Ch6-Immune Desease
... • Differentiate between the concepts of “Innate” and “Adaptive” immunity • Visually recognize and understand the basic roles of lymphocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, NK cells in the immune saga • Understand the roles of the major cytokines in immunity • Differentiate and give examples of the fo ...
... • Differentiate between the concepts of “Innate” and “Adaptive” immunity • Visually recognize and understand the basic roles of lymphocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, NK cells in the immune saga • Understand the roles of the major cytokines in immunity • Differentiate and give examples of the fo ...
Lecture Notes for Med. Tech. Class
... Medawar’s Experiment of Neonatal Tolerance Induction • Neonatal exposure of allogeneic blood cells causes tolerance to the skin grafts from the blood donor. Central and Peripheral Immunological Tolerance • Theoretically, most endogenous antigens can tolerize the immune cells during their maturation ...
... Medawar’s Experiment of Neonatal Tolerance Induction • Neonatal exposure of allogeneic blood cells causes tolerance to the skin grafts from the blood donor. Central and Peripheral Immunological Tolerance • Theoretically, most endogenous antigens can tolerize the immune cells during their maturation ...
11.2
... 3rd Lind of Defense: The Immune System Kicks in to assist the body’s 1st and 2nd lines of ...
... 3rd Lind of Defense: The Immune System Kicks in to assist the body’s 1st and 2nd lines of ...
L18: Immune System, Part 1
... • Where can pathogens enter the body? • What are the barriers to pathogen entry? ...
... • Where can pathogens enter the body? • What are the barriers to pathogen entry? ...
Proteins- (Greek: proteios means most important) Most structurally
... Proteins- (Greek: proteios means most important) Most structurally sophisticated biomolecule. Make up 50% of the dry mass of the cell. A protein monomer is called an Amino Acid. Humans require 20 amino acids, but only can produce 10 internally. The other ten are acquired through food. Structure: Ami ...
... Proteins- (Greek: proteios means most important) Most structurally sophisticated biomolecule. Make up 50% of the dry mass of the cell. A protein monomer is called an Amino Acid. Humans require 20 amino acids, but only can produce 10 internally. The other ten are acquired through food. Structure: Ami ...
Bacteria
... Tiny non-living particles Named for disease they cause. Contain genetic material Structure Genetic material, outer protein coating, (maybe a membrane) Viruses are specific to the host cell they invade. Connections are specific Marker proteins that fit together like puzzle pieces Can only enter a few ...
... Tiny non-living particles Named for disease they cause. Contain genetic material Structure Genetic material, outer protein coating, (maybe a membrane) Viruses are specific to the host cell they invade. Connections are specific Marker proteins that fit together like puzzle pieces Can only enter a few ...
11.1 HL Immune System
... 11.1.4 Explain antibody production. Limit the explanation to antigen presentation by macrophages and activation of helper T-cells lead into activation of B-cells which divide to form clones of antibody-secreting plasma cells and memory cells. 11.1.5 Describe the production of monoclonal antibodies a ...
... 11.1.4 Explain antibody production. Limit the explanation to antigen presentation by macrophages and activation of helper T-cells lead into activation of B-cells which divide to form clones of antibody-secreting plasma cells and memory cells. 11.1.5 Describe the production of monoclonal antibodies a ...
The Immune System - Clark Pleasant Community School Corp
... antibodies; the single most effective protection ...
... antibodies; the single most effective protection ...
84. Which of the following describes an adjuvant correctly? A An
... ensure a valid comparison can be made allow a statistical analysis of the results to be made ensure that researchers are unaware who has been vaccinated. ...
... ensure a valid comparison can be made allow a statistical analysis of the results to be made ensure that researchers are unaware who has been vaccinated. ...
The clonal selection hypothesis is a widely accepted
... In 1954, Danish immunologist Niels Jerne put forward a hypothesis which stated that there is already a vast array of lymphocytes in the body prior to any infection. The entrance of an antigen into the body results in the selection of only one type of lymphocyte to match it and produce a correspondin ...
... In 1954, Danish immunologist Niels Jerne put forward a hypothesis which stated that there is already a vast array of lymphocytes in the body prior to any infection. The entrance of an antigen into the body results in the selection of only one type of lymphocyte to match it and produce a correspondin ...
Immunity
... destroy the organism’s own body tissues Ex. Multiple Sclerosis (MS), Type I Diabetes 2050: Finally mad enough to act, the Earth makes antibodies against the human race ...
