REVIEW QUESTIONS – CHAPTER 26
... When the body loses tolerance for its own antigens and attacks them, autoimmune disease results. Autoimmune disease results in cellular damage of the body by its own immune system; it is treated with immunosuppressive drugs. ...
... When the body loses tolerance for its own antigens and attacks them, autoimmune disease results. Autoimmune disease results in cellular damage of the body by its own immune system; it is treated with immunosuppressive drugs. ...
Introduction to Microbial Pathogenesis
... (sialic acid); Streptococcus pyogenes (hyaluronic acid) ...
... (sialic acid); Streptococcus pyogenes (hyaluronic acid) ...
03-Chapter-8-supplement
... Most medium to large viruses (8 or more genes) encode such molecules ...
... Most medium to large viruses (8 or more genes) encode such molecules ...
specific defenses: the immune system
... 1. What signals does a T cell require in order to divide? ...
... 1. What signals does a T cell require in order to divide? ...
2. seminar 2012
... Free haptens, however, can react with products of the immune response after such products have been elicited. Haptens have the property of antigenicity but not immunogenicity. Haptenic/antigen determinant (epitope) part of the antigen which are recognized by a defined immunoglobulin (B cell receptor ...
... Free haptens, however, can react with products of the immune response after such products have been elicited. Haptens have the property of antigenicity but not immunogenicity. Haptenic/antigen determinant (epitope) part of the antigen which are recognized by a defined immunoglobulin (B cell receptor ...
Slide () - Anesthesiology - American Society of Anesthesiologists
... Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells on innate and adaptive immunity. (A) MSC can modulate innate and adaptive immune cells by: (1) promoting repolarization of macrophages from type 1 to type 2 phenotype characterized by high levels of interleukin-10 secretion, which can block polym ...
... Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells on innate and adaptive immunity. (A) MSC can modulate innate and adaptive immune cells by: (1) promoting repolarization of macrophages from type 1 to type 2 phenotype characterized by high levels of interleukin-10 secretion, which can block polym ...
The Immune System and Disease
... ii. oil and sweat create an ________ environment that kills bacteria iii. mucus in nose and throat trap __________ iv. cilia in throat push viruses away from the lungs v. stomach acid and digestive enzymes destroy _____________ vi. mucus, saliva, sweat, and tears contain ______________ that breaks d ...
... ii. oil and sweat create an ________ environment that kills bacteria iii. mucus in nose and throat trap __________ iv. cilia in throat push viruses away from the lungs v. stomach acid and digestive enzymes destroy _____________ vi. mucus, saliva, sweat, and tears contain ______________ that breaks d ...
Title - Iowa State University
... b.) Increase size of the lamella c.) Change flow of blood and water opposite to parallel d.) Decrease operculum flap size e.) None of the above 3. Which of the following is NOT true of hemoglobin? a.) A protein with four subunits b.) Binds CO2 c.) Binds O2 d.) Binds H+ e.) All of the above are true ...
... b.) Increase size of the lamella c.) Change flow of blood and water opposite to parallel d.) Decrease operculum flap size e.) None of the above 3. Which of the following is NOT true of hemoglobin? a.) A protein with four subunits b.) Binds CO2 c.) Binds O2 d.) Binds H+ e.) All of the above are true ...
The Immune System : (page 382) Recognizes and destroys
... Specialized cells that attack only certain identified pathogens. Unique to an individual. Includes “lymphocytes” ( B cells and T cells) from your bone marrow. Form the 2nd and 3rd lines of defence. To attack a pathogen, you must recognize cells that don’t belong to you ( shape of their antigens) fir ...
... Specialized cells that attack only certain identified pathogens. Unique to an individual. Includes “lymphocytes” ( B cells and T cells) from your bone marrow. Form the 2nd and 3rd lines of defence. To attack a pathogen, you must recognize cells that don’t belong to you ( shape of their antigens) fir ...
UNIVERSITY OF OSLO Faculty of Mathematics and Natural
... analyzed, and found to comprise 3-9 million different sequences. Discuss the result in light of the mechanisms described in A. Are all gene segments utilized during rearrangement? Are all used equally often? D) Describe how somatic hypermutation can be the basis for affinity maturation of antibodies ...
