study_guide_2007_hazbun - Welcome to people.pharmacy
... 1. TCR: structure, generated by random recombination 2. What are the differences between B and T cells in development and in making their respective receptors? 3. How does antigen processing and presentation occur? a. MHC I and MHC II b. extracellular versus intracellular pathogens c. remember most ...
... 1. TCR: structure, generated by random recombination 2. What are the differences between B and T cells in development and in making their respective receptors? 3. How does antigen processing and presentation occur? a. MHC I and MHC II b. extracellular versus intracellular pathogens c. remember most ...
Immuno Revision Notes
... Supportive (bronchodilators/adrenaline/fluids) Drugs o Block MC activation – sodium chromoglycate o H1‐receptor antagonists – antihistamines o Anti‐inflammatory – corticosteroids o Leukotriene receptor antagonist ‐montelukast Allergen specific immunotherapy ...
... Supportive (bronchodilators/adrenaline/fluids) Drugs o Block MC activation – sodium chromoglycate o H1‐receptor antagonists – antihistamines o Anti‐inflammatory – corticosteroids o Leukotriene receptor antagonist ‐montelukast Allergen specific immunotherapy ...
File
... i. Memory T cells are long-lived and respond faster to second exposure C. Polyclonal antibodies a. Primary immune response by an organism because the pathogen is typically being recognized as many antigens & not just one b. For example, a virus is typically made up of several different kinds of prot ...
... i. Memory T cells are long-lived and respond faster to second exposure C. Polyclonal antibodies a. Primary immune response by an organism because the pathogen is typically being recognized as many antigens & not just one b. For example, a virus is typically made up of several different kinds of prot ...
How is a vaccine prepared?
... pancreas cells that make insulin. • Rheumatoid arthritis results when the immune system attacks and destroys connective tissue such as tendons, ligaments and bone. ...
... pancreas cells that make insulin. • Rheumatoid arthritis results when the immune system attacks and destroys connective tissue such as tendons, ligaments and bone. ...
Immunology - PharmaEuphoria
... Antigen types Based upon the ability of antigens to carry out their functions, antigens are of two types complete antigens Incomplete antigens (haptens) A complete antigen is able to induce antibody formation & produce a specific and observable reaction with the antibody so produced. Haptens are su ...
... Antigen types Based upon the ability of antigens to carry out their functions, antigens are of two types complete antigens Incomplete antigens (haptens) A complete antigen is able to induce antibody formation & produce a specific and observable reaction with the antibody so produced. Haptens are su ...
test ch 12 body defenses
... 8. The type of immunity mechanisms that provides a general defense by acting against anything not recognized as “ not self” is called _________________ immunity. 9. T cell mechanisms are classified as_____________ immunity. 10. Macromolecules that induce the immune system to make certain responses a ...
... 8. The type of immunity mechanisms that provides a general defense by acting against anything not recognized as “ not self” is called _________________ immunity. 9. T cell mechanisms are classified as_____________ immunity. 10. Macromolecules that induce the immune system to make certain responses a ...
Response of Immune System to Disease
... which organism was the cause of a particular disease. These postulates are still in use today. This led the way for specific treatment for many diseasecausing pathogens. ...
... which organism was the cause of a particular disease. These postulates are still in use today. This led the way for specific treatment for many diseasecausing pathogens. ...
type III - immunology.unideb.hu
... • Recognition of self-antigens by the cells of the adaptive immunity (B and T cells) normally induce tolerance • Tolerance is achieved by different mechanisms in the body: elimination of auto-reactive (self-recognizing) lymphocytes in the bone marrow and thymus (the process is more strict regardin ...
... • Recognition of self-antigens by the cells of the adaptive immunity (B and T cells) normally induce tolerance • Tolerance is achieved by different mechanisms in the body: elimination of auto-reactive (self-recognizing) lymphocytes in the bone marrow and thymus (the process is more strict regardin ...
Immune System Period 1 - Mercer Island School District
... same disease twice. (The cold and the flu mutate rapidly and if you catch the flu multiple times, you are infected by a different mutation of the same virus.) ...
... same disease twice. (The cold and the flu mutate rapidly and if you catch the flu multiple times, you are infected by a different mutation of the same virus.) ...
Specific Immunity POGIL
... The Facts on HIV/AIDS AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome) was first recognized in North America in the early 1980s. It is caused by a virus known as HIV (human immunodeficiency virus). HIV infection has become a worldwide epidemic. About 33 million people are currently infected with the virus ...
... The Facts on HIV/AIDS AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome) was first recognized in North America in the early 1980s. It is caused by a virus known as HIV (human immunodeficiency virus). HIV infection has become a worldwide epidemic. About 33 million people are currently infected with the virus ...