... destroy the organism’s own body tissues Ex. Multiple Sclerosis (MS), Type I Diabetes 2050: Finally mad enough to act, the Earth makes antibodies against the human race ...
introduction to the immune system
... combining sites on these antibodies serve as receptors for their "matching" antigens->leave bone marrow and->lymph nodes, spleen, other lymphoid tissue SECOND STAGE-occurs when B cell is activated by an encounter with its specific antigen-when the epitopes combine with the antibody combining sites o ...
... combining sites on these antibodies serve as receptors for their "matching" antigens->leave bone marrow and->lymph nodes, spleen, other lymphoid tissue SECOND STAGE-occurs when B cell is activated by an encounter with its specific antigen-when the epitopes combine with the antibody combining sites o ...
Specific Responses
... B-cells • They do antibody-mediated immunity • When they encounter an antigen, the receptor immediately recognizes it • B-cell gives rise to plasma cells • These produce specific antibodies • The antibodies have the same specificity as the B-Cell Receptor ...
... B-cells • They do antibody-mediated immunity • When they encounter an antigen, the receptor immediately recognizes it • B-cell gives rise to plasma cells • These produce specific antibodies • The antibodies have the same specificity as the B-Cell Receptor ...
Chapter 6 - Medical School Pathology
... • Differentiate between the concepts of “Innate” and “Adaptive” immunity • Visually recognize and understand the basic roles of lymphocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, NK cells in the immune saga • Understand the roles of the major cytokines in immunity • Differentiate and give examples of the fo ...
... • Differentiate between the concepts of “Innate” and “Adaptive” immunity • Visually recognize and understand the basic roles of lymphocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, NK cells in the immune saga • Understand the roles of the major cytokines in immunity • Differentiate and give examples of the fo ...
study guide for exam 4
... 18) Hypersensitivity or allergy refers to the immune system responding __________________ What are autoimmune diseases What is Asthma? To treat generalized anaphylaxis, _________ must be administered immediately What is rhogam? Why are recipient human leukocyte antigens assayed before a transplant ...
... 18) Hypersensitivity or allergy refers to the immune system responding __________________ What are autoimmune diseases What is Asthma? To treat generalized anaphylaxis, _________ must be administered immediately What is rhogam? Why are recipient human leukocyte antigens assayed before a transplant ...
Immune system08
... Function of the system • The immune system is the system of specialized cells and organs that protect an organism from outside biological influences • Defends against pathogens and disease ...
... Function of the system • The immune system is the system of specialized cells and organs that protect an organism from outside biological influences • Defends against pathogens and disease ...
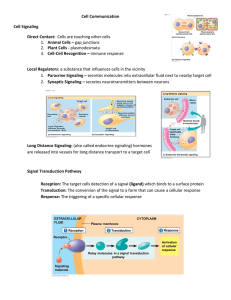
Cell Communication Cell Signaling Direct Contact: Cells are
... 4. Intracellular Responses: these involve proteins that are dissolved in the cytoplasm of the cell. The signal molecules must be able to dissolve through the plasma membrane Ex. Steroid hormones Transduction: Relay signals from receptors to cellular responses. This is usually done by protein kinase ...
... 4. Intracellular Responses: these involve proteins that are dissolved in the cytoplasm of the cell. The signal molecules must be able to dissolve through the plasma membrane Ex. Steroid hormones Transduction: Relay signals from receptors to cellular responses. This is usually done by protein kinase ...
Lecture 7: The body`s defenses
... • Complement proteins interact with antibodies to kill invading cells • Binding of antibody is followed by attachment of complement proteins • Protein complex becomes activated • Pore is formed in pathogen’s membrane • Goodbye pathogen ...
... • Complement proteins interact with antibodies to kill invading cells • Binding of antibody is followed by attachment of complement proteins • Protein complex becomes activated • Pore is formed in pathogen’s membrane • Goodbye pathogen ...
4th European CellAid-Symposium Cell Therapies for a Cure of
... Arrival, registration, media transfer 2.00 pm ...
... Arrival, registration, media transfer 2.00 pm ...
Document
... This system is activated when pathogens get past the general defence system Organs of the immune system that store WBC’s called lymphocytes and monocytes include the lymphatic vessels, tonsils, spleen lymph nodes ...
... This system is activated when pathogens get past the general defence system Organs of the immune system that store WBC’s called lymphocytes and monocytes include the lymphatic vessels, tonsils, spleen lymph nodes ...