36.1: The Nervous System
... 3 Types of neurons • 1. Sensory neurons: carry impulses from the body to the spinal cord and brain (sense receptors) • 2. Motor neurons carry the response impulses away from the brain and spinal cord to a muscle ...
... 3 Types of neurons • 1. Sensory neurons: carry impulses from the body to the spinal cord and brain (sense receptors) • 2. Motor neurons carry the response impulses away from the brain and spinal cord to a muscle ...
Central Nervous System
... (the brain and spinal cord) to serve the limbs and organs. Unlike the central nervous system, however, the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), it is not protected by bone, leaving it exposed to toxins and mechanical injuries. ...
... (the brain and spinal cord) to serve the limbs and organs. Unlike the central nervous system, however, the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), it is not protected by bone, leaving it exposed to toxins and mechanical injuries. ...
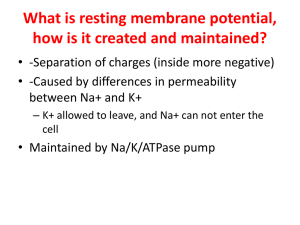
What is resting membrane potential, how is it created and maintained?
... open = rapid depolarization • 2. Action potential ends; K+ channels open leading to hyperpolarization ...
... open = rapid depolarization • 2. Action potential ends; K+ channels open leading to hyperpolarization ...
Chapter 48: The Nervous System
... (change in environment) triggers a response concentrated in sense organs Sensitivity determined by density of receptors ...
... (change in environment) triggers a response concentrated in sense organs Sensitivity determined by density of receptors ...
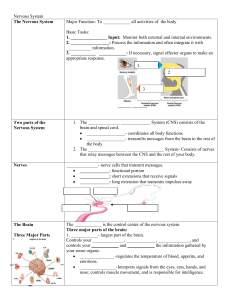
Nervous System - Effingham County Schools
... 2. _________________: Process the information and often integrate it with ___________ information. 3. ___________ ____________: If necessary, signal effecter organs to make an appropriate response. ...
... 2. _________________: Process the information and often integrate it with ___________ information. 3. ___________ ____________: If necessary, signal effecter organs to make an appropriate response. ...
The nervous system
... Messages move from dendrite, through the nerve cell body, to the axon Axons are covered with a myelin sheath (insulation), made by Schwann cells which prevent loss of charged ions from nerve cells Areas between sections of myelin are called nodes of Ranvier; nerve impulses jump from one node to ...
... Messages move from dendrite, through the nerve cell body, to the axon Axons are covered with a myelin sheath (insulation), made by Schwann cells which prevent loss of charged ions from nerve cells Areas between sections of myelin are called nodes of Ranvier; nerve impulses jump from one node to ...
The nervous system
... Messages move from dendrite, through the nerve cell body, to the axon Axons are covered with a myelin sheath (insulation), made by Schwann cells which prevent loss of charged ions from nerve cells Areas between sections of myelin are called nodes of Ranvier; nerve impulses jump from one node to ...
... Messages move from dendrite, through the nerve cell body, to the axon Axons are covered with a myelin sheath (insulation), made by Schwann cells which prevent loss of charged ions from nerve cells Areas between sections of myelin are called nodes of Ranvier; nerve impulses jump from one node to ...
Brain Jeopardy
... A branched fiber that extends outward from the main cell body and carries information into the neuron – ...
... A branched fiber that extends outward from the main cell body and carries information into the neuron – ...
Studying the concepts pg 344 1-7 Motor neurons are located in the
... Studying the concepts pg 344 1-7 ...
... Studying the concepts pg 344 1-7 ...
The Nervous System - Riverside Preparatory High School
... Cell body – contains nucleus; metabolic center Dendrite – fiber that conveys messages toward cell body Axon – conduct nerve impulses away from the cell body Axon terminals – end of axon; contain neurotransmitters & release them Synaptic cleft/synapse – gap between neurons ...
... Cell body – contains nucleus; metabolic center Dendrite – fiber that conveys messages toward cell body Axon – conduct nerve impulses away from the cell body Axon terminals – end of axon; contain neurotransmitters & release them Synaptic cleft/synapse – gap between neurons ...
The nervous system
... subdivisions The first are: a) The Central Nervous System – the brain and the spinal cord, and b) The Peripheral Nervous System – bundles of axons connecting the spinal cord and the rest of the body. ...
... subdivisions The first are: a) The Central Nervous System – the brain and the spinal cord, and b) The Peripheral Nervous System – bundles of axons connecting the spinal cord and the rest of the body. ...
Circulatory System Directs blood from the heart to the rest of the
... one another. These chemicals are called neurotransmitters. •Neurotransmitters leave one neuron, travel through a small intercellular space, to another neuron. That space is called a synapse. •At the end of each neuron is a receptor that monitors the internal condition of the body •Receptors transmit ...
