Chapter 9 Nerves
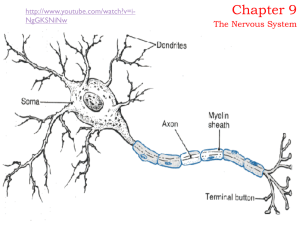
... Dendrites and the cell body provide receptive surfaces A single AXON arises from the cell body and may be enclosed in a myelin sheath and a neurilemma. ...
... Dendrites and the cell body provide receptive surfaces A single AXON arises from the cell body and may be enclosed in a myelin sheath and a neurilemma. ...
Unit 4 Test Nervous System
... a. One direction: From dendrites to axon terminals b. One direction: From axon terminals to dendrites c. Two directions: Can travel up or down the neuron d. Any direction: Whichever direction the impulse is stronger ...
... a. One direction: From dendrites to axon terminals b. One direction: From axon terminals to dendrites c. Two directions: Can travel up or down the neuron d. Any direction: Whichever direction the impulse is stronger ...
Brain Questions
... 3- The central nervous system is composed of what? The peripheral nervous system is composed of what? 4- What is the axon of a neuron wrapped in? What is its function? 5- How do signals travel down the axon? 6- What role do dendrites have in cell to cell communication? 7- What is the difference betw ...
... 3- The central nervous system is composed of what? The peripheral nervous system is composed of what? 4- What is the axon of a neuron wrapped in? What is its function? 5- How do signals travel down the axon? 6- What role do dendrites have in cell to cell communication? 7- What is the difference betw ...
Peripheral nervous system
... Once one area is positive, the positive charge moves down the axon causing more Na+ channels to open After Na+ enters, the ions channels for Na+ close but the inside is still very + Sodium-potassium pumps then use ATP to move Na+ out of the neuron and K+ in to return the charges inside and outside o ...
... Once one area is positive, the positive charge moves down the axon causing more Na+ channels to open After Na+ enters, the ions channels for Na+ close but the inside is still very + Sodium-potassium pumps then use ATP to move Na+ out of the neuron and K+ in to return the charges inside and outside o ...
Nervous System Student Notes
... carry information away from the cell in the form of a nerve impulse. Neurons commonly have only ____________ ____________ are simply bundles of axons. Axons are surrounded by a “Band-Aid” of cells called ____________. Multiple layers of these cells create __________________, around the axon called a ...
... carry information away from the cell in the form of a nerve impulse. Neurons commonly have only ____________ ____________ are simply bundles of axons. Axons are surrounded by a “Band-Aid” of cells called ____________. Multiple layers of these cells create __________________, around the axon called a ...
Nervous System Cells
... • In inflamed brain tissue, they enlarge, move about and carry on phagocytes ...
... • In inflamed brain tissue, they enlarge, move about and carry on phagocytes ...
Chapter 14
... nervous tissue in the CNS, replace damaged neurons, and assist with neuronal development. Ependymal cells and nearby blood capillaries form the choroid plexus, which produces CSF. The ependymal cells have patches of cilia on their apical surfaces that help circulate the CSF. Microglia are small phag ...
... nervous tissue in the CNS, replace damaged neurons, and assist with neuronal development. Ependymal cells and nearby blood capillaries form the choroid plexus, which produces CSF. The ependymal cells have patches of cilia on their apical surfaces that help circulate the CSF. Microglia are small phag ...
AP Ch. 9 Nervous System Part 1 Worksheets
... 7. Neurons that have a single process extending from the cell body are classified as _________, if they have two processes, they are classified as _____________ 8. White matter is composed of axons that are sheathed in _________________________ 9. Two ions necessary to create an electric current in ...
... 7. Neurons that have a single process extending from the cell body are classified as _________, if they have two processes, they are classified as _____________ 8. White matter is composed of axons that are sheathed in _________________________ 9. Two ions necessary to create an electric current in ...
chapter # 27 > human anatomy - the nervous system
... THE CEREBELLUM CONTROLS OUR SENSE OF ____________________ AND COORDINATES _______________________ SO THEY WORK TOGETHER ...
... THE CEREBELLUM CONTROLS OUR SENSE OF ____________________ AND COORDINATES _______________________ SO THEY WORK TOGETHER ...
