Set 6 Immune System and Vaccines
... Immunodeficiency: for some reason the adaptive immune system does not work Autoimmune diseases: the immune system cannot distinguish self and non-self This is for disambiguation and clarification-AIDS (Module 4) is an example of an ...
... Immunodeficiency: for some reason the adaptive immune system does not work Autoimmune diseases: the immune system cannot distinguish self and non-self This is for disambiguation and clarification-AIDS (Module 4) is an example of an ...
Immune System
... • Cytotoxic T-Cells give rise to Active Cytotoxic T-Cells and Memory Cytotoxic T-Cells • Active Cytotoxic T-Cells kill infected body cells, cancer cells, and transplant tissues • Memory Cytotoxoic T-Cell “remember” the antigen so infected cells can be killed quickly upon second exposure. ...
... • Cytotoxic T-Cells give rise to Active Cytotoxic T-Cells and Memory Cytotoxic T-Cells • Active Cytotoxic T-Cells kill infected body cells, cancer cells, and transplant tissues • Memory Cytotoxoic T-Cell “remember” the antigen so infected cells can be killed quickly upon second exposure. ...
biology 404 immunology
... Dr. David W. Buckalew Room 305A 395-2586 (or 2586 from campus) [email protected] As posted or by appointment M 1:00 – 3:00 p.m. R 9:30 – 10:30 a.m. ...
... Dr. David W. Buckalew Room 305A 395-2586 (or 2586 from campus) [email protected] As posted or by appointment M 1:00 – 3:00 p.m. R 9:30 – 10:30 a.m. ...
B CELL
... Antibodies are natural products that appear on the cell surface as receptors and selectively react with the antigen Lymphocyte receptors are variable and carry various antigen-recognizing receptors ‘Non-self’ antigens/pathogens encounter the existing lymphocyte pool (repertoire) Antigens select thei ...
... Antibodies are natural products that appear on the cell surface as receptors and selectively react with the antigen Lymphocyte receptors are variable and carry various antigen-recognizing receptors ‘Non-self’ antigens/pathogens encounter the existing lymphocyte pool (repertoire) Antigens select thei ...
chapter 22 - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... External Barriers to Invasion 1. The ________ is an inhospitable environment for ______________ growth 2. ________, _________ _________, and _____________ defend mucous membranes against microbes (Figure 22-2) B. ___________________ Internal Defenses Combat ____________ 1. __________________ cells a ...
... External Barriers to Invasion 1. The ________ is an inhospitable environment for ______________ growth 2. ________, _________ _________, and _____________ defend mucous membranes against microbes (Figure 22-2) B. ___________________ Internal Defenses Combat ____________ 1. __________________ cells a ...
Igs and the Immune System
... T-cells are involved in what are known as ‘cell mediated responses’. They respond to cells which have foreign bodies displayed on their surface and can eliminate virus-infected and cancerous cells. T-cells can also respond to chemical signals to activate and search for invading bacteria. The B-cells ...
... T-cells are involved in what are known as ‘cell mediated responses’. They respond to cells which have foreign bodies displayed on their surface and can eliminate virus-infected and cancerous cells. T-cells can also respond to chemical signals to activate and search for invading bacteria. The B-cells ...
Immune
... Antibiotics are designed to attack the specific structures present in bacteria, such as their cell membranes, or to disrupt their reproduction. Viruses are not alive in the same sense that bacteria are and they don’t have the same structures as bacteria. Viral reproduction is achieved by the virus t ...
... Antibiotics are designed to attack the specific structures present in bacteria, such as their cell membranes, or to disrupt their reproduction. Viruses are not alive in the same sense that bacteria are and they don’t have the same structures as bacteria. Viral reproduction is achieved by the virus t ...
Immunology Review
... almost every nucleated cell in the body • These antigens bind peptides that are produced within the cell – Tumors, viruses, intracellular bacteria – These peptides are termed endogenous antigens ...
... almost every nucleated cell in the body • These antigens bind peptides that are produced within the cell – Tumors, viruses, intracellular bacteria – These peptides are termed endogenous antigens ...
