Physical view of biomolecular interactions in nano
... UV laser pulses and the chemistry of the guanine radical has been developed. This technique is able to report structural information, dynamics and intra-base conformation within a nucleic acid molecule. It has shown to be a valuable tool in the study of “puzzle” pieces of gene regulation and in the ...
... UV laser pulses and the chemistry of the guanine radical has been developed. This technique is able to report structural information, dynamics and intra-base conformation within a nucleic acid molecule. It has shown to be a valuable tool in the study of “puzzle” pieces of gene regulation and in the ...
Lesson 2 * Carbohydrates
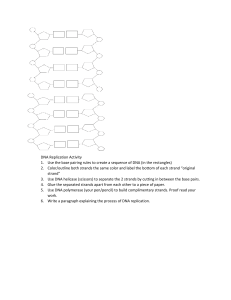
... replicated as the molecule unzips but the other strand (the 3’ to 5’ side, called the lagging strand) needs to be replicated in sections then joined together later by an enzyme called DNA ligase. ...
... replicated as the molecule unzips but the other strand (the 3’ to 5’ side, called the lagging strand) needs to be replicated in sections then joined together later by an enzyme called DNA ligase. ...
Nucleic Acids
... • Contain instructions to build proteins • 2 types: – DNA – RNA • Composed of smaller units called nucleotides – Monomer: Nucleotide – Polymer: Nucleic acid ...
... • Contain instructions to build proteins • 2 types: – DNA – RNA • Composed of smaller units called nucleotides – Monomer: Nucleotide – Polymer: Nucleic acid ...
Nucleic acid worksheet
... 2. These monomers of DNA contain the bases: __________________, ___________________, ________________________, and _____________________. 3. _________________________ is the sugar found in all DNA molecules. 4. The shape of a DNA molecules is called the __________________________. 5. _______________ ...
... 2. These monomers of DNA contain the bases: __________________, ___________________, ________________________, and _____________________. 3. _________________________ is the sugar found in all DNA molecules. 4. The shape of a DNA molecules is called the __________________________. 5. _______________ ...
Part 4
... Genetic material (genes) that are passed on from parent to offspring Codes the amino acids sequence to create a protein ...
... Genetic material (genes) that are passed on from parent to offspring Codes the amino acids sequence to create a protein ...
Nucleic Acid and Protein - Seattle Central College
... 1. At the beginning of lab you will assemble many nucleotides. A DNA nucleotide consists of deoxyribose sugar, phosphate and one of 4 bases. List the 4 bases: ...
... 1. At the beginning of lab you will assemble many nucleotides. A DNA nucleotide consists of deoxyribose sugar, phosphate and one of 4 bases. List the 4 bases: ...
File - Mrs. LeCompte
... The last two phosphate bonds are high energy, unstable, and easily broken ...
... The last two phosphate bonds are high energy, unstable, and easily broken ...
DNA nanotechnology

DNA nanotechnology is the design and manufacture of artificial nucleic acid structures for technological uses. In this field, nucleic acids are used as non-biological engineering materials for nanotechnology rather than as the carriers of genetic information in living cells. Researchers in the field have created static structures such as two- and three-dimensional crystal lattices, nanotubes, polyhedra, and arbitrary shapes, as well as functional devices such as molecular machines and DNA computers. The field is beginning to be used as a tool to solve basic science problems in structural biology and biophysics, including applications in crystallography and spectroscopy for protein structure determination. Potential applications in molecular scale electronics and nanomedicine are also being investigated.The conceptual foundation for DNA nanotechnology was first laid out by Nadrian Seeman in the early 1980s, and the field began to attract widespread interest in the mid-2000s. This use of nucleic acids is enabled by their strict base pairing rules, which cause only portions of strands with complementary base sequences to bind together to form strong, rigid double helix structures. This allows for the rational design of base sequences that will selectively assemble to form complex target structures with precisely controlled nanoscale features. A number of assembly methods are used to make these structures, including tile-based structures that assemble from smaller structures, folding structures using the DNA origami method, and dynamically reconfigurable structures using strand displacement techniques. While the field's name specifically references DNA, the same principles have been used with other types of nucleic acids as well, leading to the occasional use of the alternative name nucleic acid nanotechnology.