6th Grade Earth Science – Inside Earth Vocabulary 1. crust – the
... and the north & south poles on earth 9. compass – an instrument composed of a small, light-weight magnet called a needle, that is balanced on a frictionless bearing 10. continental drift – the hypothesis that the continents slowly move across the Earth’s surface 11. sea-floor spreading – the process ...
... and the north & south poles on earth 9. compass – an instrument composed of a small, light-weight magnet called a needle, that is balanced on a frictionless bearing 10. continental drift – the hypothesis that the continents slowly move across the Earth’s surface 11. sea-floor spreading – the process ...
Earth`s Story and those who first listened
... been determined in the laboratory geologists can calculate the age of a sample containing the radioactive element • The parent/daughter ratio is usually determined by a mass spectrometer – an instrument that measures the proportions of atoms ...
... been determined in the laboratory geologists can calculate the age of a sample containing the radioactive element • The parent/daughter ratio is usually determined by a mass spectrometer – an instrument that measures the proportions of atoms ...
Inferred Properties of the Earth`s Interior
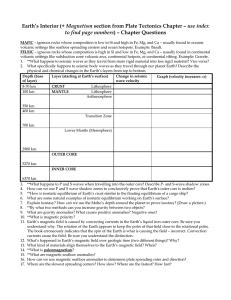
... 12. As depth increases as you go down into the center of the earth, what happens to the pressure, density and temperature trends?__________________________________________________. 13. What layer of the earth is the coolest? _________________________________ 14. What layer of the earth has the great ...
... 12. As depth increases as you go down into the center of the earth, what happens to the pressure, density and temperature trends?__________________________________________________. 13. What layer of the earth is the coolest? _________________________________ 14. What layer of the earth has the great ...
Geology Notes - My Teacher Pages
... • Geologic changes based directly or indirectly on energy from the sun and gravity – Erosion – Weathering ...
... • Geologic changes based directly or indirectly on energy from the sun and gravity – Erosion – Weathering ...
Earth and Space Science Overview
... geotechnical properties of the proposed site as to foresee any potential problems when constructing the aquatic center. The student will investigate methods that geologists use to determine the history of Earth. The student will apply geologic principles used to date Earth’s geologic and biologic ev ...
... geotechnical properties of the proposed site as to foresee any potential problems when constructing the aquatic center. The student will investigate methods that geologists use to determine the history of Earth. The student will apply geologic principles used to date Earth’s geologic and biologic ev ...
Rhythm Rhyme Results Layers of the Earth
... 1 the iron in the inner core is in _____ form 2 there are four distinct _______of the Earth 3 the Earth's surface is 70% ____________ 4 a source of 'fresh' water on Earth 8 the oceanic and continental_____ are often referred to as one 10 the inner core and the _________ are responsible for the Earth ...
... 1 the iron in the inner core is in _____ form 2 there are four distinct _______of the Earth 3 the Earth's surface is 70% ____________ 4 a source of 'fresh' water on Earth 8 the oceanic and continental_____ are often referred to as one 10 the inner core and the _________ are responsible for the Earth ...
Solutions
... atmosphere would have occurred around noon on this clock. On this clock, at what time did the dinosaurs disappear, and at what time did homo sapiens first appear? The dinosaurs became extince 65 million years ago. 24 hours = 4.55 billion years, so 65 million years /4.55 billion years × 24 hours × 60 ...
... atmosphere would have occurred around noon on this clock. On this clock, at what time did the dinosaurs disappear, and at what time did homo sapiens first appear? The dinosaurs became extince 65 million years ago. 24 hours = 4.55 billion years, so 65 million years /4.55 billion years × 24 hours × 60 ...
Solid Earth Study Guide Key
... Due to plate tectonic movement, marine environments have shifted to different parts of the globe. Areas once covered by oceans may not be today. Over time, plates that were once in a marine environment, might be uplifted to form mountains. ...
... Due to plate tectonic movement, marine environments have shifted to different parts of the globe. Areas once covered by oceans may not be today. Over time, plates that were once in a marine environment, might be uplifted to form mountains. ...
Geo 221_14 copy
... isotope excursions that have been linked to high atmospheric CO2 concentra8ons due to the erup8on of flood basalts in the Central ...
