WS 12 Notes - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... Between the two DNA strands (in an intact double helix), A bonds with T, and C bonds with G. This is due to hydrogen bonding. A and T form 2 hydrogen bonds, C and G form 3 hydrogen bonds. This "lock-and-key" model is due to hydrogen bonding and shape. ...
... Between the two DNA strands (in an intact double helix), A bonds with T, and C bonds with G. This is due to hydrogen bonding. A and T form 2 hydrogen bonds, C and G form 3 hydrogen bonds. This "lock-and-key" model is due to hydrogen bonding and shape. ...
DNA and Genetics A. 1.
... 1. The DNA of each cell carries a complete set of genes that provides instructions for making all the ...
... 1. The DNA of each cell carries a complete set of genes that provides instructions for making all the ...
Biology 102
... In your textbook, read about DNA structure. Write the term or phrase that best completes each statement. Use these choices: adenine (A) double ring nucleotides ...
... In your textbook, read about DNA structure. Write the term or phrase that best completes each statement. Use these choices: adenine (A) double ring nucleotides ...
TAKS Obj 2 -BIOLOGY
... DNA is formed of nucleotides, which have 3 parts; a sugar, a phosphate and a nitrogen base make up a nucleotide. The 4 different nitrogen bases of DNA are Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine and Guanine. They pair to form the rungs of the ladder. The process of copying DNA is called Replication ...
... DNA is formed of nucleotides, which have 3 parts; a sugar, a phosphate and a nitrogen base make up a nucleotide. The 4 different nitrogen bases of DNA are Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine and Guanine. They pair to form the rungs of the ladder. The process of copying DNA is called Replication ...
Introduction to Genetics
... – A protein molecule may contain several hundred amino acids – Each different protein has its own order, or “sequence,” of amino acids – The correct sequence of amino acids is essential for the protein’s function ...
... – A protein molecule may contain several hundred amino acids – Each different protein has its own order, or “sequence,” of amino acids – The correct sequence of amino acids is essential for the protein’s function ...
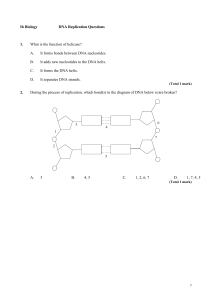
Ib Biology DNA Replication Questions 1. What is the function of
... [Freeman, Scott, Biological Science, 1st, 2002. Electronically reproduced by permission of Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, New Jersey] ...
... [Freeman, Scott, Biological Science, 1st, 2002. Electronically reproduced by permission of Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, New Jersey] ...
Bio101 Topic 5 - Nucleic Acids
... There are 3 types of RNA. mRNA: messenger RNA tRNA : transfer RNA rRNA: ribosomal RNA Function of RNA: ...
... There are 3 types of RNA. mRNA: messenger RNA tRNA : transfer RNA rRNA: ribosomal RNA Function of RNA: ...
Worksheet – DNA and Protein Synthesis Biology 11 Name: DNA
... Protein Synthesis – you will need to use your chart of mRNA codons/amino acids for many of the following questions. 5. Which of the following best describes the function of mRNA? A. it stays in the nucleus and is copied by DNA B. it carries amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain C. it makes u ...
... Protein Synthesis – you will need to use your chart of mRNA codons/amino acids for many of the following questions. 5. Which of the following best describes the function of mRNA? A. it stays in the nucleus and is copied by DNA B. it carries amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain C. it makes u ...
NUCLEIC ACID
... SIMPLE FACTS ABOUT DNA AND GENES • The information for development and specific function is stored in genes. • A gene is portion of genetic information definable according to the structure and functions. • Genes lie on chromosomes in the nuclei of the cells. • Chromosomes are made up of long chains ...
... SIMPLE FACTS ABOUT DNA AND GENES • The information for development and specific function is stored in genes. • A gene is portion of genetic information definable according to the structure and functions. • Genes lie on chromosomes in the nuclei of the cells. • Chromosomes are made up of long chains ...
DNA & Protein Synthesis Jeopardy - Warren Hills Regional School
... DNA strands in the double helix, because one strand runs in the 5’ to 3’ direction, while the other runs from the 3’ to 5’ direction. ...
... DNA strands in the double helix, because one strand runs in the 5’ to 3’ direction, while the other runs from the 3’ to 5’ direction. ...
Title - Iowa State University
... Antiparallel-Two strands that are parallel but going in different directions. Semi-conservative- The mechanism which DNA replicate, where the parent strands separate and serve as a template for the daughter strands, etc. Complementary- Opposites that combine to form the whole. Replication fork- Wher ...
... Antiparallel-Two strands that are parallel but going in different directions. Semi-conservative- The mechanism which DNA replicate, where the parent strands separate and serve as a template for the daughter strands, etc. Complementary- Opposites that combine to form the whole. Replication fork- Wher ...
Two types of nucleic acids
... usually double stranded, made up of nucleotides • State that RNA is a polynucleotide usually single stranded, made up of nucleotides ...
... usually double stranded, made up of nucleotides • State that RNA is a polynucleotide usually single stranded, made up of nucleotides ...
