Glossary of Terms – DNA and the production of proteins
... Structures found in nucleus which carry genetic information Molecule, found in the nucleus which carries the genetic code Strand of DNA which codes for a protein Subunit of DNA molecule which consists of a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar and a base Parts of the DNA structure which pair up with on ...
... Structures found in nucleus which carry genetic information Molecule, found in the nucleus which carries the genetic code Strand of DNA which codes for a protein Subunit of DNA molecule which consists of a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar and a base Parts of the DNA structure which pair up with on ...
Questions on DNA Replication and Enzymes used in DNA replication
... 1. Helicase – to unwind the DNA double helix 2. Single strand binding protein – stabilize the unwound parental DNA 3. Primase – inserts a RNA primer to help DNA nucleotides join onto the parent strand [only one needed on the continuous strand while many are seen on the ‘lagging strand’ (5’ – 3’)] 4. ...
... 1. Helicase – to unwind the DNA double helix 2. Single strand binding protein – stabilize the unwound parental DNA 3. Primase – inserts a RNA primer to help DNA nucleotides join onto the parent strand [only one needed on the continuous strand while many are seen on the ‘lagging strand’ (5’ – 3’)] 4. ...
DNA Worksheet 1. What does DNA stand for? 2. What does DNA do
... 4. Draw a diagram to show all the parts of DNA: sugars, phosphates, nucleotides(A,T,C,G), and hydrogen bonds ...
... 4. Draw a diagram to show all the parts of DNA: sugars, phosphates, nucleotides(A,T,C,G), and hydrogen bonds ...
DNA - Southington Public Schools
... Almost all functions of living things including growing, reproducing, digesting food, moving, fighting disease, even thinking rely on the production of various proteins. Without DNA, living things would not exist very long. Parts of DNA DNA is very complex and long (almost 1m in each human cell!), b ...
... Almost all functions of living things including growing, reproducing, digesting food, moving, fighting disease, even thinking rely on the production of various proteins. Without DNA, living things would not exist very long. Parts of DNA DNA is very complex and long (almost 1m in each human cell!), b ...
Name ______ Date - Net Start Class
... 9. Which of these is most responsible for carrying coded information from the nucleus? a. mRNA b. The ribosomes c. ATP d. The cell membrane 6. The picture above shows an x-ray diffraction of DNA. Who is famous for this picture? The x-ray diffraction of DNA led to the idea that DNA — a. Robert Hooke ...
... 9. Which of these is most responsible for carrying coded information from the nucleus? a. mRNA b. The ribosomes c. ATP d. The cell membrane 6. The picture above shows an x-ray diffraction of DNA. Who is famous for this picture? The x-ray diffraction of DNA led to the idea that DNA — a. Robert Hooke ...
Prentice hall Biology Worksheets
... Matching On the lines provided, match the letter of the scientist(s) with the description of his or their conclusions. a. Griffith b. Avery c. Hershey and Chase 1. concluded that the genetic material of a bacteriophage is DNA 2. concluded that DNA was the factor that transmits genetic information fr ...
... Matching On the lines provided, match the letter of the scientist(s) with the description of his or their conclusions. a. Griffith b. Avery c. Hershey and Chase 1. concluded that the genetic material of a bacteriophage is DNA 2. concluded that DNA was the factor that transmits genetic information fr ...
DNA/RNA structure
... ▪ ribose in RNA ▪ deoxyribose in DNA phosphate (PO4) group Are nucleic acids charged molecules? ...
... ▪ ribose in RNA ▪ deoxyribose in DNA phosphate (PO4) group Are nucleic acids charged molecules? ...
3.5 Genetic Modification and Biotechnology
... Gene transfer to bacteria using plasmids makes use of restriction endonucleases and DNA ligase. Assessment of the potential risks and benefits associated with genetic modification of crops. Analysis of data on risks to monarch butterflies of Bt crops. ...
... Gene transfer to bacteria using plasmids makes use of restriction endonucleases and DNA ligase. Assessment of the potential risks and benefits associated with genetic modification of crops. Analysis of data on risks to monarch butterflies of Bt crops. ...
DNA Replication
... 3. The free nucleotides in the new strands bind together. The copied DNA re-coils. The two DNA molecules are identical. The structure of the DNA molecule (two complementary strands that can separate between the base pairs) ensures that the DNA is copied efficiently (quickly and correctly). ...
... 3. The free nucleotides in the new strands bind together. The copied DNA re-coils. The two DNA molecules are identical. The structure of the DNA molecule (two complementary strands that can separate between the base pairs) ensures that the DNA is copied efficiently (quickly and correctly). ...
Structure and History of DNA 1-8
... Erwin Chargaff’s Rules • In 1950, Chargaff analyzed the base composition of DNA in a number of organisms – varied bet. species • Found regularity in the ratios of nucleotide bases - A = T and G = C • This made DNA a more credible candidate for the genetic material. ...
... Erwin Chargaff’s Rules • In 1950, Chargaff analyzed the base composition of DNA in a number of organisms – varied bet. species • Found regularity in the ratios of nucleotide bases - A = T and G = C • This made DNA a more credible candidate for the genetic material. ...
Worksheet for Biology 1107 Biological Molecules: Structure and
... 9. List the amino acids that are in the primary structure of the peptide on page 5 of the biomolecules text. ...
... 9. List the amino acids that are in the primary structure of the peptide on page 5 of the biomolecules text. ...
Match each statement with the appropriate letter: A. DNA B. RNA C
... ___ 8. forms a double helix ___ 9. contains thymine ___10. contains nitrogen ...
