* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Total energy of particles
Energetic neutral atom wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
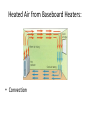
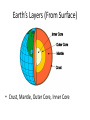
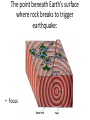
Total energy of particles: Thermal Energy Conservation of Energy • No Energy destroyed Movement of Thermal Energy • Heat Heat Transfer without particle movement. • Conduction Heat transfer occurs from: • Hot to Cold Addition or loss of thermal energy changes arrangement of particles during: • Change of State Temperature of Solid to Liquid • Melting Point Vaporization at Surface • Evaporation Expansion of Matter when heated: • Thermal Expansion Heated Air from Baseboard Heaters: • Convection Kinetic Energy of Particles: • Temperature Characteristic Property of Liquid: • Boiling Point How much matter an object contains? • Mass Mass in a given Volume: • Density Elements are composed of: • Atoms A group of atoms: • Molecule Substances not chemically combined: • Mixture How are liquid water, ice, and water vapor different ? • Different states of matter Distance is changing, an object is in: • Motion Speed is: • Distance / Time You know speed and direction you know: • Velocity Graphing Motion the steepness of the slope shows how: • How quickly or slowly the object is moving. Distance vs time graph a horizontal line shows: • Object is not moving 300 kilometers in 3 hours you can find: • Average Speed When Speed vs Time graph is a straight line: • Acceleration is constant Model where Earth is at the center of the system of planets is: • Geocentric system The heliocentric system was supported by Galileo when he discovered: • The phases of Venus Day and night are caused by: • Earth’s Rotation Earth has seasons because: • Earth’s axis is tilted as it moves around the sun. The phase of the moon you see depends on: • How much of the sunlit side of the moon faces Earth. During a Solar Eclipse: • The moon is directly between Earth and the sun. Phase of the moon during lunar eclipse: • Full Moon Tides are caused by: • Differences in how much the moon pulls on different parts of Earth. You are less likely to see a solar eclipse than a lunar eclipse because: • You must be in the moon’s shadow to see a solar eclipse. Process that moves weathered rock: • Erosion Erosion when runoff flows in thin layer: • Sheet Erosion Wind removes surface materials: • Deflation Mechanical weathering rock is worn away by grinding of other rocks: • abrasion Earth’s Layers (From Surface) • Crust, Mantle, Outer Core, Inner Core Transfer of Energy through empty space: • Radiation Heat Transfer within a fluid: • Convection Currents The point beneath Earth’s surface where rock breaks to trigger earthquake: • Focus Risk of earthquakes on the Pacific Coast is high because: • That is where the North American and Pacific plates meet. Volcanic belts form along: • The boundaries of the Earth’s plates. The volcanoes along converging oceanic plate boundaries may form: • An island arc A volcano that may erupt in the distant future is: • dormant The place where an organism lives: • Habitat Environmental Factor that prevents a population from increasing: • Limiting Factor An organism’s role: • Niche’ Study of how things interact with each other and their environment: • Ecology