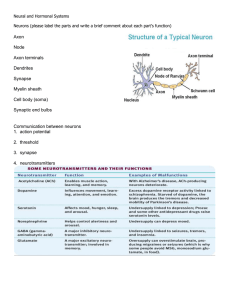
The Nervous System
... Describe the structure and function of a neuron, with reference only to cell body, dendrites, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cell, and neurotransmitter vesicles 5. Give the role and position of three types of neuron: a. sensory neurons - carry messages from the sense organ to the CNS b. motor neurons ...
... Describe the structure and function of a neuron, with reference only to cell body, dendrites, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cell, and neurotransmitter vesicles 5. Give the role and position of three types of neuron: a. sensory neurons - carry messages from the sense organ to the CNS b. motor neurons ...
Review questions: Neuroanatomy
... Schwann cells (PNS): Provide myelin sheath in PNS Nodes of Ranvier (PNS): Gaps between Schwann cells on axon. 3. Describe cellular organisation in both the CNS and the PNS. Grey matter: Cluster of neuron bodies in the CNS and unmyelinated fibres. White matter: bundles of myelinated axons in CNS. Nuc ...
... Schwann cells (PNS): Provide myelin sheath in PNS Nodes of Ranvier (PNS): Gaps between Schwann cells on axon. 3. Describe cellular organisation in both the CNS and the PNS. Grey matter: Cluster of neuron bodies in the CNS and unmyelinated fibres. White matter: bundles of myelinated axons in CNS. Nuc ...
Nervous System - ocw@unimas - Universiti Malaysia Sarawak
... • Neuron (or nerve cell) is the structural and func8onal unit of the nervous system. • Sensory informa
... • Neuron (or nerve cell) is the structural and func8onal unit of the nervous system. • Sensory informa
The Nervous System
... a chemical called dopamine die or do not work properly. Dopamine normally sends signals that help coordinate your movements. No one knows what damages these cells. Symptoms of Parkinson's disease may include; Trembling of hands, arms, legs, jaw and face, stiffness of the arms, legs and trunk, slowne ...
... a chemical called dopamine die or do not work properly. Dopamine normally sends signals that help coordinate your movements. No one knows what damages these cells. Symptoms of Parkinson's disease may include; Trembling of hands, arms, legs, jaw and face, stiffness of the arms, legs and trunk, slowne ...
Neurons, neurotransmitters and other stuff we did last term…
... Neurons, neurotransmitters and other stuff we did last term… Psychology 2617 ...
... Neurons, neurotransmitters and other stuff we did last term… Psychology 2617 ...
The Nervous System - Marblehead High School
... A nerve will only transmit an impulse if the initial stimulus that is picked up at the dendrites is larger than the threshold Threshold - the lowest level of stimulus that will create an impulse If the stimulus is weaker than threshold NO IMPULSE will be produced ...
... A nerve will only transmit an impulse if the initial stimulus that is picked up at the dendrites is larger than the threshold Threshold - the lowest level of stimulus that will create an impulse If the stimulus is weaker than threshold NO IMPULSE will be produced ...
Welcome [www.sciencea2z.com]
... conduct the electrochemical stimulation received from other neural cells to the cell body or soma • Soma – the cell body, contains the nucleus • Axon – long, slender projection of a neuron that conducts electrical impulses away from the soma • Myelin Sheath – electrically insulating layer around the ...
... conduct the electrochemical stimulation received from other neural cells to the cell body or soma • Soma – the cell body, contains the nucleus • Axon – long, slender projection of a neuron that conducts electrical impulses away from the soma • Myelin Sheath – electrically insulating layer around the ...
Nervous System Formative Study Guide File
... 1. Identify the “job” of each of the following: a. Motor neurons Motor neurons are efferent nerves (also called effector neurons), that carry signals from the spinal cord to the muscles to produce (effect) movement. b. Sensory neurons Sensory neurons are nerve cells that transmit sensory information ...
... 1. Identify the “job” of each of the following: a. Motor neurons Motor neurons are efferent nerves (also called effector neurons), that carry signals from the spinal cord to the muscles to produce (effect) movement. b. Sensory neurons Sensory neurons are nerve cells that transmit sensory information ...
Neural and Hormonal Systems Neurons (please label the parts and
... hemispheres of the brains. This is used as a form of treatment for epileptic seizures. ...
