Earth`s Surface
... which is thought to have been a great cosmic explosion of matter and energy from a single point, occurred about 13.7 billion years ago. From that explosion, dust particles began to collide and clump together. These clumps collided with other clumps until eventually, the Earth and other planets were ...
... which is thought to have been a great cosmic explosion of matter and energy from a single point, occurred about 13.7 billion years ago. From that explosion, dust particles began to collide and clump together. These clumps collided with other clumps until eventually, the Earth and other planets were ...
Ch 5 S 1 Earth`s Interior
... iii. Geologists have used 2 main types of evidence to learn about Earth’s interior 1.Evidence from rock samples a.Rocks from inside Earth give clues about Earth’s structure b.Geologists have drilled holes up to 12 km i. The drills bring up samples of the rock c.Geologists can make inferences about ...
... iii. Geologists have used 2 main types of evidence to learn about Earth’s interior 1.Evidence from rock samples a.Rocks from inside Earth give clues about Earth’s structure b.Geologists have drilled holes up to 12 km i. The drills bring up samples of the rock c.Geologists can make inferences about ...
Ch. 8 Vocab Study Guide
... Alfred Wegner hypothesized that continents move. What did he call this? __________________________ 2. The ________________________ is located directly under the lithosphere. This is a layer of hotter and softer rock in the mantle. 3. The switch in the Earth’s magnetic field is called: ______________ ...
... Alfred Wegner hypothesized that continents move. What did he call this? __________________________ 2. The ________________________ is located directly under the lithosphere. This is a layer of hotter and softer rock in the mantle. 3. The switch in the Earth’s magnetic field is called: ______________ ...
3.1_structure_of_the_earth
... 3. What is the deepest humans have ever drilled down into the earth? 4. The earth is made of several layers. Each layer has its on characteristics. How do we know all this if we haven’t been there? 5. How are the plates (large sections that make up the crust) able to move? ...
... 3. What is the deepest humans have ever drilled down into the earth? 4. The earth is made of several layers. Each layer has its on characteristics. How do we know all this if we haven’t been there? 5. How are the plates (large sections that make up the crust) able to move? ...
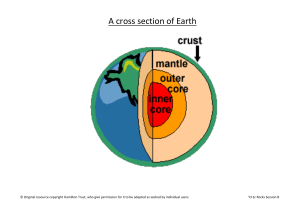
Cross section of the Earth
... We live on this outer layer. It is made of hard rocks that have been wrinkled & bent to make mountains and valleys. The thinnest parts of the crust are under the oceans; the thickest parts are in mountainous regions on the continents. The Mantle is the layer under the crust. It is a very thick lay ...
... We live on this outer layer. It is made of hard rocks that have been wrinkled & bent to make mountains and valleys. The thinnest parts of the crust are under the oceans; the thickest parts are in mountainous regions on the continents. The Mantle is the layer under the crust. It is a very thick lay ...
inside earth ppt
... How do we know what inside Earth is like if we can’t travel through it? • Scientist know this by studying seismic waves/data from earthquakes ...
... How do we know what inside Earth is like if we can’t travel through it? • Scientist know this by studying seismic waves/data from earthquakes ...
Dynamic Earth – Earth`s crust, plate tectonics, earthquakes and
... The Ocean Floor lesson plan, interactive PowerPoint, and worksheet for students to work on in pairs (could also be done in whole‐class format). A second Ocean Floor lesson plan. This is from Enhanced Scope and Sequence (ESS). Students create a 3D model of the ocean floor in a shoebox using c ...
... The Ocean Floor lesson plan, interactive PowerPoint, and worksheet for students to work on in pairs (could also be done in whole‐class format). A second Ocean Floor lesson plan. This is from Enhanced Scope and Sequence (ESS). Students create a 3D model of the ocean floor in a shoebox using c ...
Ecology: Interactions of Life
... 3. They both deal with life and where organisms live. 4. Population is organisms of a certain species and community includes all the organisms. 5. Yes it does because different organisms require different amounts of rain to survive. ...
... 3. They both deal with life and where organisms live. 4. Population is organisms of a certain species and community includes all the organisms. 5. Yes it does because different organisms require different amounts of rain to survive. ...
plate tectonics review - Hicksville Public Schools
... THE THEORY OF PLATE TECTONICS STATES THAT THE EARTH’S EXTERIOR CRUST IS BROKEN INTO PIECES CALLED PLATES THAT MOVE. 15. What causes the Earth’s magnetic field? CONVECTION CURRENTS IN THE OUTER CORE 16. What layers of the Earth do convection currents flow in? MANTLE AND OUTER CORE. 17. What is a foss ...
... THE THEORY OF PLATE TECTONICS STATES THAT THE EARTH’S EXTERIOR CRUST IS BROKEN INTO PIECES CALLED PLATES THAT MOVE. 15. What causes the Earth’s magnetic field? CONVECTION CURRENTS IN THE OUTER CORE 16. What layers of the Earth do convection currents flow in? MANTLE AND OUTER CORE. 17. What is a foss ...
Notes 11 – Earth`s Interior
... of sea floor spreading led to: • A. The Theory of Plate Tectonics pieces of Earth’s crust are in constant, slow motion driven by convection currents in the mantle. • Every plate affects the other plates around it by colliding together, ripping apart or grinding past each other. ...
