Orientation to the Human Body
... Protects and supports body organs; provides a framework the muscles use to cause movement; blood cells are formed within bones; stores minerals. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Protects and supports body organs; provides a framework the muscles use to cause movement; blood cells are formed within bones; stores minerals. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
General Anatomy Handout
... pelvis seen from above lumbar vertebra hipbone ischial spine pubococcygeus m: rectus pubic crest genital hiatus puborectalis m. tendinous arch of pelvic iascia iliococcygeus m. coccygeus m. ...
... pelvis seen from above lumbar vertebra hipbone ischial spine pubococcygeus m: rectus pubic crest genital hiatus puborectalis m. tendinous arch of pelvic iascia iliococcygeus m. coccygeus m. ...
Sponges
... • Other sponges have a material called spongin which is similar to foam rubber and makes them soft and flexible • Some have both ...
... • Other sponges have a material called spongin which is similar to foam rubber and makes them soft and flexible • Some have both ...
Anatomy
... Nonetheless, in most species it is divided into right and left lobes; exceptions to this general rule include snakes, where the shape of the body necessitates a simple cigar-like form. The internal structure of the liver is broadly similar in all vertebrates.[7] An organ sometimes referred to as a l ...
... Nonetheless, in most species it is divided into right and left lobes; exceptions to this general rule include snakes, where the shape of the body necessitates a simple cigar-like form. The internal structure of the liver is broadly similar in all vertebrates.[7] An organ sometimes referred to as a l ...
Arterial Supply of the Guinea Pig Mandible
... temploralis muscle, attaching to the coronoid processes, has vessels that follow along this muscle to its mandibular insertion to supply the coronoid process. Passing very close to the condyle and coronoid process is the maxillary artery, and branches either directly from it or those destined for ot ...
... temploralis muscle, attaching to the coronoid processes, has vessels that follow along this muscle to its mandibular insertion to supply the coronoid process. Passing very close to the condyle and coronoid process is the maxillary artery, and branches either directly from it or those destined for ot ...
Shoulder
... “Hooklike Projection” arises anteriorly from the scapula. Curves upward, forward, and outward in front of the glenoid fossa ...
... “Hooklike Projection” arises anteriorly from the scapula. Curves upward, forward, and outward in front of the glenoid fossa ...
The Muscular System Terms
... extension of the thigh Soleus - muscle in the calf of the leg, behind the gastrocnemius muscle, that helps extend the foot forward Achilles Tendon - tendon joining the calf muscles to the heel bone Frontalis - frontal belly is muscle which covers parts of the skull Trapezius - flat muscle on each si ...
... extension of the thigh Soleus - muscle in the calf of the leg, behind the gastrocnemius muscle, that helps extend the foot forward Achilles Tendon - tendon joining the calf muscles to the heel bone Frontalis - frontal belly is muscle which covers parts of the skull Trapezius - flat muscle on each si ...
Anatomy of neck + innervation of structures. Anatomy (gross
... Anatomy of neck + innervation of structures. Anatomy (gross and histological) and physiology of the lymphoid system, and of the head and neck –light, clinically relevant summary - DAN From now I will pay more attention when we formulate FQs because this one sucked ...
... Anatomy of neck + innervation of structures. Anatomy (gross and histological) and physiology of the lymphoid system, and of the head and neck –light, clinically relevant summary - DAN From now I will pay more attention when we formulate FQs because this one sucked ...
Chapter 24 - Bellbrook
... and a series of cell divisions to form new cells. After the first cell division, in which the zygote forms two cells, the developing animal is called an embryo. The embryo continues to undergo mitosis and cell division, forming a solid ball of cells. These cells continue to divide, forming a fluid-f ...
... and a series of cell divisions to form new cells. After the first cell division, in which the zygote forms two cells, the developing animal is called an embryo. The embryo continues to undergo mitosis and cell division, forming a solid ball of cells. These cells continue to divide, forming a fluid-f ...
Multiple inflammatory arthropathies can affect the TMJ
... avascular fibrocartilaginous structure with three segments: ...
... avascular fibrocartilaginous structure with three segments: ...
Anatomical Studies with Clinical Importance of Unusual
... The muscles must be split in the direction of their fibres, rather than cut across. The incisions must not divide nerves. The rectus muscles may be cut transversely without seriously weakening the abdominal wall, as such a cut passes between two adjacent nerves without injuring them. The rectus has ...
... The muscles must be split in the direction of their fibres, rather than cut across. The incisions must not divide nerves. The rectus muscles may be cut transversely without seriously weakening the abdominal wall, as such a cut passes between two adjacent nerves without injuring them. The rectus has ...
Topic 1 The Chordata
... Pharyngeal slits occur in aquatic chordates and lead from the pharyngeal cavity to the outside. ...
... Pharyngeal slits occur in aquatic chordates and lead from the pharyngeal cavity to the outside. ...
Sacrotuberous Ligament Sprains Sacrotuberous
... 4. A side-lying position puts the sacrotuberous ligament on the stretch so it is easily treated. True or False? 5. The sacrotuberous ligament is in part attached to the coccyx. True or False? ...
... 4. A side-lying position puts the sacrotuberous ligament on the stretch so it is easily treated. True or False? 5. The sacrotuberous ligament is in part attached to the coccyx. True or False? ...
TEST-Chapter 38 Arthropods
... Circle the letter for the answer that BEST completes the statement or answers the question. All arthropods have a(n)__________________________. A. acoelom B. pseudocoelom C. eucoelom D. none of these; they don’t need a coelom with an exoskeleton Arthropods are __________________________________ A. i ...
... Circle the letter for the answer that BEST completes the statement or answers the question. All arthropods have a(n)__________________________. A. acoelom B. pseudocoelom C. eucoelom D. none of these; they don’t need a coelom with an exoskeleton Arthropods are __________________________________ A. i ...
