Host Defenses Immune System Terminology White Blood Cells
... specific AG-MHC of the infecting microbe). • Memory T Cells which recognize the same AG-MHC but are not active. They circulate and reproduce but die off faster. So eventually, they become depleted. • Cytotoxic T cells which recognize the same antigen. 8a. Cytotoxic T cells bind to infected body cell ...
... specific AG-MHC of the infecting microbe). • Memory T Cells which recognize the same AG-MHC but are not active. They circulate and reproduce but die off faster. So eventually, they become depleted. • Cytotoxic T cells which recognize the same antigen. 8a. Cytotoxic T cells bind to infected body cell ...
Pathogenicity
... is caused by a variety of serotypes (most commonly S. enteritidis) and is transmitted from contaminated food (such as poultry and eggs). ...
... is caused by a variety of serotypes (most commonly S. enteritidis) and is transmitted from contaminated food (such as poultry and eggs). ...
Model of Wild Type (3A) Picornovirus Infection The Secretory
... Acute respiratory illnesses (colds), hepatitis, poliomyelitis, and livestock diseases are caused by members of the viral family Picornaviridae. The common cold is the most prevalent infectious disease in humans and results in major economic impact through loss of productivity and strain on healthcar ...
... Acute respiratory illnesses (colds), hepatitis, poliomyelitis, and livestock diseases are caused by members of the viral family Picornaviridae. The common cold is the most prevalent infectious disease in humans and results in major economic impact through loss of productivity and strain on healthcar ...
T cells - Cal State LA - Instructional Web Server
... the same antigen (memory), and the ability to discriminate self antigens from nonself antigens (tolerance) (Figure 22.8). ...
... the same antigen (memory), and the ability to discriminate self antigens from nonself antigens (tolerance) (Figure 22.8). ...
Lecture #19 Date ______
... • TC cell releases perforin, a protein that forms pores in the target cell membrane; cell lysis and pathogen exposure to circulating antibodies ...
... • TC cell releases perforin, a protein that forms pores in the target cell membrane; cell lysis and pathogen exposure to circulating antibodies ...
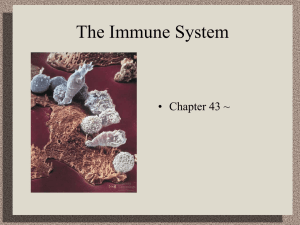
The Immune System
... • B cells produce antibodies that circulate in the blood and lymph streams and attach to foreign antigens to mark them for destruction by other immune cells. • B cells are part of what is known as antibody-mediated or humoral immunity ...
... • B cells produce antibodies that circulate in the blood and lymph streams and attach to foreign antigens to mark them for destruction by other immune cells. • B cells are part of what is known as antibody-mediated or humoral immunity ...
The Lymphatic and System and the Immune System
... system overreacts to the presence of an antigen such as pollen. 2. An autoimmune disease is one in which the immune system attacks its own body cells. Ex. M.S. and Arthritis 3. Rejection of organ transplants (cells are foreign). 4. Cancer cells are naturally destroyed by the body; however, when the ...
... system overreacts to the presence of an antigen such as pollen. 2. An autoimmune disease is one in which the immune system attacks its own body cells. Ex. M.S. and Arthritis 3. Rejection of organ transplants (cells are foreign). 4. Cancer cells are naturally destroyed by the body; however, when the ...
the body`s defenses
... The cells of the immune system can distinguish between different kinds of pathogens. The immune system cells react to each kind of pathogen with a defense targeted to that pathogen ...
... The cells of the immune system can distinguish between different kinds of pathogens. The immune system cells react to each kind of pathogen with a defense targeted to that pathogen ...
HOST and the MICROBE
... 4. Microbes has the ability to multiply upon reaching its specific niche (blood, lungs, tissues, etc) and the potential to be transmitted to a new susceptible host. - this determine the outcome of the events, either in the form of alteration of host physiology and tissue damage or death of the host ...
... 4. Microbes has the ability to multiply upon reaching its specific niche (blood, lungs, tissues, etc) and the potential to be transmitted to a new susceptible host. - this determine the outcome of the events, either in the form of alteration of host physiology and tissue damage or death of the host ...
Benlysta(belimumab)
... • is a systemic autoimmune disease (or autoimmune connective tissue disease) that can affect any part of the body. As occurs in other autoimmune diseases, the immune system attacks the body's cells and tissue, resulting in inflammation and tissue damage. It is a Type III hypersensitivity reaction ca ...
