20150923_koyasu
... RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Sciences, Keio University School of Medicine ...
... RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Sciences, Keio University School of Medicine ...
20141203_kurosaki
... One striking feature of humoral memory response is quick generation of neutralizing antibodies (Abs) upon re-invasion of pathogenic micro-organisms and eliminating them from our body. However, it is still unclear about cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying such quick humoral responses. By usi ...
... One striking feature of humoral memory response is quick generation of neutralizing antibodies (Abs) upon re-invasion of pathogenic micro-organisms and eliminating them from our body. However, it is still unclear about cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying such quick humoral responses. By usi ...
Chapter 19
... • Major histocompatibility complex (MHC): Genes encoding histocompatibility antigens • Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) complex: MHC genes in humans ...
... • Major histocompatibility complex (MHC): Genes encoding histocompatibility antigens • Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) complex: MHC genes in humans ...
Immune Tolerance in Cancer and Autoimmune Disease
... Invited speaker 1 – Larry Pease: Activation of self reactive CTL reveals a strong focus of the CD8+ T cell repertoire on self ...
... Invited speaker 1 – Larry Pease: Activation of self reactive CTL reveals a strong focus of the CD8+ T cell repertoire on self ...
LN #13 Immune
... temperature until the infection is controlled. • Low fevers 100°F (37.7°C) – Stimulate production of Interferons (prevent viruses from reproducing) – Increase activity of white blood cell maturation ...
... temperature until the infection is controlled. • Low fevers 100°F (37.7°C) – Stimulate production of Interferons (prevent viruses from reproducing) – Increase activity of white blood cell maturation ...
final exam of medical immunology
... C. An immunologically incompetent host. D. Patients receiving immunosuppressive drugs. 22. Which of the following cell types is not involve in antibody production… A. Cytotoxic T cells. C. Th2 cells. B. B cells. D. Macrophages. 23. On the B cell surface, receptors for antigen are associated with… A. ...
... C. An immunologically incompetent host. D. Patients receiving immunosuppressive drugs. 22. Which of the following cell types is not involve in antibody production… A. Cytotoxic T cells. C. Th2 cells. B. B cells. D. Macrophages. 23. On the B cell surface, receptors for antigen are associated with… A. ...
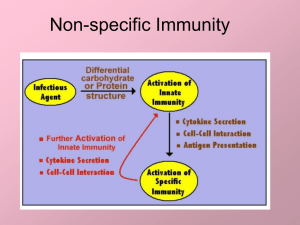
Non-specific Immunity
... • Inflammation works to allow both specific and non-specific immune response to accelerate • Fever also allows for better performance in both specific and non-specific function • Specific immune response and “antigen presentation” further stimulates non-specific ...
... • Inflammation works to allow both specific and non-specific immune response to accelerate • Fever also allows for better performance in both specific and non-specific function • Specific immune response and “antigen presentation” further stimulates non-specific ...
The_Specific_Immune_Response
... the body that is recognised as foreign. They may kill the invading organism itself, or they may kill body cells that have been infected with the organism. The cells literally line up, membrane to membrane, then the killer cell punches holes in the other cell’s membrane. It loses cytoplasm and dies. ...
... the body that is recognised as foreign. They may kill the invading organism itself, or they may kill body cells that have been infected with the organism. The cells literally line up, membrane to membrane, then the killer cell punches holes in the other cell’s membrane. It loses cytoplasm and dies. ...
T cell-mediated immune response
... Processing and presentation of antigen • Professional antigen-presenting cells: macrophages, dendritic cells, B lymphocytes (they express constitutionally class II MHC) a/ exogenous antigens – e.g. bacterial, parasitic, viral (if they are ingested in IC or during the processing of infected cells) - ...
... Processing and presentation of antigen • Professional antigen-presenting cells: macrophages, dendritic cells, B lymphocytes (they express constitutionally class II MHC) a/ exogenous antigens – e.g. bacterial, parasitic, viral (if they are ingested in IC or during the processing of infected cells) - ...