Anatomy 2
... 19. Which action is not affected by damage to nerve III? a. Raising eyelid. b. Lowering eyelid. c. Inability to move eye laterally. d. Dilated pupil. 20. Which of the following most characterizes the orbital septum? a. It has a lateral and medial ligament to hold onto bones. b. It is an important ph ...
... 19. Which action is not affected by damage to nerve III? a. Raising eyelid. b. Lowering eyelid. c. Inability to move eye laterally. d. Dilated pupil. 20. Which of the following most characterizes the orbital septum? a. It has a lateral and medial ligament to hold onto bones. b. It is an important ph ...
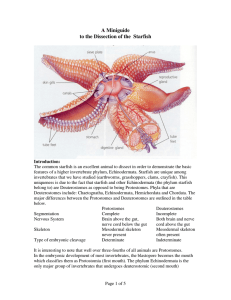
A Miniguide to the Dissection of the Starfish
... processes, dermal branchiae. These thin-walled structures are the major surface in contact with the aquatic environment, and they therefore function in respiration. In addition, small jaw-like pincers, or pedicellariae, rise from the surface for use in food handling and for protection against small ...
... processes, dermal branchiae. These thin-walled structures are the major surface in contact with the aquatic environment, and they therefore function in respiration. In addition, small jaw-like pincers, or pedicellariae, rise from the surface for use in food handling and for protection against small ...
File
... Initially, these canals, the pleural (pericardioperitoneal) canals, represent the spaces into which the developing lungs grow. The pleural canals enlarge greatly as the lungs increase in size and ultimately form the pleural cavities. The pleural canals are partially bounded by two paired folds of ti ...
... Initially, these canals, the pleural (pericardioperitoneal) canals, represent the spaces into which the developing lungs grow. The pleural canals enlarge greatly as the lungs increase in size and ultimately form the pleural cavities. The pleural canals are partially bounded by two paired folds of ti ...
Ca Ba V - VCOMcc
... Sclerotomal cells (paraxial mesoderm) migrate medially and surround the nucleus pulposus to form the Annulus fibrosus (AF) ...
... Sclerotomal cells (paraxial mesoderm) migrate medially and surround the nucleus pulposus to form the Annulus fibrosus (AF) ...
respiratory system
... • Pleura – separates each lung from the thoracic wall. • Pleura which surround each lung has two layers – Visceral Pleura [inner layer] which surrounds the lung and Parietal Pleura [outer layer] which is under thorax. • Interior of pleural sac(space between parietal and visceral pleura) is known as ...
... • Pleura – separates each lung from the thoracic wall. • Pleura which surround each lung has two layers – Visceral Pleura [inner layer] which surrounds the lung and Parietal Pleura [outer layer] which is under thorax. • Interior of pleural sac(space between parietal and visceral pleura) is known as ...
four heads of sternocleidomastoid: a case report
... sternal head. Usually the clavicular origin is narrower than the sternal head .When the clavicular origin is broad; it is subdivided into several slips separated by narrow intervals. Embryology of developing human is a valuable asset in understanding anatomic variations. The sternocleidomastoid and ...
... sternal head. Usually the clavicular origin is narrower than the sternal head .When the clavicular origin is broad; it is subdivided into several slips separated by narrow intervals. Embryology of developing human is a valuable asset in understanding anatomic variations. The sternocleidomastoid and ...
The trigeminal nerve Ophthalmic division Maxillary division
... It divides into the following branches 1. Frontal nerve – goes through the top of the orbit and divides into the supra orbital and supra trochlea nerves. Both supply the skin of the forehead and the frontal sinus. 2. Lachrymal nerve – passes further laterally through the orbit – it supplies the skin ...
... It divides into the following branches 1. Frontal nerve – goes through the top of the orbit and divides into the supra orbital and supra trochlea nerves. Both supply the skin of the forehead and the frontal sinus. 2. Lachrymal nerve – passes further laterally through the orbit – it supplies the skin ...
REVERSE MYO FASCIAL PECTORALIS MAJOR FLAP IN CHEST
... attachments of the external oblique muscle.The pectoralis major flap is an axial flap and is based primarily on the pectoral branch of the thoracoacromial artery and its accompanying veins. The thoracoacromial artery is a branch of the axillary artery, itself a continuation of the subclavian artery. ...
... attachments of the external oblique muscle.The pectoralis major flap is an axial flap and is based primarily on the pectoral branch of the thoracoacromial artery and its accompanying veins. The thoracoacromial artery is a branch of the axillary artery, itself a continuation of the subclavian artery. ...
SESSION 11 - Posterior Mediastinum, Diaphragm, Thoracic Wall
... 35. The intercostal neurovascular bundle can be damaged during cannulation of the pleural cavity. The bundle lies (a) Outside the external intercostal (b) Between the external and internal intercostal (c) Between the internal intercostal and the innermost intercostals (d) Just inside the innermost i ...
... 35. The intercostal neurovascular bundle can be damaged during cannulation of the pleural cavity. The bundle lies (a) Outside the external intercostal (b) Between the external and internal intercostal (c) Between the internal intercostal and the innermost intercostals (d) Just inside the innermost i ...
Normal Anatomy and Imaging Stations
... Celiac axis Celiac axis The celiac axis is usually best scanned from just inside the GE junction, where it can be identified as it arises anteriorly from the aorta. It bifurcates into hepatic and splenic artery, an appearance often described as the "whale’s tail". It is important to scan carefully ...
... Celiac axis Celiac axis The celiac axis is usually best scanned from just inside the GE junction, where it can be identified as it arises anteriorly from the aorta. It bifurcates into hepatic and splenic artery, an appearance often described as the "whale’s tail". It is important to scan carefully ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.