* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download inside earth ppt
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
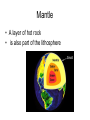
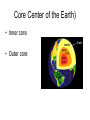
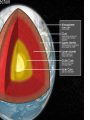
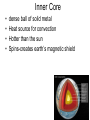
Earth’s Interior Interior=inside Geologist • A geologist is a scientist that studies the forces that shape earth’s surface • 200 years ago was the start of geology • Geology is fairly new Rock • The material that forms Earth’s surface • Geologists study rocks Forces that shape Earth • Constructive • Destructive Constructive • Building up Ex. Construction The building (MS) was changed constructively. Constructive • Mountain ranges forming(slowly) • Over millions of years Destructive • Forces that slowly wear down the Earth’s surface • Destroy =Destruction Destructive • Erosion by wind and water • Think of our local beaches Journey to the Center of the Earth • Temperature increases • Pressure increases How do we know what inside Earth is like if we can’t travel through it? • Scientist know this by studying seismic waves/data from earthquakes If you took that journey you would find layers of the Earth • Crust • Mantel • Core Crust • • • • “skin” of earth Like the shell of an egg or onion skin VERY THIN!!!!!! Includes land on bottom of ocean floor – Thinnest under the ocean(basalt) – Thickest under mountains(granite) • Is part of the lithosphere • Most abundant element oxygen then silicon Lithosphere • Lithosphere means stone • Crust and uppermost mantle • Rigid • Contains plates Oceanic vs. Continental Crust Oceanic Continental Under oceans Under continents thinner thicker Made of basalt(think salty ocean) Made of granite More dense Less dense Asthenosphere • • • • • • Gooey/bendable Plastic like rock Convection take place here Found in Upper mantle only NOT A LIQUID!!!! SOLID Mantle • A layer of hot rock • is also part of the lithosphere Core Center of the Earth) • Inner core • Outer core Outer core • Acts like a thick liquid Inner Core • • • • dense ball of solid metal Heat source for convection Hotter than the sun Spins-creates earth’s magnetic shield The Lithosphere • Crust and uppermost mantle Floats on the asthenosphere Broken into pieces- tectonic plates Crust • Crust part of the (Lithosphere) – Continental – Less dense – Oceanic – More dense Mantle – Upper Mantle called the asthenosphere