Immune System Review Sheet
... 3. What is the difference between active and passive immunity? Give an example of each. 31-5 Disorders and Allergies 1. Know all terms. 2. What is an autoimmune disease, and how does it affect your body? 3. What’s the difference between an autoimmune disease and AIDS? What happens in the case of AID ...
... 3. What is the difference between active and passive immunity? Give an example of each. 31-5 Disorders and Allergies 1. Know all terms. 2. What is an autoimmune disease, and how does it affect your body? 3. What’s the difference between an autoimmune disease and AIDS? What happens in the case of AID ...
Disorders in Immunity
... Immunity process is a powerful system of _______ Seek out, recognize, and ______ foreign materials to prevent disease BUT, On the other side, overreactivity or underreactivity of immune system can be ...
... Immunity process is a powerful system of _______ Seek out, recognize, and ______ foreign materials to prevent disease BUT, On the other side, overreactivity or underreactivity of immune system can be ...
Medical Immunology
... unique to individual tumors, whereas others are shared among tumors of the same type. ...
... unique to individual tumors, whereas others are shared among tumors of the same type. ...
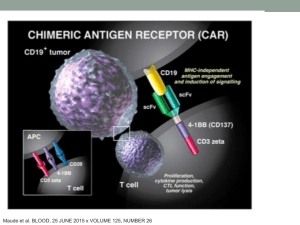
CAR T cell lecture 11.25
... • Best of both worlds of the immune system • B cell specificity • T cell cytotoxicity without presentation • Form of Adoptive T cell therapy ...
... • Best of both worlds of the immune system • B cell specificity • T cell cytotoxicity without presentation • Form of Adoptive T cell therapy ...
Immunology Review
... • TCR is coupled to CD3. • CD3 signals the interior of the T cell that antigen is present. • T cell then secretes cytokines that effect surrounding cells. • Some T cells mature into memory T cells. These assist with rapid recognition of the foreign antigen the next time it is encountered, thus speed ...
... • TCR is coupled to CD3. • CD3 signals the interior of the T cell that antigen is present. • T cell then secretes cytokines that effect surrounding cells. • Some T cells mature into memory T cells. These assist with rapid recognition of the foreign antigen the next time it is encountered, thus speed ...
Teacher Immunology Project
... to the immune system for evaluation Appropriate Helper T cell binds with the APC's MHCII/Antigen This activates a Helper T cell which then finds a B-cell expressing the same surface protein. When the activated Helper T cell binds to the B cell it releases Interleukin II (IL-II) which activates B cel ...
... to the immune system for evaluation Appropriate Helper T cell binds with the APC's MHCII/Antigen This activates a Helper T cell which then finds a B-cell expressing the same surface protein. When the activated Helper T cell binds to the B cell it releases Interleukin II (IL-II) which activates B cel ...
Using Cutting Edge Accurate Identification of the GI Microbiota in the
... in several autoimmune diseases and is involved in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diabetes. Zonulin upregulation seems to precede the onset of the disease, providing a possible link between increased intestinal permeability, environmental exposure to non-self antigens, and the development of autoimmu ...
... in several autoimmune diseases and is involved in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diabetes. Zonulin upregulation seems to precede the onset of the disease, providing a possible link between increased intestinal permeability, environmental exposure to non-self antigens, and the development of autoimmu ...
Host Microbe Interations
... 2- M proteins found in strains of Streptococcus pyogenes also inactivate the C3b complement component. 3- Fc receptors found on the surface of Staphylococcus and Streptococcus bind to the fc region of an antibody preventing it from binding correctly! ...
... 2- M proteins found in strains of Streptococcus pyogenes also inactivate the C3b complement component. 3- Fc receptors found on the surface of Staphylococcus and Streptococcus bind to the fc region of an antibody preventing it from binding correctly! ...
Immunity Ch. 11.1-6
... 11.3 Antigen-presenting B & T cells • Recognizes antigens derived from pathogens. • If you have a secondary infection from the same or a similar pathogen, memory B and T cells will give you immunity. • This natural process of creating immunity is enhanced artificially by the use of vaccines. ...
