and make them work faster (like an insulator). • Gray Matter- Nerve tissue found wrapped inside white matter. Not coated by myelin. More fragile and slow. ...
ACP Level 2 Lesson Twelve
... On the outside you have the Dura mater which is the strong mother. A double thickness wraps around the outside of the brain and then a single thickness around the spine. Inside of that is a web-like layer. I like to imagine the spider creating her terrible lair around her child. Keeping it safe from ...
... On the outside you have the Dura mater which is the strong mother. A double thickness wraps around the outside of the brain and then a single thickness around the spine. Inside of that is a web-like layer. I like to imagine the spider creating her terrible lair around her child. Keeping it safe from ...
Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells, neurons and glial
... Nervous Tissue By the end of this section, you will be able to: * Describe the basic structure of a neuron * Identify the different types of neurons on the basis of polarity * List the glial cells of the CNS and describe their function * List the glial cells of the PNS and describe their function Ne ...
... Nervous Tissue By the end of this section, you will be able to: * Describe the basic structure of a neuron * Identify the different types of neurons on the basis of polarity * List the glial cells of the CNS and describe their function * List the glial cells of the PNS and describe their function Ne ...
nervous system - Cloudfront.net
... - The left side of human brain controls the right side of the body and the right side of the brain controls the left side of the body. - A New born baby loses about half of their nerve cells before they are born. - As we get older, the brain loses almost one gram per year. - There are about 13, 500, ...
... - The left side of human brain controls the right side of the body and the right side of the brain controls the left side of the body. - A New born baby loses about half of their nerve cells before they are born. - As we get older, the brain loses almost one gram per year. - There are about 13, 500, ...
The Nervous System
... which make up the white matter in the nervous system; while axons that have no myelin sheath are called unmyelinated axons which make up the gray matter in the nervous system. ...
... which make up the white matter in the nervous system; while axons that have no myelin sheath are called unmyelinated axons which make up the gray matter in the nervous system. ...
The Nervous System
... Myelin: whitish, fatty material covering long nerve fibers; has waxy appearance Protects and provides an electrical insulation covering for large and long nerve fibers Increases speed of transmission of nerve impulses Unmyelinated fibers conduct impulses slowly Associated only with axons; De ...
... Myelin: whitish, fatty material covering long nerve fibers; has waxy appearance Protects and provides an electrical insulation covering for large and long nerve fibers Increases speed of transmission of nerve impulses Unmyelinated fibers conduct impulses slowly Associated only with axons; De ...
36.1: The Nervous System
... • 1. Resting: no impulse, cell is polarized ( + on outside & - on inside) – Sodium/Potassium pump in axon using ATP maintains this polarity ...
... • 1. Resting: no impulse, cell is polarized ( + on outside & - on inside) – Sodium/Potassium pump in axon using ATP maintains this polarity ...
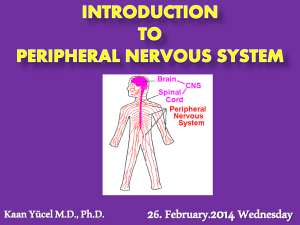
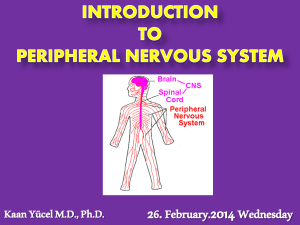
Peripheral Nervous System
... • The autonomic system is largely involuntary, its control originates in the brainstem and hypothalamus. • Autonomic nervous system innervates the heart, smooth muscles, organs and glands. • The autonomic system makes one ganglion after leaving the CNS. The post ganglionic cell then makes contact wi ...
... • The autonomic system is largely involuntary, its control originates in the brainstem and hypothalamus. • Autonomic nervous system innervates the heart, smooth muscles, organs and glands. • The autonomic system makes one ganglion after leaving the CNS. The post ganglionic cell then makes contact wi ...
Neurons and Functional Neuroanatomy
... The action potential moves down the length of the axon in one direction The action potential moves in one direction because the membrane is refractory (unable to respond) once the action potential has been initiated at any particular place on the membrane ...
... The action potential moves down the length of the axon in one direction The action potential moves in one direction because the membrane is refractory (unable to respond) once the action potential has been initiated at any particular place on the membrane ...