... ___ 8. forms a double helix ___ 9. contains thymine ___10. contains nitrogen ...
DISCOVERY OF DNAhandout
... Read the Nature article by Watson & Crick Discuss how they used the work of others to come up with the structure of DNA. How does the structure account for identical replication of DNA to be the conveyer of inheritance? ...
... Read the Nature article by Watson & Crick Discuss how they used the work of others to come up with the structure of DNA. How does the structure account for identical replication of DNA to be the conveyer of inheritance? ...
Carbohydrate Tutorial
... Glucose can have a straight line of carbon atoms or form a ring structure. The 5 carbon sugars called pentose are used in nucleic acid synthesis are deoxyribose and ribose Give 3 examples of disaccharides. a. Sucrose b. Lactose c. Maltose Polysaccharides include starch, cellulose and glycogen Starch ...
... Glucose can have a straight line of carbon atoms or form a ring structure. The 5 carbon sugars called pentose are used in nucleic acid synthesis are deoxyribose and ribose Give 3 examples of disaccharides. a. Sucrose b. Lactose c. Maltose Polysaccharides include starch, cellulose and glycogen Starch ...
Ch 16 homework
... Which enzyme functions here to deal with supercoils in DNA? What enzyme functions here to unwind the DNA? Which enzyme functions to synthesize these small RNA sequences? What are these ~1000 nucleotide long DNA fragments called? Is this strand the leading or lagging strand ...
... Which enzyme functions here to deal with supercoils in DNA? What enzyme functions here to unwind the DNA? Which enzyme functions to synthesize these small RNA sequences? What are these ~1000 nucleotide long DNA fragments called? Is this strand the leading or lagging strand ...
DNA Worksheet
... 22. Where are proteins made in the cell? _____________________________ 23. Use the amino acid chart in your notes to translate the sequence of codons (from #16) and write the ...
... 22. Where are proteins made in the cell? _____________________________ 23. Use the amino acid chart in your notes to translate the sequence of codons (from #16) and write the ...
SBI3U - misshoughton.net
... o If an incorrect or damaged base is added, it will be replaced with a proper base ...
... o If an incorrect or damaged base is added, it will be replaced with a proper base ...
Evidence for Evolu[[[irtion
... The greatest shark to have ever lived! An apex predator, the Carcharodon megalodon comes from the Greek word for “big tooth”. This shark was as big as a bus at a length of 60 feet and estimated to weigh between 30-60 tons. Their skeletons were made of cartilage, like those of modern sharks. This ...
... The greatest shark to have ever lived! An apex predator, the Carcharodon megalodon comes from the Greek word for “big tooth”. This shark was as big as a bus at a length of 60 feet and estimated to weigh between 30-60 tons. Their skeletons were made of cartilage, like those of modern sharks. This ...
Nucleotides and DNA Structure
... 1. Purine(s) which are found mainly in both deoxyribonucleotides and ribonucleotides are A) thymine and cytosine. B) cytosine and uracil. C) cytosine. D) guanine and cytosine. E) adenine and guanine. 2. The abbreviation dGp indicates A) 5' deoxyguanylate. B) 3' deoxyguanylate. C) 3', 5' deoxyguanyl ...
... 1. Purine(s) which are found mainly in both deoxyribonucleotides and ribonucleotides are A) thymine and cytosine. B) cytosine and uracil. C) cytosine. D) guanine and cytosine. E) adenine and guanine. 2. The abbreviation dGp indicates A) 5' deoxyguanylate. B) 3' deoxyguanylate. C) 3', 5' deoxyguanyl ...
No Slide Title
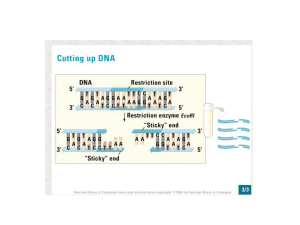
... Restriction Enzymes • Restriction enzymes cut DNA from any source into fragments • Sticky ends can pair up with complementary DNA with the help of ligase producing recombinant DNA • Example: EcoRI, HindII ...
... Restriction Enzymes • Restriction enzymes cut DNA from any source into fragments • Sticky ends can pair up with complementary DNA with the help of ligase producing recombinant DNA • Example: EcoRI, HindII ...
DNA nanotechnology

DNA nanotechnology is the design and manufacture of artificial nucleic acid structures for technological uses. In this field, nucleic acids are used as non-biological engineering materials for nanotechnology rather than as the carriers of genetic information in living cells. Researchers in the field have created static structures such as two- and three-dimensional crystal lattices, nanotubes, polyhedra, and arbitrary shapes, as well as functional devices such as molecular machines and DNA computers. The field is beginning to be used as a tool to solve basic science problems in structural biology and biophysics, including applications in crystallography and spectroscopy for protein structure determination. Potential applications in molecular scale electronics and nanomedicine are also being investigated.The conceptual foundation for DNA nanotechnology was first laid out by Nadrian Seeman in the early 1980s, and the field began to attract widespread interest in the mid-2000s. This use of nucleic acids is enabled by their strict base pairing rules, which cause only portions of strands with complementary base sequences to bind together to form strong, rigid double helix structures. This allows for the rational design of base sequences that will selectively assemble to form complex target structures with precisely controlled nanoscale features. A number of assembly methods are used to make these structures, including tile-based structures that assemble from smaller structures, folding structures using the DNA origami method, and dynamically reconfigurable structures using strand displacement techniques. While the field's name specifically references DNA, the same principles have been used with other types of nucleic acids as well, leading to the occasional use of the alternative name nucleic acid nanotechnology.