Unraveling the Tissue Specific Antigen Presentation That Results in
... A large number of studies in experimental animal models have demonstrated the significant potential of adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors as a therapeutic tool for in vivo gene transfer. Unfortunately, there has been only minimal success in translation of these results into clinical studies. Data ...
... A large number of studies in experimental animal models have demonstrated the significant potential of adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors as a therapeutic tool for in vivo gene transfer. Unfortunately, there has been only minimal success in translation of these results into clinical studies. Data ...
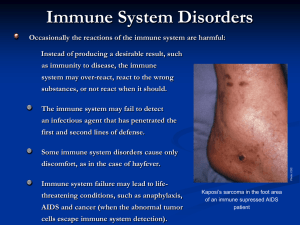
Immune System Disorders
... vigorous overreaction of the immune system to a previously encountered antigen. Mast cells are immune cells involved in allergic responses, they are non- motile, found around blood vessels, in connective tissue and in the lungs. Mast cells release active agents such as Histamine, which cause contrac ...
... vigorous overreaction of the immune system to a previously encountered antigen. Mast cells are immune cells involved in allergic responses, they are non- motile, found around blood vessels, in connective tissue and in the lungs. Mast cells release active agents such as Histamine, which cause contrac ...
final exam of medical immunology
... 20. All of the following are true about delayed-type hypersensitivity except… A. is mediated by T lymphocytes. B. includes contact sensitivity. C. includes the tuberculin reaction. D. includes Farmer’s lung. 21. Live vaccines are dangerous to the following people except… A. a pregnant woman. B. Tee ...
... 20. All of the following are true about delayed-type hypersensitivity except… A. is mediated by T lymphocytes. B. includes contact sensitivity. C. includes the tuberculin reaction. D. includes Farmer’s lung. 21. Live vaccines are dangerous to the following people except… A. a pregnant woman. B. Tee ...
- SGTB Khalsa College
... cells, substances and processes involved in endogenous or cytosolic pathway of antigen presentation Understanding of the cells, substances... .... and processes involved in exogenous or endocytic pathway of antigen presentation. Summary of chapter and linkage with concepts learnt earlier ...
... cells, substances and processes involved in endogenous or cytosolic pathway of antigen presentation Understanding of the cells, substances... .... and processes involved in exogenous or endocytic pathway of antigen presentation. Summary of chapter and linkage with concepts learnt earlier ...
CH 40 The Immune System and Disease
... disease came from curses, evils spirits, night vapors, Ideas about germs are called Germ Theory of Disease ...
... disease came from curses, evils spirits, night vapors, Ideas about germs are called Germ Theory of Disease ...
There are
... acidity, phagocytosis, inflammation, complement proteins, and interferons. Specific response: T and B cells, antibodies, helper T cells, cytotoxic T cells. Humoral and cell mediated immunity. What is the immune system? What is its function? What is the difference between non specific and specific im ...
... acidity, phagocytosis, inflammation, complement proteins, and interferons. Specific response: T and B cells, antibodies, helper T cells, cytotoxic T cells. Humoral and cell mediated immunity. What is the immune system? What is its function? What is the difference between non specific and specific im ...
TOPIC 11.1
... produced antibodies, extract mouse plasma cells 3. Fuse these antibody containing mouse B plasma cells with tumour cells (called hybridoma cells) 4. Allow to grow and produce the antibody 5. The hybridoma cells produce antibodies (B plasma cells) and are long-lived (tumour cells) ...
... produced antibodies, extract mouse plasma cells 3. Fuse these antibody containing mouse B plasma cells with tumour cells (called hybridoma cells) 4. Allow to grow and produce the antibody 5. The hybridoma cells produce antibodies (B plasma cells) and are long-lived (tumour cells) ...
Immunology – Immune System Overview
... The immune system provides tissue incompatibility this can be detrimental effect because we are unable to readily have transplantation of organs from one individual to another. Although immunosuppressive drugs are widely used nowadays when transplantation is necessary. What comprises the immune ...