... one another. These chemicals are called neurotransmitters. •Neurotransmitters leave one neuron, travel through a small intercellular space, to another neuron. That space is called a synapse. •At the end of each neuron is a receptor that monitors the internal condition of the body •Receptors transmit ...
Nociceptive system
... glucose and cuprum level in plasma, activation of hemostasis. • It considered to cause the majority of both visceral and biochemical reactions by excitation of sympathetic nervous system, which is presented by neurons of hypothalamus, hypophisis and cells in medullar substance of adrenal glands. ...
... glucose and cuprum level in plasma, activation of hemostasis. • It considered to cause the majority of both visceral and biochemical reactions by excitation of sympathetic nervous system, which is presented by neurons of hypothalamus, hypophisis and cells in medullar substance of adrenal glands. ...
Class Topics
... – Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) • all nerves outside of CNS – cranial nerves - from brain » 12 pairs – spinal nerves - from spinal cord Page: 3 ...
... – Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) • all nerves outside of CNS – cranial nerves - from brain » 12 pairs – spinal nerves - from spinal cord Page: 3 ...
Unit XIV: Regulation
... - nerves are bundles of neurons 1 – Sensory Neurons – located in sense organs – receptors carry impulses to the spinal cord and brain 2 – Interneurons – located in the central nervous system interpret impulses 3 – Motor Neurons – located at effectors carry impulses from the CNS to muscles and glands ...
... - nerves are bundles of neurons 1 – Sensory Neurons – located in sense organs – receptors carry impulses to the spinal cord and brain 2 – Interneurons – located in the central nervous system interpret impulses 3 – Motor Neurons – located at effectors carry impulses from the CNS to muscles and glands ...
HONORS BIOLOGY Chapter 28 Nervous Systems
... Chapter 28 Nervous Systems Introduction: Can an Injured Spinal Cord Be Fixed? ...
... Chapter 28 Nervous Systems Introduction: Can an Injured Spinal Cord Be Fixed? ...
Page 1
... breathing, blood pressure, and the digestive system. ________3. What are the two parts of the nervous system? A. the brain and the spinal cord B. the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system C. the neurons and dendrites D. the cerebrum and medulla _________4. What are the three main ...
... breathing, blood pressure, and the digestive system. ________3. What are the two parts of the nervous system? A. the brain and the spinal cord B. the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system C. the neurons and dendrites D. the cerebrum and medulla _________4. What are the three main ...
3 Types of nervous systems
... • They do not have a central nervous system. They just have a network of interconnected neurons running along the walls of their bodies. Network of neurons ...
... • They do not have a central nervous system. They just have a network of interconnected neurons running along the walls of their bodies. Network of neurons ...
The Nervous System : communication
... inhalation, swallowing or absorption through eyes or mouth Strychnine is a neurotoxin which acts as an antagonist of acetylcholine receptors. It primarily affects the motor nerves in the spinal cord which control muscle contraction. An impulse is triggered at one end of a nerve by the binding of neu ...
... inhalation, swallowing or absorption through eyes or mouth Strychnine is a neurotoxin which acts as an antagonist of acetylcholine receptors. It primarily affects the motor nerves in the spinal cord which control muscle contraction. An impulse is triggered at one end of a nerve by the binding of neu ...
Chapter 9: Nervous System guide—Please complete these notes on
... -allows feeling, thinking, moving, and awareness -coordinates all body functions to maintain homeostasis and enables the body to respond to changing conditions 1. Nerve cells are also known as _neurons, which are the structural and functional units of the nervous system. ...
... -allows feeling, thinking, moving, and awareness -coordinates all body functions to maintain homeostasis and enables the body to respond to changing conditions 1. Nerve cells are also known as _neurons, which are the structural and functional units of the nervous system. ...
The Nervous System
... • Is expanded area of axon • Contains synaptic vesicles of neurotransmitters – Chemical messengers – Released at presynaptic membrane – Affect receptors of postsynaptic membrane ...
... • Is expanded area of axon • Contains synaptic vesicles of neurotransmitters – Chemical messengers – Released at presynaptic membrane – Affect receptors of postsynaptic membrane ...
MicroRNA ablation affects Bergmann glial morphology and disrupts
... MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play important roles during development of the central nervous system (CNS). Several reports indicate that tissue development and cellular differentiation in the developing forebrains are disrupted in the absence of miRNAs. However, miRNA functions during cerebellar development ha ...
... MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play important roles during development of the central nervous system (CNS). Several reports indicate that tissue development and cellular differentiation in the developing forebrains are disrupted in the absence of miRNAs. However, miRNA functions during cerebellar development ha ...
Nervous Regulation
... The autonomic nervous system is made entirely of ________________. Impulses in this system start in motor neurons in the ______________ __________. The axons of these nerves ________________________ _________________________________________________________. The axon of the original neuron syna ...
... The autonomic nervous system is made entirely of ________________. Impulses in this system start in motor neurons in the ______________ __________. The axons of these nerves ________________________ _________________________________________________________. The axon of the original neuron syna ...