CHAPTER 11 Nervous Tissue - Austin Community College
... Such pathways may create converging, diverging or reverberating circuits as is shown in the next slide. Such circuits may produce EPSP’s or IPSP’s and help modulate the neuronal signals. ...
... Such pathways may create converging, diverging or reverberating circuits as is shown in the next slide. Such circuits may produce EPSP’s or IPSP’s and help modulate the neuronal signals. ...
ch. 48 Nervous System notes
... environments to CNS Interneurons: integrate sensory input and motor output (carry stimuli in the brain and spinal cord) Motor Neurons: convey impulses from CNS to effector cells in muscles or glands Glial cells: support, protect, and nourish neurons ...
... environments to CNS Interneurons: integrate sensory input and motor output (carry stimuli in the brain and spinal cord) Motor Neurons: convey impulses from CNS to effector cells in muscles or glands Glial cells: support, protect, and nourish neurons ...
Part 1 (nerve impulses, ppt file)
... permeable to Na+ momentarily. Some Na+ rushes in and causes depolarization, which in turn, shuts off the permeability to Na+. Then repolarization occurs. ...
... permeable to Na+ momentarily. Some Na+ rushes in and causes depolarization, which in turn, shuts off the permeability to Na+. Then repolarization occurs. ...
Nervous System - wondersofscience
... • carries information from the various parts of the body to the brain. It is also the reflex center. – A reflex is a rapid and involuntary reaction to a stimulus – A reflex arc is the path taken by a nerve impulse during a reflex ...
... • carries information from the various parts of the body to the brain. It is also the reflex center. – A reflex is a rapid and involuntary reaction to a stimulus – A reflex arc is the path taken by a nerve impulse during a reflex ...
Human Nerve Chapter
... Nervous systems perform these basic functions: Receiving sensory input from the internal and external environments through receptors. Integrating the inputs in a central location to determine an appropriate response. Producing a motor response that causes one or more muscles to contract and move a b ...
... Nervous systems perform these basic functions: Receiving sensory input from the internal and external environments through receptors. Integrating the inputs in a central location to determine an appropriate response. Producing a motor response that causes one or more muscles to contract and move a b ...
7th sci Nervous System and Brain ppt nervous system and
... • Motor: sending of signals to muscles and/or glands to elicit a response ...
... • Motor: sending of signals to muscles and/or glands to elicit a response ...
Power Point
... – Mature neurons cannot undergo mitosis so damage to nervous tissue can be permanent – Neurons have a limited capacity to repair themselves and can be repaired if the damage is not extensive ...
... – Mature neurons cannot undergo mitosis so damage to nervous tissue can be permanent – Neurons have a limited capacity to repair themselves and can be repaired if the damage is not extensive ...
Nervous System
... It begins in the dendrites, moves rapidly towards the neurons cells body, and then down the axon until it reaches the axon tips. It travels along the neuron in the form of electricity. ...
... It begins in the dendrites, moves rapidly towards the neurons cells body, and then down the axon until it reaches the axon tips. It travels along the neuron in the form of electricity. ...
Nervous_System
... lipid and protein sheath covering neuron axons (not all axons are myelinated) Electrically insulates axon and increases conduction speed (Ex. Leaky garden hose) Multiple Sclerosis: Autoimmune disease that breaks down the myelin sheath in the CNS. Tremors: Unregulated electrical impulses ...
... lipid and protein sheath covering neuron axons (not all axons are myelinated) Electrically insulates axon and increases conduction speed (Ex. Leaky garden hose) Multiple Sclerosis: Autoimmune disease that breaks down the myelin sheath in the CNS. Tremors: Unregulated electrical impulses ...
BIOLOGY 12: U NIT M/N - C A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. What are the
... 15. What happens to the postsynaptic membrane if the released product is excitatory? Result when released product is inhibitory? _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ ...
... 15. What happens to the postsynaptic membrane if the released product is excitatory? Result when released product is inhibitory? _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ ...
file - Athens Academy
... responsible for ridding the brain of debris and foreign substances – it acts as an immune system for the nervous system. ...
... responsible for ridding the brain of debris and foreign substances – it acts as an immune system for the nervous system. ...
Ch. 48-49 Nervous System 9e S13
... Organization of the Nervous System • Central nervous system (CNS) = brain + spinal cord • Peripheral nervous system (PNS) = nerves throughout body – Sensory receptors: collect info – Sensory neurons: body CNS – Motor neurons: CNS body (muscles, glands) – Interneurons: connect sensory & motor n ...
... Organization of the Nervous System • Central nervous system (CNS) = brain + spinal cord • Peripheral nervous system (PNS) = nerves throughout body – Sensory receptors: collect info – Sensory neurons: body CNS – Motor neurons: CNS body (muscles, glands) – Interneurons: connect sensory & motor n ...
