What Can Changes Inside Earth Communicate? Pre/Post Test 1
... mantle, inner core, lithosphere, outer core outer core, lithosphere, core, mantle lithosphere, mantle, inner core, outer core lithosphere, mantle, outer core, inner core ...
... mantle, inner core, lithosphere, outer core outer core, lithosphere, core, mantle lithosphere, mantle, inner core, outer core lithosphere, mantle, outer core, inner core ...
Practice Questions - Earth`s History 1
... 10. What is the main reason Earth’s layers formed as they did? A. density B. radioactivity C. heat D. light 11. Why are there so few fossils from the Precambrian time? A. The Precambrian climate was not conducive to fossil formation B. No life forms were present during that time C. Life forms were ...
... 10. What is the main reason Earth’s layers formed as they did? A. density B. radioactivity C. heat D. light 11. Why are there so few fossils from the Precambrian time? A. The Precambrian climate was not conducive to fossil formation B. No life forms were present during that time C. Life forms were ...
8.1 powerpoint
... • Decide if each statement is true. If not, correct it. Write out every sentence. 1. The rock cycle describes the natural processes that form, change, break down and form rocks again. 2. The most common type of rocks in the Earth’s crust are sedimentary and igneous. 3. Heat and pressure can change a ...
... • Decide if each statement is true. If not, correct it. Write out every sentence. 1. The rock cycle describes the natural processes that form, change, break down and form rocks again. 2. The most common type of rocks in the Earth’s crust are sedimentary and igneous. 3. Heat and pressure can change a ...
Chapter 5 Test - Bloomsburg Area School District
... 1. What is the rock that makes up the Earth’s outer layer? ...
... 1. What is the rock that makes up the Earth’s outer layer? ...
Chapter 15 Outline
... How fast do tectonic plates move per year on average? (p. 407)___________________________________________ What is evidence Wegener used to support his hypothesis? (p. 400) ________________________________________________ How do scientists know what the inside of the Earth is like if we can’t dig int ...
... How fast do tectonic plates move per year on average? (p. 407)___________________________________________ What is evidence Wegener used to support his hypothesis? (p. 400) ________________________________________________ How do scientists know what the inside of the Earth is like if we can’t dig int ...
Earth Inside Ch 1 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... • The lithosphere is broken into a series of plates that diverge, converge, and ...
... • The lithosphere is broken into a series of plates that diverge, converge, and ...
Chapter 17 Vocabulary
... tectonic plates are moving apart; is associated with volcanism, earthquakes, and high heat flow, and is found primarily on the seafloor. Rift Valley (p. 456) Long, narrow depression that forms when continental crust begins to separate at a divergent boundary. Subduction (p. 457) Process by which one ...
... tectonic plates are moving apart; is associated with volcanism, earthquakes, and high heat flow, and is found primarily on the seafloor. Rift Valley (p. 456) Long, narrow depression that forms when continental crust begins to separate at a divergent boundary. Subduction (p. 457) Process by which one ...
Olivia-module3
... The observed “vigour” of mantle convection suggests that the adiabatic gradient must be ...
... The observed “vigour” of mantle convection suggests that the adiabatic gradient must be ...
Total energy of particles
... Addition or loss of thermal energy changes arrangement of particles during: ...
... Addition or loss of thermal energy changes arrangement of particles during: ...
External Forces Affecting Earth
... External Forces Affecting Earth • EARTH IS ALSO AFFECTED AND ...
... External Forces Affecting Earth • EARTH IS ALSO AFFECTED AND ...
Today`s Warm-Up Friday, January 10
... Today’s Warm-Up Friday, January 10 • Write What You Know! Write as much as you can for five minutes on the prompt below, try for at least 3-4 complete sentences. • Astronomy Throwback! Do other planets in our solar system also have layered atmospheres and layered interiors like the Earth does? Why? ...
