* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download nervous system - Cloudfront.net
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neuroprosthetics wikipedia , lookup
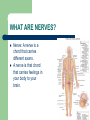
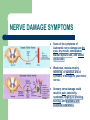
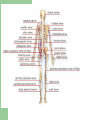
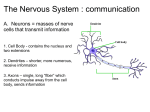
NERVOUS SYSTEM WHAT ARE NERVES? Nerve: A nerve is a chord that carries different axons. A nerve is that chord that carries feelings in your body to your brain. TYPES OF PERIPHERAL NERVES There are three types of nerves. They are Motor, Sensory, and Autonomic. The motor nerves send signals from the brain to all of the muscles in your body. The sensory nerves send signals the opposite way, from your muscles to your spinal chord and to your brain. The Autonomic nerves controls functions, such as heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and sweating. NERVE DAMAGE SYMPTOMS Some of the symptoms of Autonomic nerve damage are dry eyes, dry mouth, constipation, bladder dysfunction, and sexual dysfunction Weakness, muscle atrophy, twitching, or paralysis are all symtoms of damage to your motor nerves. Sensory nerve damage could result in pain, sensitivity, numbness, tingling or prickling, burning, and problems with positional awareness. WHAT CAUSES NERVE PAIN AND NERVE DAMAGE? There are a lot of different types of nerve damage. The different types may have different symptoms and may require different types of treatment. More than 20 million Americans have peripheral nerve damage. This damage becomes more common when you get older. In one out of every 3 people with peripheral nerve damage, the damage comes from diabetes. Fun Facts About Nerves - There are more nerve cells in the human brain than there are stars in the Milky Way. - If we lined up all the neurons in our body it would be around 600 miles long. - There are 100 billion neurons in your brain alone. - A newborn baby's brain grows almost 3 times during the course of its first year. - The left side of human brain controls the right side of the body and the right side of the brain controls the left side of the body. - A New born baby loses about half of their nerve cells before they are born. - As we get older, the brain loses almost one gram per year. - There are about 13, 500,00 neurons in the human spinal cord. - The total surface area of the human brain is about 25, 000 square cm. - The base of the spinal cord has a cluster of nerves, which are most sensitive. - An average adult male brain weighs about 1375 grams. - An average adult female brain is about 1275 grams. - Only four percent of the brain's cells work while the remaining cells are kept in reserve. - Neurons do not under go mitosis - Neurons are the largest cells in the human body. (They can be up to 3 feet long) - The Nervous System can transmit impulses as fast as 100 meters per second. - Potassium and sodium ions are vital to the proper functioning of the Nervous System