* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download C7 Revision Earth and atmosphere[1].
Survey
Document related concepts
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Abiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Atmosphere of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
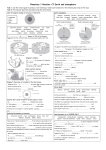
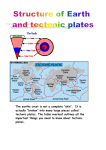
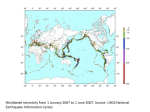
Chemistry 1 Revision: C7 Earth and atmosphere Task 1: Use the revision guide to produce a mini mind map or bullet point summary for the following key areas on this topic. Task 2: Practise past questions and assess using the mark scheme Label the diagram showing the structure of the Earth: Earth’s atmosphere ammonia condensed bacteria decreased dissolves energy fossil fuels increased limestone oceans photosynthesis plants shells space volcanic eruptions atmosphere crust mantle core convection currents cooled continental drift core dense different earthquakes expert fossils land bridges mantle no evidence radioactivity rocks shapes slowly volcanoes wrinkled C…………………………………… d…………………. theory: In 1915 Alfred Wegener suggested that the continents had once been joined together but then s………………. drifted apart: The gases in the Earth’s early atmosphere came from v……………………………….. e……………………………. The gases in the atmosphere changed over time: carbon dioxide has d……………………………. due to: p…………………. / micro-organisms absorbed carbon dioxide in p……………………………………… Wegener’s evidence: • d….………………….. in o………………… 1. s………………….. of continents fit together, like a jigsaw • used to form the s…..………………… / skeletons of marine organisms 2. f………………. and r…………. match up when continents are put together • locked up as l……………………………………… / carbonates • locked up as f………………………. f………………….. oxygen has i…………………………… due to: Other scientists theories: p……………………… / bacteria 1. as hot Earth c…………….. the surface releasing oxygen in p………………………………… w…………………., forming mountains nitrogen has i…………………….. due to: 2. continents had once been joined by l..………. a…………………………… reacted with oxygen b………………… – explained matching fossils and rocks b……………………………. / micro-organisms release nitrogen Wegener’s ideas were not accepted at the time because Water vapour has d………………………………… due to: • Wegener had n..….. e……………………………….. to explain how continents could move as Earth’s temperature cooled, water vapour c………………………………….. and formed the oceans • other scientists had d…………………………………….. ideas / views Life on Earth • Wegener was not an e……………………. geologist ammonia asteroids comets meteorites energy oceans hydrocarbons space lightning On the early Earth e………….……… from the Sun, volcanoes, or l…………………………… could have formed a ‘primordial soup’: o…………….……. filled with a dilute Describe what causes the Earth’s tectonic plates to move: solution of complex organic molecules needed for life (amino acids). 1. R…………………………………….. in the c…………. releases heat energy. The Miller-Urey experiment demonstrated that amino acids could be made 2. This makes m………………….. material less d……………….. so it rises from the interaction of h…………………………….…….., a………………………….. and 3. This causes c……………………………….. c…………………….. in the mantle. lightning. Other theories suggest that life started in s…………….… and 4. Plates are forced apart or collide together, causing e………………………..…………… was brought to Earth on c……………………, a……………………………………. and some and v……………………………….. m……………………………………. Predicting Earthquakes and volcanoes convection currents crust earthquakes measure pressure slowly Separating gases in air (HIGHER ONLY) forces where heat limit These occur at plate boundaries. H………..…. from radioactive processes in the core causes c……….……………………. c……………………. in the mantle which make plates move. Plates normally move s………..….. (a few centimetres per year) but sudden release of strain energy causes e…………………………. Scientists cannot accurately predict when earthquakes and volcanic eruptions will occur because they can’t be certain boiling points carbon dioxide condenses cooled decrease expand fractional distillation liquids lower pressure water F…………………………………….. d…………………………………….. is used to separate a mixture of l……………………….. with different b……………………… p……………………… 1. Gaseous air is c…………………… below – 200oC so it c………………………… to a liquid – achieved using high p……………………….. 2. Pressure is released so air e………………………. rapidly – this causes • what is happening under the c……………………….……. temperature to d……………………… further so c…………………….. d…………………….. and • w…………..……… the forces / p……………………………….. are building up w………………. solidify and are removed • we cannot m……………………………… the forces 3. Liquid air is allowed to warm up, l…………….. boiling point gases boil off first and are separated • when the f…………………. reach their l………………