... hemispheres of the brains. This is used as a form of treatment for epileptic seizures. ...
Document
... __A__3. Which of the following is true about a motor neuron? a. Dendrites carry information toward the cell body. b. Dendrites carry information away from the cell body. c. Axons carry information toward the cell body. d. None of the above __C__4. Neurons that have repolarized will have a high conce ...
... __A__3. Which of the following is true about a motor neuron? a. Dendrites carry information toward the cell body. b. Dendrites carry information away from the cell body. c. Axons carry information toward the cell body. d. None of the above __C__4. Neurons that have repolarized will have a high conce ...
The Nervous System
... chemical message to adjacent neurons via Axon/Terminals • Myelin: insulates & protects Axons w/a fatty substance ...
... chemical message to adjacent neurons via Axon/Terminals • Myelin: insulates & protects Axons w/a fatty substance ...
nervous system power point
... ions are pumped into the cell, making that point more positive on inside this is called depolarization ...
... ions are pumped into the cell, making that point more positive on inside this is called depolarization ...
Neural Tissue
... Cell body or Soma with Perikaryon Dendrites Axon with axon hillock Synaptic terminals ...
... Cell body or Soma with Perikaryon Dendrites Axon with axon hillock Synaptic terminals ...
Nervous System
... • Dendrites = receive impulses (messages) • Axon = send messages away • Myelin sheath = insulates axon to speed up the message ...
... • Dendrites = receive impulses (messages) • Axon = send messages away • Myelin sheath = insulates axon to speed up the message ...
Nervous Tissues
... central spherical nucleus with one or more nucleoli. Cytoplasm contains: Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, lysosomes as well as other common cytoplasmic organelles and inclusions No centriole. ...
... central spherical nucleus with one or more nucleoli. Cytoplasm contains: Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, lysosomes as well as other common cytoplasmic organelles and inclusions No centriole. ...
Animal Form and Function are Correlated at all levels of organization
... -It consists of scattered cells within an extracellular matrix -Some connective tissues are cartilage, tendons, ligaments, bone, and blood ...
... -It consists of scattered cells within an extracellular matrix -Some connective tissues are cartilage, tendons, ligaments, bone, and blood ...
Study Concepts for Exam V - Nervous System
... The different types of nervous system cells and their function The location of ganglia, the number of neurons, the types of targets, and the neurotransmitters involved in all the synapses of the somatic motor, sympathetic, and parasympathetic divisions Sensory pathways that ascend the spinal cord to ...
... The different types of nervous system cells and their function The location of ganglia, the number of neurons, the types of targets, and the neurotransmitters involved in all the synapses of the somatic motor, sympathetic, and parasympathetic divisions Sensory pathways that ascend the spinal cord to ...
“Definitions” section of your binder Central nervous system
... messages travel to and from the brain Synapse: the gap that exists between individual nerve cells Neurotransmitters: the chemicals released by neurons which determine the rate at which other neurons fire. ...
... messages travel to and from the brain Synapse: the gap that exists between individual nerve cells Neurotransmitters: the chemicals released by neurons which determine the rate at which other neurons fire. ...
Parts and Functions of a Nervous System
... Parts and Functions of a Nervous System The nervous system can be divided into two main parts: 1. ________________which includes the brain and spinal cord 2. ________________ which consists of nerves that lie outside the brain and the spinal cord Peripheral nervous system ...
... Parts and Functions of a Nervous System The nervous system can be divided into two main parts: 1. ________________which includes the brain and spinal cord 2. ________________ which consists of nerves that lie outside the brain and the spinal cord Peripheral nervous system ...
Nervous Systems
... Two Main Parts of Vertebrate Nervous Systems • Central nervous system (CNS) – brain and spinal cord – integration ...
... Two Main Parts of Vertebrate Nervous Systems • Central nervous system (CNS) – brain and spinal cord – integration ...
Chapter 2: Brain Development
... • A variety of chemicals signal cells to turn into specialized cells • Ectodermal cells are inhibited by molecules, signalling a development into neural cells and not skin cells • After neural cell determination: ...
... • A variety of chemicals signal cells to turn into specialized cells • Ectodermal cells are inhibited by molecules, signalling a development into neural cells and not skin cells • After neural cell determination: ...






![Welcome [www.sciencea2z.com]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008568661_1-062fb6959798aae5bb439e7880889016-300x300.png)