Preview - Quintessence Publishing!
... There are a number of excellent anatomical atlases and textbooks available to dental clinicians, but often these atlases fail to meet the clinical demands of defining intraoperative structures for oral implantologists because of the overwhelmingly detailed minutia. The aim of this book is to present ...
... There are a number of excellent anatomical atlases and textbooks available to dental clinicians, but often these atlases fail to meet the clinical demands of defining intraoperative structures for oral implantologists because of the overwhelmingly detailed minutia. The aim of this book is to present ...
Squid Dissection Addendum - Long Beach Marine Institute
... 2. bodies covered with a tissue layer called the mantle 3. well developed, segmented heart 4. use radula to scrape and manipulate food (those that are not filter feeders such as clams) Cephalopods are said to be the most advanced molluscs because they have well-developed brains and eyes. Their heads ...
... 2. bodies covered with a tissue layer called the mantle 3. well developed, segmented heart 4. use radula to scrape and manipulate food (those that are not filter feeders such as clams) Cephalopods are said to be the most advanced molluscs because they have well-developed brains and eyes. Their heads ...
Practice Anatomy Questions – Semester 2
... 23 - Which posterior abdominal wall muscle is NOT present in everyone? a) psoas major b) psoas minor c) quadratus lumborum d) iliacus 24 - Which statement is incorrect a) Psoas major attachs intervertebral disks t12 -> l5 superiorly b) The inferior tendon of psoas called the iliopsoas tendon c) Psoa ...
... 23 - Which posterior abdominal wall muscle is NOT present in everyone? a) psoas major b) psoas minor c) quadratus lumborum d) iliacus 24 - Which statement is incorrect a) Psoas major attachs intervertebral disks t12 -> l5 superiorly b) The inferior tendon of psoas called the iliopsoas tendon c) Psoa ...
Slide 1
... Origin: Posterior aspect of pubic bone, fascia of pelvic side wall, ischial spine Insertion: Perineal body, anal sphincter, coccyx Constitute pelvic diaphragm Surfaces covered by fascia ...
... Origin: Posterior aspect of pubic bone, fascia of pelvic side wall, ischial spine Insertion: Perineal body, anal sphincter, coccyx Constitute pelvic diaphragm Surfaces covered by fascia ...
Your Body`s Systems
... work together. Groups of similar cells that have a common function form a tissue. Tissue cells are often stuck together with fibres or other sticky material. Groups of tissues having a common function are organized into organs. Many organs are made up of several different types of tissues. Some exam ...
... work together. Groups of similar cells that have a common function form a tissue. Tissue cells are often stuck together with fibres or other sticky material. Groups of tissues having a common function are organized into organs. Many organs are made up of several different types of tissues. Some exam ...
ARP11handout1.
... endometrium is the layer of mucous membrane while the mesometrium is made of circular and longitudinal muscle. In cow, the uterus is cornuate in shape with two horns. The body of the uterus is about 2.5-5 cm in length; 1.25-5cm in diameter while the horms measure about 2-040 cm in length. The horns ...
... endometrium is the layer of mucous membrane while the mesometrium is made of circular and longitudinal muscle. In cow, the uterus is cornuate in shape with two horns. The body of the uterus is about 2.5-5 cm in length; 1.25-5cm in diameter while the horms measure about 2-040 cm in length. The horns ...
An unusual variation in the anatomy of the uncinate
... part of the lacrimal fossa. The uncinate process was adjacent to the maxillary bone [i.e. further forward on the lacrimal fossa] (55.8% cases) at the middle and adjacent to the middle turbinate (61%) at the upper levels of the lacrimal fossa. Hence in many cases of endonasal DCR it is necessary to p ...
... part of the lacrimal fossa. The uncinate process was adjacent to the maxillary bone [i.e. further forward on the lacrimal fossa] (55.8% cases) at the middle and adjacent to the middle turbinate (61%) at the upper levels of the lacrimal fossa. Hence in many cases of endonasal DCR it is necessary to p ...
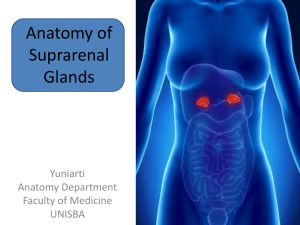
Location of Suprarenal Glands
... axillary and pubic hair in boys and girls and contribute to the prepubertal growth spurt. ...
... axillary and pubic hair in boys and girls and contribute to the prepubertal growth spurt. ...
Lesson Overview - Mater Academy of International Studies
... dioxide as a waste product. For that reason, all animals must obtain oxygen from their environment and release carbon dioxide. Humans can drown because our lungs can’t extract the oxygen we need from water. Most fishes have the opposite problem; out of water, their ...
... dioxide as a waste product. For that reason, all animals must obtain oxygen from their environment and release carbon dioxide. Humans can drown because our lungs can’t extract the oxygen we need from water. Most fishes have the opposite problem; out of water, their ...
chapter
... one side of the body faces up (dorsal) and the other side, specialized for locomotion, faces down (ventral). What results is a bilaterally symmetrical animal in which the body could be divided along only one plane of symmetry to yield two halves that are mirror images of each other. Furthermore, bec ...