... of sea floor spreading led to: • A. The Theory of Plate Tectonics pieces of Earth’s crust are in constant, slow motion driven by convection currents in the mantle. • Every plate affects the other plates around it by colliding together, ripping apart or grinding past each other. ...
Oceanography Test #1
... _______. 40. Mud is made of silt and __________-sized materials. 41. The average particle size of a deposit is proportional to the __________ level present at the time of deposition. 42. Under high-energy conditions, which of the following would be most likely to be deposited? 43. On the basis of wa ...
... _______. 40. Mud is made of silt and __________-sized materials. 41. The average particle size of a deposit is proportional to the __________ level present at the time of deposition. 42. Under high-energy conditions, which of the following would be most likely to be deposited? 43. On the basis of wa ...
Structure of the Earth powerpoint
... Structure of the Earth • Earth was formed roughly 4.6 billion ears ago and for a long time was entirely molten. • The various materials (elements) that make up the earth were stratified (separated) according to their density. • The densest elements formed the core and the lighter elements floated t ...
... Structure of the Earth • Earth was formed roughly 4.6 billion ears ago and for a long time was entirely molten. • The various materials (elements) that make up the earth were stratified (separated) according to their density. • The densest elements formed the core and the lighter elements floated t ...
How Do You Study the Past? (The Rock Record: Absolute
... 5. What do we call what is happening between layer “F” and “M”? ...
... 5. What do we call what is happening between layer “F” and “M”? ...
DR Fossil Record
... 28. Why are fossils found in some places very different from the organisms now living in the same area? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ Orig ...
... 28. Why are fossils found in some places very different from the organisms now living in the same area? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ Orig ...
Indirect evidence
... Continental Drift Convection Currents, and How Heat Works Chapter 5 Updated January 2012 ...
... Continental Drift Convection Currents, and How Heat Works Chapter 5 Updated January 2012 ...
C7 Revision Earth and atmosphere[1].
... These occur at plate boundaries. H………..…. from radioactive processes in the core causes c……….……………………. c……………………. in the mantle which make plates move. Plates normally move s………..….. (a few centimetres per year) but sudden release of strain energy causes e…………………………. Scientists cannot accurately pre ...
... These occur at plate boundaries. H………..…. from radioactive processes in the core causes c……….……………………. c……………………. in the mantle which make plates move. Plates normally move s………..….. (a few centimetres per year) but sudden release of strain energy causes e…………………………. Scientists cannot accurately pre ...
C7 Revision Earth and Atmosphere
... These occur at plate boundaries. H………..…. from radioactive processes in the core causes c……….……………………. c……………………. in the mantle which make plates move. Plates normally move s………..….. (a few centimetres per year) but sudden release of strain energy causes e…………………………. Scientists cannot accurately pre ...
... These occur at plate boundaries. H………..…. from radioactive processes in the core causes c……….……………………. c……………………. in the mantle which make plates move. Plates normally move s………..….. (a few centimetres per year) but sudden release of strain energy causes e…………………………. Scientists cannot accurately pre ...
Forces Inside Earth
... Volcanoes also blast large amount of rocks, ash, and poisonous gases into the air during an eruption ...
... Volcanoes also blast large amount of rocks, ash, and poisonous gases into the air during an eruption ...
Inside Earth Unit Study Guide
... Answer these questions on a separate piece of paper. 1. Who was Alfred Wegener and what theory was he famous for? 2. What were the 6 evidences Wegener had for his Continental Drift Hypothesis? 3. Why was Alfred Wegener’s hypothesis rejected? 4. What is the Theory of Plate Tectonics? 5. Compare and c ...
... Answer these questions on a separate piece of paper. 1. Who was Alfred Wegener and what theory was he famous for? 2. What were the 6 evidences Wegener had for his Continental Drift Hypothesis? 3. Why was Alfred Wegener’s hypothesis rejected? 4. What is the Theory of Plate Tectonics? 5. Compare and c ...
earth interior - Red Hook Central Schools
... crust of the Earth rip and break apart, releasing tremendous energy in the form of seismic waves. What’s it like to be in an Earthquake? “Its like trying to stand up in an airplane during severe turbulence” ...
... crust of the Earth rip and break apart, releasing tremendous energy in the form of seismic waves. What’s it like to be in an Earthquake? “Its like trying to stand up in an airplane during severe turbulence” ...
ScienceChapter6Study..
... sand, but it can also act like sandpaper or a sandblaster as it blows these loose particles against rock. What forces coastline changes? Waves beating against the coast. How can gravity and water change Earth’s surface? Causes landslides and mudslides What happens to form a delta? Running water drop ...
... sand, but it can also act like sandpaper or a sandblaster as it blows these loose particles against rock. What forces coastline changes? Waves beating against the coast. How can gravity and water change Earth’s surface? Causes landslides and mudslides What happens to form a delta? Running water drop ...
9. Lithosphere - Structure of the Earth
... Lithosphere is a geosphere created by the Earth’s Crust and the uppermost part of the Mantle which is the most solid part. It lies upon layer of plastic, molten mantle rocks called Asthenosphere. ...
... Lithosphere is a geosphere created by the Earth’s Crust and the uppermost part of the Mantle which is the most solid part. It lies upon layer of plastic, molten mantle rocks called Asthenosphere. ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.
















![C7 Revision Earth and atmosphere[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001217671_1-b9cc347117db8dff9935614904a55b09-300x300.png)