... isotope excursions that have been linked to high atmospheric CO2 concentra8ons due to the erup8on of flood basalts in the Central ...
Geologic Time
... When something is filled with atoms of rock material; this makes them very hard (rock). *Commonly found with wood. ...
... When something is filled with atoms of rock material; this makes them very hard (rock). *Commonly found with wood. ...
Seafloor Spreading PPT
... ship Atlantis found that the sediment layer on the floor of the Atlantic was much thinner than originally thought. ...
... ship Atlantis found that the sediment layer on the floor of the Atlantic was much thinner than originally thought. ...
Review Packet Inside the Earth - JBHA-Science-tri3
... 2. Which layer is under more pressure, the inner core or the outer core? Why? _________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. According to the ...
... 2. Which layer is under more pressure, the inner core or the outer core? Why? _________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. According to the ...
general_science_syllabus
... 1. The Earth system has internal and external sources of energy, which produce heat and drive the motion of material in the oceans, atmosphere and solid earth. 2. Global climate is ...
... 1. The Earth system has internal and external sources of energy, which produce heat and drive the motion of material in the oceans, atmosphere and solid earth. 2. Global climate is ...
Earth`s Interior (+ Magnetism section from Plate Tectonics Chapter
... volcanic settings like seafloor spreading centers and ocean hotspots. Example: Basalt. FELSIC – igneous rocks whose composition is high in Si and low in Fe, Mg, and Ca – usually found in continental volcanic settings like subduction zone volcanic arcs, continental hotpots, or continental rifting. Ex ...
... volcanic settings like seafloor spreading centers and ocean hotspots. Example: Basalt. FELSIC – igneous rocks whose composition is high in Si and low in Fe, Mg, and Ca – usually found in continental volcanic settings like subduction zone volcanic arcs, continental hotpots, or continental rifting. Ex ...
A Brief History of the Earth
... means you may not copy and paste in someone else’s words or you will get a zero on the assignment. At the bottom of the page make a numbered Citations subsection. Paste in the urls of the websites you use. Do not move on to the next question without citing because that is also a form of plagiarism i ...
... means you may not copy and paste in someone else’s words or you will get a zero on the assignment. At the bottom of the page make a numbered Citations subsection. Paste in the urls of the websites you use. Do not move on to the next question without citing because that is also a form of plagiarism i ...
Plate tectonics, earthquakes, and volcanoes 1. Hypothesis that
... 1. Hypothesis that states that the continents have moved around the earth into their present positions. 2. The boundary between two tectonics plates that are moving away from each other. 3. The driving force in plate tectonics in which lava from the mantle rises to the lithosphere, moves horizontall ...
... 1. Hypothesis that states that the continents have moved around the earth into their present positions. 2. The boundary between two tectonics plates that are moving away from each other. 3. The driving force in plate tectonics in which lava from the mantle rises to the lithosphere, moves horizontall ...
The Earth’s movement - Thomas Tallis Science Department
... During the first billion years of the Earth’s existence there was intense volcanic activity. This activity released the gases that formed the early atmosphere and water vapour that condensed to form the oceans. There may also have been water vapour and small proportions of methane and ammonia. Plant ...
... During the first billion years of the Earth’s existence there was intense volcanic activity. This activity released the gases that formed the early atmosphere and water vapour that condensed to form the oceans. There may also have been water vapour and small proportions of methane and ammonia. Plant ...
download a .pdf of this paper: 1.6 MB
... Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences Rutgers University Piscataway, NJ 08854 USA and Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University Palisades, NY 10968 USA ...
... Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences Rutgers University Piscataway, NJ 08854 USA and Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University Palisades, NY 10968 USA ...
Chapter 21 – Section 1 - Earth`s Interior and Plate Tectonics
... The Earth’s core makes up approximately 32.8% of the Earth’s mass, the mantle represents 66.4%, and the crust represents 0.8%. The Earth’s core, however, makes up only 18% of the Earth’s volume while the mantle makes up nearly 84% of the Earth’s volume. What does this data suggest about the Earth’s ...
... The Earth’s core makes up approximately 32.8% of the Earth’s mass, the mantle represents 66.4%, and the crust represents 0.8%. The Earth’s core, however, makes up only 18% of the Earth’s volume while the mantle makes up nearly 84% of the Earth’s volume. What does this data suggest about the Earth’s ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.