Guided Notes
... ii. ________ nerve axons can regenerate successfully if cell body is not destroyed iii. Uninjured cell body swells to prepare to synthesize proteins to support regeneration 1. axon regeneration = ______________________ 2. greater distance = less recovery chance = possible ______________ formation 3. ...
... ii. ________ nerve axons can regenerate successfully if cell body is not destroyed iii. Uninjured cell body swells to prepare to synthesize proteins to support regeneration 1. axon regeneration = ______________________ 2. greater distance = less recovery chance = possible ______________ formation 3. ...
NOVEL APPROACHES TO TRAUMATIC BRAIN AND SPINAL
... • Traumatic brain and spinal cord injuries (TBI & SCI) are incurred by over 1.7M individuals yearly in the US alone • There are currently no effective treatments for TBI and SCI resulting in significant unmet need • Recovery from these central nervous system (CNS) injuries is poor due to the limited ...
... • Traumatic brain and spinal cord injuries (TBI & SCI) are incurred by over 1.7M individuals yearly in the US alone • There are currently no effective treatments for TBI and SCI resulting in significant unmet need • Recovery from these central nervous system (CNS) injuries is poor due to the limited ...
File
... Leafy vegetables such as spinach and turnip greens dried beans and peas, fortified cereal products,sunflower seeds and certain other fruits and vegatables are rich sources of folate. Some breakfast cereals are fortified with 25% to 100% of the recommended dietary allowance ...
... Leafy vegetables such as spinach and turnip greens dried beans and peas, fortified cereal products,sunflower seeds and certain other fruits and vegatables are rich sources of folate. Some breakfast cereals are fortified with 25% to 100% of the recommended dietary allowance ...
Nervous System
... out from the cell body; receive and carry impulses to the cell body 3. axon- long, fibrous part of neuron; conducts nerve impulses away from cell body 4. at the end of the axon, the impulse travels across the synapse, a tiny gap separating the axon of one neuron from the dendrite of another. Once th ...
... out from the cell body; receive and carry impulses to the cell body 3. axon- long, fibrous part of neuron; conducts nerve impulses away from cell body 4. at the end of the axon, the impulse travels across the synapse, a tiny gap separating the axon of one neuron from the dendrite of another. Once th ...
Unit 4 – Coordination Reflex Arc
... – cover brain surfaces – formation of blood-brain barrier – regulate composition of cerebrospinal fluid – remove neurotransmitters and potassium ions from ICF – repairing damaged tissue with scar tissue Occur in the Peripheral Nervous System • Schwann cells – form myelin sheath in PNS • Satellite ce ...
... – cover brain surfaces – formation of blood-brain barrier – regulate composition of cerebrospinal fluid – remove neurotransmitters and potassium ions from ICF – repairing damaged tissue with scar tissue Occur in the Peripheral Nervous System • Schwann cells – form myelin sheath in PNS • Satellite ce ...
Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System
... Central Nervous System (CNS)Control center of the nervous system controlling both voluntary and involuntary actions ...
... Central Nervous System (CNS)Control center of the nervous system controlling both voluntary and involuntary actions ...
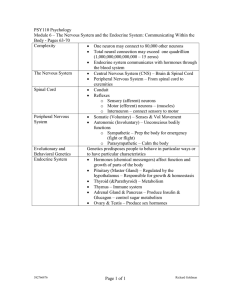
PSY110 Psychology
... Endocrine system communicates with hormones through the blood system The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) – Brain & Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System – From spinal cord to exremities Spinal Cord Conduit Reflexes o Sensory (afferent) neurons o Motor (efferent) neurons – (musc ...
... Endocrine system communicates with hormones through the blood system The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) – Brain & Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System – From spinal cord to exremities Spinal Cord Conduit Reflexes o Sensory (afferent) neurons o Motor (efferent) neurons – (musc ...
Nervous Systems
... The mechanisms of impulse transmission in a neuron. The process that leads to release of neurotransmitters, and what happens at the synapse. ...
... The mechanisms of impulse transmission in a neuron. The process that leads to release of neurotransmitters, and what happens at the synapse. ...
Neuron (Nerve Cell)
... Medical Procedures & the Brain • How do we know about the brain, its regions, parts & functions? • How have we been able to diagnose problems within the nervous system? • Where & how did the first medical procedures investigating the nervous system occur? ...
... Medical Procedures & the Brain • How do we know about the brain, its regions, parts & functions? • How have we been able to diagnose problems within the nervous system? • Where & how did the first medical procedures investigating the nervous system occur? ...
- Describe the roles of the different types of glial cells
... the tight junctions and prevent any leakage of unwanted substances into the brain. This helps create a very finely and tightly regulated environment and keeps out any potential toxins. Astrocytes also release various neurotrophic factors which regulate axonal growth and neuronal transport - Schwann ...
... the tight junctions and prevent any leakage of unwanted substances into the brain. This helps create a very finely and tightly regulated environment and keeps out any potential toxins. Astrocytes also release various neurotrophic factors which regulate axonal growth and neuronal transport - Schwann ...