Vaccination and HIV
... A copy of the plasmid is transferred through conjugation. Resistance is quickly spread through many bacteria. ...
... A copy of the plasmid is transferred through conjugation. Resistance is quickly spread through many bacteria. ...
Human Blood Groups
... – One inherited from each parent – AA and A_ type A – BB and B_ type B – AB type AB – Neither type O ...
... – One inherited from each parent – AA and A_ type A – BB and B_ type B – AB type AB – Neither type O ...
canine autoimmune mediated disease `awareness guidelines`
... Addison’s Disease (Hypoadrenocorticism) This is an insufficient production of adrenal hormones by the adrenal gland. Since these hormones are essential for life, this is an extremely serious disease and must be treated as such. Initial symptoms can include stomach disturbances such as vomiting. Poor ...
... Addison’s Disease (Hypoadrenocorticism) This is an insufficient production of adrenal hormones by the adrenal gland. Since these hormones are essential for life, this is an extremely serious disease and must be treated as such. Initial symptoms can include stomach disturbances such as vomiting. Poor ...
INFECTIOUS BIOFE
... New Area of Focus: HIV/AIDS HIV=Human Immunodeficiency Virus The virus attacks the cells of our immune system. This makes the host susceptible to disease. Please record the ways in which you can be infected with HIV as a class. Unprotected sexual intercourse with an infected person. That i ...
... New Area of Focus: HIV/AIDS HIV=Human Immunodeficiency Virus The virus attacks the cells of our immune system. This makes the host susceptible to disease. Please record the ways in which you can be infected with HIV as a class. Unprotected sexual intercourse with an infected person. That i ...
Aids and HIV
... • T cells circulate in your body looking for cells that “don’t belong” • They will attack and destroy invading bacterial cells and cancer cells • When infected with HIV, the virus begins to reproduce within the T Cell (this destroys the T Cell) ...
... • T cells circulate in your body looking for cells that “don’t belong” • They will attack and destroy invading bacterial cells and cancer cells • When infected with HIV, the virus begins to reproduce within the T Cell (this destroys the T Cell) ...
Aids and HIV
... • T cells circulate in your body looking for cells that “don’t belong” • They will attack and destroy invading bacterial cells and cancer cells • When infected with HIV, the virus begins to reproduce within the T Cell (this destroys the T Cell) ...
... • T cells circulate in your body looking for cells that “don’t belong” • They will attack and destroy invading bacterial cells and cancer cells • When infected with HIV, the virus begins to reproduce within the T Cell (this destroys the T Cell) ...
document
... descendant of a B lymphocyte that is programmed to respond quickly to the same subsequent encounters with the same antigen ...
... descendant of a B lymphocyte that is programmed to respond quickly to the same subsequent encounters with the same antigen ...
Nrsg 407 Disorders of the Immune System
... • The initial exposure produces no symptoms but sets the stage for exposure, the antigen combines with IGE antibody already present on the surface of mast cells ...
... • The initial exposure produces no symptoms but sets the stage for exposure, the antigen combines with IGE antibody already present on the surface of mast cells ...
Lecture 21: Virus offence meets host defense
... • Highly conserved, arose early in evolution • Non-specific responses to stresses, e.g. – Starvation – Irradiation – Infection ...
... • Highly conserved, arose early in evolution • Non-specific responses to stresses, e.g. – Starvation – Irradiation – Infection ...
Document
... expression of MHC I and viral antigen presentation induces CD8 T cell killing of the infected cell or protection from NK cells if the cell is uninfected ...
... expression of MHC I and viral antigen presentation induces CD8 T cell killing of the infected cell or protection from NK cells if the cell is uninfected ...
Ch 43 Notes
... Cytotoxic T cells recognize fragments of foreign proteins produced by infected cells and possess an accessory protein that binds to class I MHC molecules ...
... Cytotoxic T cells recognize fragments of foreign proteins produced by infected cells and possess an accessory protein that binds to class I MHC molecules ...