File
... Concluded that the viral DNA was injected into the cell and provided the genetic information needed to produce new viruses ...
... Concluded that the viral DNA was injected into the cell and provided the genetic information needed to produce new viruses ...
Answers
... 6. Three sequential nucleotides on an RNA molecule that code for an amino acid are called a(n) A. gene B. exon C. intron D. codex E. codon 7. The synthesis of the growing chain of DNA is carried out by adding nucleotides to the ___ end. A. 8' B. 3' C. 5' D. 1' E. 2' 8. The method of DNA replication, ...
... 6. Three sequential nucleotides on an RNA molecule that code for an amino acid are called a(n) A. gene B. exon C. intron D. codex E. codon 7. The synthesis of the growing chain of DNA is carried out by adding nucleotides to the ___ end. A. 8' B. 3' C. 5' D. 1' E. 2' 8. The method of DNA replication, ...
Nucleic Acids PP
... Just like an iPod stores your favorite songs, DNA stores your species favorite biological instructions. ...
... Just like an iPod stores your favorite songs, DNA stores your species favorite biological instructions. ...
Chapter 25
... DNA has 2 polynucleotide strands that are held together by hydrogen bonds. The two strands are coiled together to form a helical structure known as the double helix. ...
... DNA has 2 polynucleotide strands that are held together by hydrogen bonds. The two strands are coiled together to form a helical structure known as the double helix. ...
Type of sugar
... biomolecule called ________________ ____________. DNA is found in the __________________ of a cell. It is made up of millions of tiny subunits called ____________________. In each nucleotide, there is a ______________, a phosphate, and a ____________________ base (_______________, guanine, _________ ...
... biomolecule called ________________ ____________. DNA is found in the __________________ of a cell. It is made up of millions of tiny subunits called ____________________. In each nucleotide, there is a ______________, a phosphate, and a ____________________ base (_______________, guanine, _________ ...
Unit 8 Test Review Answers do not have to be in complete
... Unit 8 Test Review Answers do not have to be in complete sentences but must be complete. 1. What is transformation as it relates to Griffith’s experiment? 2. What were Avery’s findings? 3. What is a bacteriophage? 4. How did radioactive markers prove that DNA was the genetic material in Hershey and ...
... Unit 8 Test Review Answers do not have to be in complete sentences but must be complete. 1. What is transformation as it relates to Griffith’s experiment? 2. What were Avery’s findings? 3. What is a bacteriophage? 4. How did radioactive markers prove that DNA was the genetic material in Hershey and ...
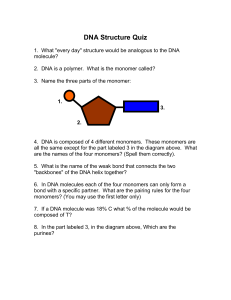
DNA Structure quick review/quiz
... DNA Structure Quiz 1. What "every day" structure would be analogous to the DNA molecule? 2. DNA is a polymer. What is the monomer called? 3. Name the three parts of the monomer: ...
... DNA Structure Quiz 1. What "every day" structure would be analogous to the DNA molecule? 2. DNA is a polymer. What is the monomer called? 3. Name the three parts of the monomer: ...
Secret of Photo 51
... Secret of Photo 51 1. Why is DNA called the blueprint for all life on earth? 2. Who are Francis Crick a. James Watson b. Rosalind Franklin c. Maurice Wilkins 3. How did Rosalind Franklin’s remarkable X-ray image of DNA lead to one of the greatest discoveries in science, and, some believe, to one of ...
... Secret of Photo 51 1. Why is DNA called the blueprint for all life on earth? 2. Who are Francis Crick a. James Watson b. Rosalind Franklin c. Maurice Wilkins 3. How did Rosalind Franklin’s remarkable X-ray image of DNA lead to one of the greatest discoveries in science, and, some believe, to one of ...
DNA nanotechnology

DNA nanotechnology is the design and manufacture of artificial nucleic acid structures for technological uses. In this field, nucleic acids are used as non-biological engineering materials for nanotechnology rather than as the carriers of genetic information in living cells. Researchers in the field have created static structures such as two- and three-dimensional crystal lattices, nanotubes, polyhedra, and arbitrary shapes, as well as functional devices such as molecular machines and DNA computers. The field is beginning to be used as a tool to solve basic science problems in structural biology and biophysics, including applications in crystallography and spectroscopy for protein structure determination. Potential applications in molecular scale electronics and nanomedicine are also being investigated.The conceptual foundation for DNA nanotechnology was first laid out by Nadrian Seeman in the early 1980s, and the field began to attract widespread interest in the mid-2000s. This use of nucleic acids is enabled by their strict base pairing rules, which cause only portions of strands with complementary base sequences to bind together to form strong, rigid double helix structures. This allows for the rational design of base sequences that will selectively assemble to form complex target structures with precisely controlled nanoscale features. A number of assembly methods are used to make these structures, including tile-based structures that assemble from smaller structures, folding structures using the DNA origami method, and dynamically reconfigurable structures using strand displacement techniques. While the field's name specifically references DNA, the same principles have been used with other types of nucleic acids as well, leading to the occasional use of the alternative name nucleic acid nanotechnology.