... • is a systemic autoimmune disease (or autoimmune connective tissue disease) that can affect any part of the body. As occurs in other autoimmune diseases, the immune system attacks the body's cells and tissue, resulting in inflammation and tissue damage. It is a Type III hypersensitivity reaction ca ...
09 Antibodies
... The ability of T cells to recognize antigen is dependent on association of the antigen with either class 1 or class II proteins. For example, cytotoxic T cells respond to antigen in association with class 1 MHC proteins. Thus, a cytotoxic Tcell that kills a virus-infected cell will not kill a cell i ...
... The ability of T cells to recognize antigen is dependent on association of the antigen with either class 1 or class II proteins. For example, cytotoxic T cells respond to antigen in association with class 1 MHC proteins. Thus, a cytotoxic Tcell that kills a virus-infected cell will not kill a cell i ...
18 Immune system part 1 - Nicole
... First Line of Defence Provides Physical and Chemical barriers: 1. Physical Barrier – hard to penetrate, made of ...
... First Line of Defence Provides Physical and Chemical barriers: 1. Physical Barrier – hard to penetrate, made of ...
35_Organ-specific autoimmune diseases
... MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS Pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis • CNS is a relatively immunologically privileged site from which antigens do not normally reach the lymphoid tissues. • In MS, an unknown injurious event is presumed to provoke the release of CNS antigens and their presentation to lymphocytes in ...
... MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS Pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis • CNS is a relatively immunologically privileged site from which antigens do not normally reach the lymphoid tissues. • In MS, an unknown injurious event is presumed to provoke the release of CNS antigens and their presentation to lymphocytes in ...
Chapter 1 – What is Microbiology and Why Does it Matter
... function during an infection. Both cell-mediated and chemical factors participate. The second type of defense is known as the adaptive immune response, which takes longer to become fully activated but also produces a form of immunological memory that will protect the host if re-infected by the same ...
... function during an infection. Both cell-mediated and chemical factors participate. The second type of defense is known as the adaptive immune response, which takes longer to become fully activated but also produces a form of immunological memory that will protect the host if re-infected by the same ...
Macronutrients
... • Build, keep up, and replace the tissues in your body. • Acts as hormones (sending messages around the body) • Antibodies (immune system – helps fight disease/infection) • Hemoglobin (responsible for delivering oxygen to your blood cells) • Signaling cells what to do and when to do it • Transportin ...
... • Build, keep up, and replace the tissues in your body. • Acts as hormones (sending messages around the body) • Antibodies (immune system – helps fight disease/infection) • Hemoglobin (responsible for delivering oxygen to your blood cells) • Signaling cells what to do and when to do it • Transportin ...
Document
... In plasma - activates complement Reacts with blood cells in transfusions B cell activation ...
... In plasma - activates complement Reacts with blood cells in transfusions B cell activation ...
File
... b. Active – antigen deliberately introduced into individ. to stimulate their immune system EX: VACCINATION * dead organism or live altered one (produces no symptoms) ...
... b. Active – antigen deliberately introduced into individ. to stimulate their immune system EX: VACCINATION * dead organism or live altered one (produces no symptoms) ...
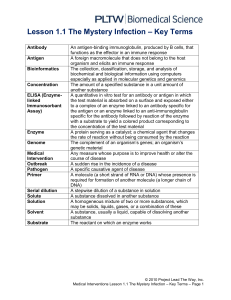
Ch. 43 The Immune System notes
... disruptions to dynamic homeostasis in biological systems. LO 2.29 The student can create representations and models to describe immune responses. LO 2.30 The student can create representations or models to describe nonspecific immune defenses in plants and animals. LO 2.34 The student is able to des ...
... disruptions to dynamic homeostasis in biological systems. LO 2.29 The student can create representations and models to describe immune responses. LO 2.30 The student can create representations or models to describe nonspecific immune defenses in plants and animals. LO 2.34 The student is able to des ...
Definition of Immunologic Terms
... o Antibody (or immunoglobulin): protein produced by B cells which binds antigen in an immune response. Monoclonal vs polyclonal refers to either a single antibody with a single specificity for antigen (monoclonal) vs a mixture of antibodies with different specificities for antigen (polyclonal). o An ...
... o Antibody (or immunoglobulin): protein produced by B cells which binds antigen in an immune response. Monoclonal vs polyclonal refers to either a single antibody with a single specificity for antigen (monoclonal) vs a mixture of antibodies with different specificities for antigen (polyclonal). o An ...