... The immune system provides tissue incompatibility this can be detrimental effect because we are unable to readily have transplantation of organs from one individual to another. Although immunosuppressive drugs are widely used nowadays when transplantation is necessary. What comprises the immune ...
The Human Immune System - De Soto Area School District
... called antibody-mediated immunity, meaning that is controlled by antibodies • This represents the third line of defense in the immune system ...
... called antibody-mediated immunity, meaning that is controlled by antibodies • This represents the third line of defense in the immune system ...
antibodies - Canvas by Instructure
... called antibody-mediated immunity, meaning that is controlled by antibodies • This represents the third line of defense in the immune system ...
... called antibody-mediated immunity, meaning that is controlled by antibodies • This represents the third line of defense in the immune system ...
Immunity Talk selected slides
... A substance (usually protein) recognised as 'foreign' that stimulate antibody formation ...
... A substance (usually protein) recognised as 'foreign' that stimulate antibody formation ...
Tuberculosis
... This leads to the formation of a larger well-organised solid granuloma when adaptive immunity is initiated with the infiltration of specific T lymphocytes and also CD8+, NK and γδT cells. Macrophages at the centre will often be infected, have an activated appearance or be differentiated into epithel ...
... This leads to the formation of a larger well-organised solid granuloma when adaptive immunity is initiated with the infiltration of specific T lymphocytes and also CD8+, NK and γδT cells. Macrophages at the centre will often be infected, have an activated appearance or be differentiated into epithel ...
The Immune System
... If an invader gets inside the body, the internal defenses (2nd line of defense!) take over A) Phagocytes (“to eat”/”cell”) • White blood cells that “eat”/engulf invaders ...
... If an invader gets inside the body, the internal defenses (2nd line of defense!) take over A) Phagocytes (“to eat”/”cell”) • White blood cells that “eat”/engulf invaders ...
Adaptive immune system

The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune or, more rarely, as the specific immune system, is a subsystem of the overall immune system that is composed of highly specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate or prevent pathogen growth. The adaptive immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies found in vertebrates (the other being the innate immune system). Adaptive immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, leads to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination. Like the innate system, the adaptive system includes both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components.Unlike the innate immune system, the adaptive immune system is highly specific to a specific pathogen. Adaptive immunity can also provide long-lasting protection: for example; someone who recovers from measles is now protected against measles for their lifetime but in other cases it does not provide lifetime protection: for example; chickenpox. The adaptive system response destroys invading pathogens and any toxic molecules they produce. Sometimes the adaptive system is unable to distinguish foreign molecules, the effects of this may be hayfever, asthma or any other allergies. Antigens are any substances that elicit the adaptive immune response. The cells that carry out the adaptive immune response are white blood cells known as lymphocytes. Two main broad classes—antibody responses and cell mediated immune response—are also carried by two different lymphocytes (B cells and T cells). In antibody responses, B cells are activated to secrete antibodies, which are proteins also known as immunoglobulins. Antibodies travel through the bloodstream and bind to the foreign antigen causing it to inactivate, which does not allow the antigen to bind to the host.In acquired immunity, pathogen-specific receptors are ""acquired"" during the lifetime of the organism (whereas in innate immunity pathogen-specific receptors are already encoded in the germline). The acquired response is called ""adaptive"" because it prepares the body's immune system for future challenges (though it can actually also be maladaptive when it results in autoimmunity).The system is highly adaptable because of somatic hypermutation (a process of accelerated somatic mutations), and V(D)J recombination (an irreversible genetic recombination of antigen receptor gene segments). This mechanism allows a small number of genes to generate a vast number of different antigen receptors, which are then uniquely expressed on each individual lymphocyte. Because the gene rearrangement leads to an irreversible change in the DNA of each cell, all progeny (offspring) of that cell inherit genes that encode the same receptor specificity, including the memory B cells and memory T cells that are the keys to long-lived specific immunity.A theoretical framework explaining the workings of the acquired immune system is provided by immune network theory. This theory, which builds on established concepts of clonal selection, is being applied in the search for an HIV vaccine.