... one side of the body faces up (dorsal) and the other side, specialized for locomotion, faces down (ventral). What results is a bilaterally symmetrical animal in which the body could be divided along only one plane of symmetry to yield two halves that are mirror images of each other. Furthermore, bec ...
Name: Date: ______ Period: ______ 2015-16
... reproductive rate, and ease of maintenance. Rats typically begin to breed at 3 months of age and can produce a litter of about 8 young every 21-25 days. The average lab rat’s lifespan is about 36 months, whereas rats in the wild typically live about 12-18 months. Rats and humans belong to Kingdom An ...
... reproductive rate, and ease of maintenance. Rats typically begin to breed at 3 months of age and can produce a litter of about 8 young every 21-25 days. The average lab rat’s lifespan is about 36 months, whereas rats in the wild typically live about 12-18 months. Rats and humans belong to Kingdom An ...
Shoulder Joint
... The shoulder joint has a wide range of movements, and this on the expense of the stability of the joint. The inferior part of the capsule is the weakest area. The shoulder joint is the most commonly dislocated large joint in the body. The strength of the joint depends mainly on the tone of the ...
... The shoulder joint has a wide range of movements, and this on the expense of the stability of the joint. The inferior part of the capsule is the weakest area. The shoulder joint is the most commonly dislocated large joint in the body. The strength of the joint depends mainly on the tone of the ...
A case with subclavius posticus muscle
... differed. They proposed that both muscles are derived from the intermediate region between the subclavius muscle and the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle, and could be innervated by the nerve to the subclavius muscle or by the branch to the omohyoid muscle arising from the ansa cervicalis. It i ...
... differed. They proposed that both muscles are derived from the intermediate region between the subclavius muscle and the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle, and could be innervated by the nerve to the subclavius muscle or by the branch to the omohyoid muscle arising from the ansa cervicalis. It i ...
A case with subclavius posticus muscle
... differed. They proposed that both muscles are derived from the intermediate region between the subclavius muscle and the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle, and could be innervated by the nerve to the subclavius muscle or by the branch to the omohyoid muscle arising from the ansa cervicalis. It i ...
... differed. They proposed that both muscles are derived from the intermediate region between the subclavius muscle and the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle, and could be innervated by the nerve to the subclavius muscle or by the branch to the omohyoid muscle arising from the ansa cervicalis. It i ...
Upper Cross System Head Injuries & Neck Injuries
... • MUST SEND TO EMERGENCY IF: – Blood out of ears &/or nose (from blow to head) – Any unconscious episode – Symptoms increase during 20 minute waiting period or when activity resumes ...
... • MUST SEND TO EMERGENCY IF: – Blood out of ears &/or nose (from blow to head) – Any unconscious episode – Symptoms increase during 20 minute waiting period or when activity resumes ...
Chapter 4
... • _____________Fat Pad – Generally ______________radiograph – Deep within olecranon fossa ...
... • _____________Fat Pad – Generally ______________radiograph – Deep within olecranon fossa ...
exam 2
... answer more than 50 questions, then you will be graded on only the first 50 of these, regardless of whether the extra questions are answered correctly. Choose any 50 questions on the basis of your knowledge of the material. A good strategy is to first attempt to answer all 60 questions, but spend no ...
... answer more than 50 questions, then you will be graded on only the first 50 of these, regardless of whether the extra questions are answered correctly. Choose any 50 questions on the basis of your knowledge of the material. A good strategy is to first attempt to answer all 60 questions, but spend no ...
Preview Sample 1
... I. Mapping the Human Body A. Body positions 1. To standardize the orientation for the study of anatomy, the anatomical position was developed: stand erect, face forward, feet apart, arms at side, palms forward 2. Supine: faceup 3. Prone: facedown 4. Trendelenburg: head lower than feet 5. Fowler’s: s ...
... I. Mapping the Human Body A. Body positions 1. To standardize the orientation for the study of anatomy, the anatomical position was developed: stand erect, face forward, feet apart, arms at side, palms forward 2. Supine: faceup 3. Prone: facedown 4. Trendelenburg: head lower than feet 5. Fowler’s: s ...
The Skeletal System
... SPPA 2050 Speech Anatomy and Physiology The Skeletal System For some, things do not get much drier than skeletal anatomy. The main skeletal components of the body are skull, mandible and hyoid bone, the vertebral column, the ribcage, the pelvic girdle, pectoral girdle, upper limb and lower limb. You ...
... SPPA 2050 Speech Anatomy and Physiology The Skeletal System For some, things do not get much drier than skeletal anatomy. The main skeletal components of the body are skull, mandible and hyoid bone, the vertebral column, the ribcage, the pelvic girdle, pectoral girdle, upper limb and lower limb. You ...
Frog Dissection
... STOP! If you have not located each of the organs above, do not continue on to the next sections! You will each be completing a formal biological drawing of the internal anatomy of the frog with emphasis on the digestive and circulatory organs. Make some sketches and take pictures before moving on. R ...
... STOP! If you have not located each of the organs above, do not continue on to the next sections! You will each be completing a formal biological drawing of the internal anatomy of the frog with emphasis on the digestive and circulatory organs. Make some sketches and take pictures before moving on. R ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.