Immune System Definition
... • Antibody production by immune cells • Antibodies are made in response to an antigen (foreign proteins) found on a foreign substance or invading organism • T (from thymus) and B (from bone marrow) cells involved in antibody production • Certain T cells activate some B cells to produce antibodies • ...
... • Antibody production by immune cells • Antibodies are made in response to an antigen (foreign proteins) found on a foreign substance or invading organism • T (from thymus) and B (from bone marrow) cells involved in antibody production • Certain T cells activate some B cells to produce antibodies • ...
09Immunological Tolerance
... Mechanisms of Tolerance Induction • Clonal deletion: physically deleting cells from the repertoire at come stage during their lifespan. • Clonal anergy: downregulating the intrinsic mechaism of the immune response. • Suppression: inhibiting cellular activity through interaction with other cells, su ...
... Mechanisms of Tolerance Induction • Clonal deletion: physically deleting cells from the repertoire at come stage during their lifespan. • Clonal anergy: downregulating the intrinsic mechaism of the immune response. • Suppression: inhibiting cellular activity through interaction with other cells, su ...
Aankondiging_Immuno_7nov
... and thus determines the outcome of antigen-specific responses. Specific immune responses are driven by antigen-specific T cells, which do not only expand after initial MHC-dependent antigen contact, but do also polarize into effector cells.These differentiated cells are characterized by their functi ...
... and thus determines the outcome of antigen-specific responses. Specific immune responses are driven by antigen-specific T cells, which do not only expand after initial MHC-dependent antigen contact, but do also polarize into effector cells.These differentiated cells are characterized by their functi ...
Co-receptors
... characterised one is CD28, among others (ICOS, OX40, CD46…). Without receiving a second signal, the T cells remain mainly unresponsive, becoming anergic cells, or die. Cleverly, most of the ligands for these costimulatory molecules are induced by activation/maturation of the cells that present the p ...
... characterised one is CD28, among others (ICOS, OX40, CD46…). Without receiving a second signal, the T cells remain mainly unresponsive, becoming anergic cells, or die. Cleverly, most of the ligands for these costimulatory molecules are induced by activation/maturation of the cells that present the p ...
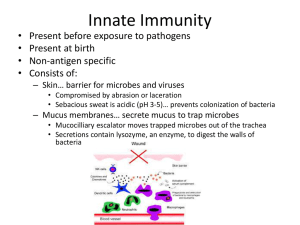
Innate Immunity - Santa Susana High School
... – Activated by the presence of cytokines – Antigens (foreign particles) elicit the immune response • Epitote… small part of the antigen molecule that is recognized by a specific lymphocyte – Each lymphocyte may contain up to 100,000 identical epitote recognition sites ...
... – Activated by the presence of cytokines – Antigens (foreign particles) elicit the immune response • Epitote… small part of the antigen molecule that is recognized by a specific lymphocyte – Each lymphocyte may contain up to 100,000 identical epitote recognition sites ...
Immune response part 1
... recognise phagocytes and lymphocytes under the light microscope; describe the origin, maturation and mode of action of phagocytes explain the meaning of the term immune response; distinguish between B- and Tlymphocytes in their mode of action in fighting infection and describe their origin and funct ...
... recognise phagocytes and lymphocytes under the light microscope; describe the origin, maturation and mode of action of phagocytes explain the meaning of the term immune response; distinguish between B- and Tlymphocytes in their mode of action in fighting infection and describe their origin and funct ...
Document
... All cells except red blood cells and platelets have three main components: a nucleus, cytoplasm, and a cell membrane. There are four major tissue types: epithelial tissue; connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. When cells are exposed to adverse conditions, they go through a process of ...
... All cells except red blood cells and platelets have three main components: a nucleus, cytoplasm, and a cell membrane. There are four major tissue types: epithelial tissue; connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. When cells are exposed to adverse conditions, they go through a process of ...
T Cell Development and Selection, Part I
... 3) Involution of thymus with aging. 4) DiGeorge’s syndrome (human). Nude mice. ...
... 3) Involution of thymus with aging. 4) DiGeorge’s syndrome (human). Nude mice. ...
Unit 8 Communicable Diseases
... Your immune system has a memory of every antigen it has encountered. Active Immunity develops naturally and artificially. Vaccinations are prepared dead or weakened pathogens that are introduced into the body to stimulate an immune response. ...
... Your immune system has a memory of every antigen it has encountered. Active Immunity develops naturally and artificially. Vaccinations are prepared dead or weakened pathogens that are introduced into the body to stimulate an immune response. ...