* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Indirect evidence
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
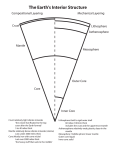
The Inner Earth Continental Drift Convection Currents, and How Heat Works Chapter 5 Updated January 2012 1.The Earth does not look the same today as it did millions of years ago because it’s surface has been lifted up, pushed down, bent, and broken apart. 2.Scientists use both direct and indirect evidence to study the inside of the earth. Direct evidence- rock samples Indirect evidence- seismic waves through the earth Rock samples can tell us what the conditions may have been like on Earth when the rock formed. Seismic waves Geologists can measure the speed at which the waves travel through the earth to determine the structure of the planet. Just as you may knock on a wall to find a stud while hanging a picture. It sounds hallow if there is nothing behind it; and solid if there is. A Journey to the center of the Earth Temperature 5. As you travel toward the center of the earth it gets hotter because you are getting closer to the core, just as you get warmer the closer you get to a camp fire. 6. The center of the Earth is hot because of two reasons: 1. There is leftover heat from the formation of the planet billions of years ago 2. The main reasons is because of radioactive materials decaying in the core. The core is basically a nuclear reactor. Pressure 7. Pressure increases the deeper you go because there is more and more weight on top. If you go down one mile, there is a mile of rock above pushing down. The Crust 8. The crust is the outer layer of rock that forms the outer skin that includes dry land and the ocean floor. a). The crust beneath the ocean is called the oceanic crust it is made from basalt. b).In most places the crust is between 5 and 40 km thick. It can be up to 70 km thick under mountains. The Mantle 9.The mantle is made up of very hot rock but solid. It is divided up into layers depending on the physical characteristics of that layer. The mantle is approximately 3,000 km thick. 10.The lithosphere is the uppermost part of the mantle similar to the crust. Approximately 100 km thick. 11.The asthenosphere is the soft part of the mantle just below the lithosphere. 12.The lower mantle is beneath the asthenosphere and extends all the way to the core. The Core 13. The core consists of two parts, the inner and outer. It is made mostly of the metals iron and nickel. -The outer core is liquid -The inner core is solid Together the core is approximately 3, 486 km thick. The immense pressure does not allow the inner core to become a liquid. The core and the Earth’s magnetic field 14. Scientists believe the earth’s magnetic field is caused by the movements in the liquid outer core.