BOX 2.1 THE NEURON DOCTRINE The cell theory, which states
... The cell theory, which states that all organisms are composed of individual cells, was developed around the middle of the nineteenth century by Mattias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, this unitary vision of the cellular nature of life was not immediately applied to the nervous system, as mos ...
... The cell theory, which states that all organisms are composed of individual cells, was developed around the middle of the nineteenth century by Mattias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, this unitary vision of the cellular nature of life was not immediately applied to the nervous system, as mos ...
Fundamentals of Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... (nerve impulse) to the cell body. A single longer appendage is called Axon. It takes information away from cell body. It branches at the end into terminal knobs. A terminal knob secretes a chemical called Neurotransmitter in the gap to the next neuron or muscle membrane. 3-types of neurons (on basis ...
... (nerve impulse) to the cell body. A single longer appendage is called Axon. It takes information away from cell body. It branches at the end into terminal knobs. A terminal knob secretes a chemical called Neurotransmitter in the gap to the next neuron or muscle membrane. 3-types of neurons (on basis ...
Lecture 13: The Nervous System
... B. Play a role in forming the blood brain barrier and can form scar tissue in the brain following an injury C. Found primarily in gray matter because they are associated with the cell bodies of neurons. D. They are the neuron Mamas...they remove NT from synapses, help form new synapses, help main ...
... B. Play a role in forming the blood brain barrier and can form scar tissue in the brain following an injury C. Found primarily in gray matter because they are associated with the cell bodies of neurons. D. They are the neuron Mamas...they remove NT from synapses, help form new synapses, help main ...
nervous system outline PPT
... Autonomic Nervous System Carry impulses from the central nervous system to glands, various involuntary muscles, cardiac muscle, and membranes Stimulates organs, glands and senses by stimulating secretions of substances Divided into sympathetic and ...
... Autonomic Nervous System Carry impulses from the central nervous system to glands, various involuntary muscles, cardiac muscle, and membranes Stimulates organs, glands and senses by stimulating secretions of substances Divided into sympathetic and ...
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A
... • Release neurotransmitters to excite or inhibit other cells ...
... • Release neurotransmitters to excite or inhibit other cells ...
File
... **White Matter + myelin ***Grey Matter – myelin Nodes of Ranvier • gaps between myelin sheath ...
... **White Matter + myelin ***Grey Matter – myelin Nodes of Ranvier • gaps between myelin sheath ...
file - Athens Academy
... responsible for ridding the brain of debris and foreign substances – it acts as an immune system for the nervous system. ...
... responsible for ridding the brain of debris and foreign substances – it acts as an immune system for the nervous system. ...
The autonomic nervous system
... - In the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, efferent nerve signals are carried from the central nervous system to their targets by a system of two neurons. - The axons of preganglionic parasympathetic neurons are usually long, extending from the CNS into a ganglion that is either very c ...
... - In the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, efferent nerve signals are carried from the central nervous system to their targets by a system of two neurons. - The axons of preganglionic parasympathetic neurons are usually long, extending from the CNS into a ganglion that is either very c ...
Nervous-histology
... allows the passage of water, some gases, and lipid-soluble molecules by passive diffusion, as well as the selective transport of molecules such as glucose and amino acids that are crucial to neural function. On the other hand, the blood–brain barrier may prevent the entry of lipophilic, potential ...
... allows the passage of water, some gases, and lipid-soluble molecules by passive diffusion, as well as the selective transport of molecules such as glucose and amino acids that are crucial to neural function. On the other hand, the blood–brain barrier may prevent the entry of lipophilic, potential ...
nervous system
... Form myelin sheaths around the larger nerve fibers in the PNS. Vital to neuronal regeneration ...
... Form myelin sheaths around the larger nerve fibers in the PNS. Vital to neuronal regeneration ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... Long axons are called nerve fibers Usually there is only one unbranched axon per neuron Rare branches, if present, are called axon collaterals Axonal terminal – branched terminus of an axon ...
... Long axons are called nerve fibers Usually there is only one unbranched axon per neuron Rare branches, if present, are called axon collaterals Axonal terminal – branched terminus of an axon ...