... Today’s Warm-Up Friday, January 10 • Write What You Know! Write as much as you can for five minutes on the prompt below, try for at least 3-4 complete sentences. • Astronomy Throwback! Do other planets in our solar system also have layered atmospheres and layered interiors like the Earth does? Why? ...
Vocabulary 1 - Cobb Learning
... Ab/abs: from; away; off Absent—not present Abdicate—to give up formally (a throne, etc.) ...
... Ab/abs: from; away; off Absent—not present Abdicate—to give up formally (a throne, etc.) ...
The Earths interior overview
... It is imperative to understand the earth's structure before you can understand tectonic forces. ...
... It is imperative to understand the earth's structure before you can understand tectonic forces. ...
Planetary Accretion and the Origin of Crust
... • Convinced astronomers that such events were still possible • Focused attention on near-Earth objects • Showed how little we know of such objects • Showed how completely unprepared we are ...
... • Convinced astronomers that such events were still possible • Focused attention on near-Earth objects • Showed how little we know of such objects • Showed how completely unprepared we are ...
The History of Life
... of the first life on Earth was the presence of liquid water – Microspheres: 1st molecules that had some characteristics of living systems • Had permeable membranes, simple energy systems • Were similar to modern-day bacteria ...
... of the first life on Earth was the presence of liquid water – Microspheres: 1st molecules that had some characteristics of living systems • Had permeable membranes, simple energy systems • Were similar to modern-day bacteria ...
Turtle
... File for the TURTLE/Earth Science of the 5 pointed star* *Activities/Ideas like Stars-Ancestors-Descendants in the Tree/MilkyWay/River of Sky & Earth ...
... File for the TURTLE/Earth Science of the 5 pointed star* *Activities/Ideas like Stars-Ancestors-Descendants in the Tree/MilkyWay/River of Sky & Earth ...
Vocabulary - Bibb County Schools
... 11. Cinder Cone – A volcano formed from explosive eruptions that shoot small pieces of magma and ash into the air. 12. Composite Volcano – A volcano that has explosive eruptions as a result of more gassy magma. 13. Cross-section – A slice of an object made by cutting through it in a plane, usually ...
... 11. Cinder Cone – A volcano formed from explosive eruptions that shoot small pieces of magma and ash into the air. 12. Composite Volcano – A volcano that has explosive eruptions as a result of more gassy magma. 13. Cross-section – A slice of an object made by cutting through it in a plane, usually ...
Geothermal Studies on Earth`s Mantle and Crust
... - Integrate 3 global models for the crust - New crust model with uncertainties ...
... - Integrate 3 global models for the crust - New crust model with uncertainties ...
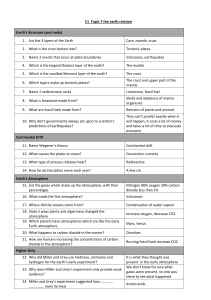
C1 Topic 7 the earth revision Earth`s Structure (and rocks) 1. List the
... hydrogen for the earth’s early experiment? 23. Why does Miller and Urey’s experiment only provide weak evidence? 24. Miller and Urey’s experiment suggested how ………….. …………….. were formed ...
... hydrogen for the earth’s early experiment? 23. Why does Miller and Urey’s experiment only provide weak evidence? 24. Miller and Urey’s experiment suggested how ………….. …………….. were formed ...
Chemical elements
... Part IV: Early History of the Solar System and the Earth Chemical elements symbols of common ones structure of atoms (nucleus with protons, neutrons; outer electrons) structure of simplest elements – H and He meaning of isotope – isotopes of H, He, C ages of universe, sun, earth Stars what is a star ...
... Part IV: Early History of the Solar System and the Earth Chemical elements symbols of common ones structure of atoms (nucleus with protons, neutrons; outer electrons) structure of simplest elements – H and He meaning of isotope – isotopes of H, He, C ages of universe, sun, earth Stars what is a star ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.