* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
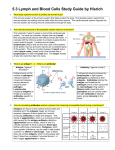
WARM UP NOTES CH 29 Lymphatic System and Immunity Intro PARTS: Lymph, lymphocytes, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils FUNCTIONS: 1. FLUID BALANCE 2. FAT ABSORPTION 3. DEFENSE ** * filter microorganisms in lymph nodes and spleen * destroy micro. in tissues LYMPHOCYTES Cells that destroy microbes LYMPH • Clear fluid that is in tissues after leaving the blood • Made of ions, water, nutrients, gases, hormones, wastes • Circulates through lymph vessels and into nearest lymph node LYMPH NODE About small seed to almond size Lymph passes through here before returning to blood 1. Stimulates lymphocytes to divide and go into bloodstream 2. Destroy microorganism there 3 main places of nodes 1. INGUINAL 2. AXILLARY 3. CERVICAL TONSILS • Areas in the mouth that collect and destroy microbes 1. Palantine – sides 2. Adenoid – back top of throat 3. Lingual – back of tongue SPLEEN • Size of fist, let upper side FUNCTION: 1. Filters blood – cells detect microbes or old rbc in blood and destroy 2. Stores extra blood for emergencies 3. Makes lymphocytes THYMUS • Lower neck area ( after 60 decrease in size) FUNCTION: 1. Produce lymphocytes NOTES Ch 29 Immunity IMMUNE SYSTEM PARTS: white blood cells, antibodies FUNCTION: to destroy microbes in tissues and protect body from disease LEUKOCYTES – white blood cells Leave the blood vessels and go into infected area to destroy microbe TYPES: 1. neutrophils 2. macrophages 3. lymphocytes NEUTROPHILS • 1st to enter infected area • Die after killing a microbe • Phagocytosis – engulfing the microbe or cell to destroy it PUS – fluid, dead neutrophils, bacteria, dead cells MACROPHAGE • 2nd to enter an infected area • Can digest more and live longer • Can wait in uninfected tissue B CELLS • Secrete antibodies T CELLS IMMUNITY Ability to resist damage from foreign substances ANTIGEN ANTIBODY Foreign substance in the body Protein that destroys a specific antigen EX: virus, bacteria, allergen (pollen, animal hair, foods, etc.) 2 TYPES 1. INNATE 2. ADAPTIVE Body born with ability to recognize and destroy foreign molecules Body learns to recognize and destroy (each time exposed, destroy better) INNATE Protections such as Skin, mucus, tears, saliva Chemicals: Histamine, lysozyme, prostoglandins, leukotrienes These promote inflammation and cause white blood cells to rush there 2 TYPES OF ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY 1. NATURAL a. Passive – mother to child (umbilical cord or milk) b. Active – natural exposure (exposed to a virus, etc.) 2. ARTIFICIAL a. Passive – antibodies placed into person (from another organism) * won’t last long (antiserum is an example) b. Active – antigen deliberately introduced into individ. to stimulate their immune system EX: VACCINATION * dead organism or live altered one (produces no symptoms) 2 main types of vaccinations DTP MMR Diptheria Tetanus Pertussis (whooping cough) Mumps Measles Rubella HOW IMMUNITY WORKS Every cell has surface marker on the cell membrane. When body does not recognize these markers, it will respond to it. THE RESPONSE: • B cell exposed to antigen • Binds to it • B cell starts to divide to form 1) memory B cells 2) plasma cells PLASMA CELLS MEMORY B CELLS • Produce antibodies – takes 3-14 days to make enough to destroy it • When exposed to antigen already in the body, these divide and from plasma cells which make the antibodies fast • No time for symptoms to develop • Antigen can cause symptoms in the meantime