... analyzed, and found to comprise 3-9 million different sequences. Discuss the result in light of the mechanisms described in A. Are all gene segments utilized during rearrangement? Are all used equally often? D) Describe how somatic hypermutation can be the basis for affinity maturation of antibodies ...
Unit 8 Seminar
... people to live in very tight quarters and come into contact with possibly hundreds or thousands of people in a single day. Consider cities like New York City and Tokyo, Japan. Occupants in these cities are packed in tightly into subway systems and overcrowded conditions. When people in Japan are ill ...
... people to live in very tight quarters and come into contact with possibly hundreds or thousands of people in a single day. Consider cities like New York City and Tokyo, Japan. Occupants in these cities are packed in tightly into subway systems and overcrowded conditions. When people in Japan are ill ...
bch424 tutorial kit - Covenant University
... 11. What are antibodies, how do they interact with antigens or foreign compounds Antibodies are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells (white blood cells) used for recognition of a unique part of the foreign target. They are specialized receptor protein that binds to a specific antigen, imm ...
... 11. What are antibodies, how do they interact with antigens or foreign compounds Antibodies are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells (white blood cells) used for recognition of a unique part of the foreign target. They are specialized receptor protein that binds to a specific antigen, imm ...
Immunity
... Students should understand the following: The essential difference between humoral and cellular ...
... Students should understand the following: The essential difference between humoral and cellular ...
Document
... leukocytes that stimulate or inhibit the proliferation or function of immune cells. – Interleukin – cytokines that only affect leukocytes. • Lymphocyte – A type of leukocyte (white blood cell) of the immune system. – T-Regulatory Cell – slows down and stops immune response – T-Helper Cell – has anti ...
... leukocytes that stimulate or inhibit the proliferation or function of immune cells. – Interleukin – cytokines that only affect leukocytes. • Lymphocyte – A type of leukocyte (white blood cell) of the immune system. – T-Regulatory Cell – slows down and stops immune response – T-Helper Cell – has anti ...
The Human Body Systems
... (2) Lymphocytes (T cells and B cells) produce antibodies b) Antibodies are proteins that react with antigens (foreign molecules that have attacked the body) to deactivate them. (1) T Cells – Identify one kind of pathogen from another – (a) Over 10 million T Cells in your body, each able to recognize ...
... (2) Lymphocytes (T cells and B cells) produce antibodies b) Antibodies are proteins that react with antigens (foreign molecules that have attacked the body) to deactivate them. (1) T Cells – Identify one kind of pathogen from another – (a) Over 10 million T Cells in your body, each able to recognize ...
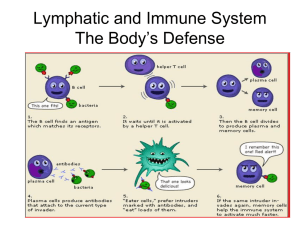
Lymphatic and Immune System
... foreign particles and digest them with enzymes – Natural Killer Cells are lymphocytes that lyse and kill cancer cells and virus infected cells and act spontaneously without need to “recognize” intruder, they react to sugars on the cell surface and release perforins to disintegrate the target cell’s ...
... foreign particles and digest them with enzymes – Natural Killer Cells are lymphocytes that lyse and kill cancer cells and virus infected cells and act spontaneously without need to “recognize” intruder, they react to sugars on the cell surface and release perforins to disintegrate the target cell’s ...
OTHER DISEASE CAUSING FACTORS
... • If you want to wait till 9 to come, just pull up in the parking lot, come knock on the window, and someone will let you in. • Please make arrangements to have something to do before 9 and after 12 because I will not be ...
... • If you want to wait till 9 to come, just pull up in the parking lot, come knock on the window, and someone will let you in. • Please make arrangements to have something to do before 9 and after 12 because I will not be ...
Antigen recognition in innate and adaptive immunity
... Antibodies – block and direct receptor mediated phagocytosis and complement killing. • T cells provide cellular immunity – kill virally infected cells. Also essential in driving B cell and T cell maturation – cytokines ...
... Antibodies – block and direct receptor mediated phagocytosis and complement killing. • T cells provide cellular immunity – kill virally infected cells. Also essential in driving B cell and T cell maturation – cytokines ...