... 11.3 Antigen-presenting B & T cells • Recognizes antigens derived from pathogens. • If you have a secondary infection from the same or a similar pathogen, memory B and T cells will give you immunity. • This natural process of creating immunity is enhanced artificially by the use of vaccines. ...
File
... 1. NK Cells attack virus-infected cells and cancer cells in general 2. NK Cells releases molecules of a protein which forms pores in the target cell’s membrane 3. The pores allow a “signal” molecule from the NK cell to enter the target cell and trigger a genetically controlled series of events 4. Th ...
... 1. NK Cells attack virus-infected cells and cancer cells in general 2. NK Cells releases molecules of a protein which forms pores in the target cell’s membrane 3. The pores allow a “signal” molecule from the NK cell to enter the target cell and trigger a genetically controlled series of events 4. Th ...
The Immune System - Hatzalah of Miami-Dade
... Cytotoxic (Killer) T-Cells • Respond to presence of antigens and lymphokines produced by T-4 cells • Seek out, bind to, and destroy: – Cells infected by viruses – Some tumor cells – Cells of tissue transplants ...
... Cytotoxic (Killer) T-Cells • Respond to presence of antigens and lymphokines produced by T-4 cells • Seek out, bind to, and destroy: – Cells infected by viruses – Some tumor cells – Cells of tissue transplants ...
Autoimmunity
... The actual damage in lupus is done by the accumulation of immune complex, the combination of antibody and antigen Macrophages usually clean up the mess, but because the alien cells are the body’s own, the supply is essentially unlimited, and eventually the macrophages can’t eat fast enough to ...
... The actual damage in lupus is done by the accumulation of immune complex, the combination of antibody and antigen Macrophages usually clean up the mess, but because the alien cells are the body’s own, the supply is essentially unlimited, and eventually the macrophages can’t eat fast enough to ...
Chapter 3
... - IP3 interacts with endoplasmic reticulum vesicles, release of stored calcium, altering activity of other proteins - For example – in lymphocytes, calcium ions bind calmodulin altering its conformation allowing dephosphorylation of NFAT (nuclear factor of Activated T cells) ...
... - IP3 interacts with endoplasmic reticulum vesicles, release of stored calcium, altering activity of other proteins - For example – in lymphocytes, calcium ions bind calmodulin altering its conformation allowing dephosphorylation of NFAT (nuclear factor of Activated T cells) ...
Διαφάνεια 1 - Aristotle University of Thessaloniki
... 2) Immune hemolytic anemia: Cause: - Premature destruction of red blood cells by the immune system ...
... 2) Immune hemolytic anemia: Cause: - Premature destruction of red blood cells by the immune system ...
Prentice Hall Biology - Valhalla High School
... » The fever also increases heart rate so wbc can get to the infection site faster. ...
... » The fever also increases heart rate so wbc can get to the infection site faster. ...
The Immune System
... dysentery from contaminated water and Salmonella from eggs, turkey, etc. › Animal Bites are also concern for the transmission of disease, because of the fact that animals can be a vector for many viruses, i.e. bubonic plague was spread by fleas, Lyme disease is spread by ticks, rabies is spread in t ...
... dysentery from contaminated water and Salmonella from eggs, turkey, etc. › Animal Bites are also concern for the transmission of disease, because of the fact that animals can be a vector for many viruses, i.e. bubonic plague was spread by fleas, Lyme disease is spread by ticks, rabies is spread in t ...
HIV and immunity
... We can use the same approach to study the evolution of a single virus after it infects a single person ...
... We can use the same approach to study the evolution of a single virus after it infects a single person ...
B cells and T cells Immunoglobulins
... - many different types of cells mediate the immune response to destroy bacteria and viruses as well as pre-cancerous cells ...
... - many different types of cells mediate the immune response to destroy bacteria and viruses as well as pre-cancerous cells ...
Immune_11
... B-cell activated: antibody binds to antigen to mark it for destruction B-memory cells “remember” antigen in case of second infection ...
... B-cell activated: antibody binds to antigen to mark it for destruction B-memory cells “remember” antigen in case of second infection ...