Introduction to Psychology Quiz #1 1. The main divisions of the
... According to the hospital records, Ray is suffering from multiple sclerosis. When a laboratory technician examines a sample of Ray's nerves what is she likely to find? a. excessive growth of dendrites b. degeneration of the myelin sheath c. wide gaps between adjacent neurons d. high levels of dopami ...
... According to the hospital records, Ray is suffering from multiple sclerosis. When a laboratory technician examines a sample of Ray's nerves what is she likely to find? a. excessive growth of dendrites b. degeneration of the myelin sheath c. wide gaps between adjacent neurons d. high levels of dopami ...
Document
... _ Lacks rough endoplasmic reticulum and polysomes _ Smooth endoplasmic reticulum _ Mitochondria _ Axon hillock. Region of the cell body where axon originates _ Devoid of rough endoplasmic reticulum _ Continuous with initial segment of the axon that is a highly electrically excitable zone for initiat ...
... _ Lacks rough endoplasmic reticulum and polysomes _ Smooth endoplasmic reticulum _ Mitochondria _ Axon hillock. Region of the cell body where axon originates _ Devoid of rough endoplasmic reticulum _ Continuous with initial segment of the axon that is a highly electrically excitable zone for initiat ...
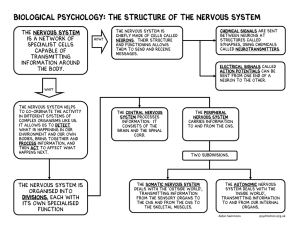
Biological Psychology: The structure of the nervous system
... Electrical signals called action potentials can be sent from one end of a neuron to the other. ...
... Electrical signals called action potentials can be sent from one end of a neuron to the other. ...
Cardiovascular system
... • Whitish, fatty (protein-lipoid), segmented sheath around most long (NOT ALL) axons ...
... • Whitish, fatty (protein-lipoid), segmented sheath around most long (NOT ALL) axons ...
Neuroscience01_Introduction
... system, which consists of a nerve cell body, dendrites, and an axon. ...
... system, which consists of a nerve cell body, dendrites, and an axon. ...
Nervous System
... dendrites of many other nerve cells (synapses) • In a synapse, the axon and dendrite don’t touch, there is a gap • At each axon terminal, there are vesicles containing a neurotransmitter • Once the neurotransmitter is released, it binds to receptors on the dendrite ...
... dendrites of many other nerve cells (synapses) • In a synapse, the axon and dendrite don’t touch, there is a gap • At each axon terminal, there are vesicles containing a neurotransmitter • Once the neurotransmitter is released, it binds to receptors on the dendrite ...
Of nerves and neurons - Case Western Reserve University
... in neurological research, and his studies on nerve injury When and why did you first become interested in the adult nervous system? I attended Harvard College, USA, with the intention of studying history; however, during my first year I took a fascinating course by Professor George Wald (winner of t ...
... in neurological research, and his studies on nerve injury When and why did you first become interested in the adult nervous system? I attended Harvard College, USA, with the intention of studying history; however, during my first year I took a fascinating course by Professor George Wald (winner of t ...
Nervous System - North Mac Schools
... Neural Response to Injury Wallerian Degeneration- PNS • 1. fragmentation of axon & myelin occurs in distal stump • 2. Schwann cells form cord, grow into cut, & unite stumps • Macrophages engulf debris ...
... Neural Response to Injury Wallerian Degeneration- PNS • 1. fragmentation of axon & myelin occurs in distal stump • 2. Schwann cells form cord, grow into cut, & unite stumps • Macrophages engulf debris ...
Nervous System Student Notes
... ii. ________ nerve axons can regenerate successfully if cell body is not destroyed iii. Uninjured cell body swells to prepare to synthesize proteins to support regeneration 1. axon regeneration = ______________________ 2. greater distance = less recovery chance = possible ______________ formation 3. ...
... ii. ________ nerve axons can regenerate successfully if cell body is not destroyed iii. Uninjured cell body swells to prepare to synthesize proteins to support regeneration 1. axon regeneration = ______________________ 2. greater distance = less recovery chance = possible ______________ formation 3. ...