Lobsters - csnmarsci
... •The part of the exoskeleton that covers the head and chest regions is called the carapace. •Lobsters have five pairs of legs located under their carapace. •Therefore, they are referred to as the decapods (meaning “ten legs”) •The claws are the first pair of legs; the other four pairs are the walkin ...
... •The part of the exoskeleton that covers the head and chest regions is called the carapace. •Lobsters have five pairs of legs located under their carapace. •Therefore, they are referred to as the decapods (meaning “ten legs”) •The claws are the first pair of legs; the other four pairs are the walkin ...
Invertebrate Zoology Laboratory Exercises
... prostomium and pygidium are derived from anterior and posterior ends of the larva whereas the intervening segments arise through mitotic activity of mesodermal cells in the pygidium. The body wall consists of a collagenous cuticle secreted by the monolayered epidermis. A connective tissue dermis lie ...
... prostomium and pygidium are derived from anterior and posterior ends of the larva whereas the intervening segments arise through mitotic activity of mesodermal cells in the pygidium. The body wall consists of a collagenous cuticle secreted by the monolayered epidermis. A connective tissue dermis lie ...
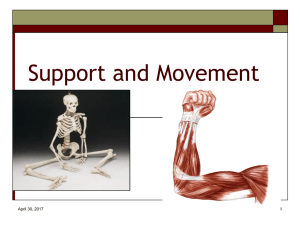
Support and Movement
... bones, encompasses all your upper body bones. It is subdivided into three groups: the skull, the vertebral column, and the bony thorax. ...
... bones, encompasses all your upper body bones. It is subdivided into three groups: the skull, the vertebral column, and the bony thorax. ...
Crayfish Lab - c214science
... TAGMATA). The body of a crayfish is divided into 2 major sections: the CEPHALOTHORAX and ABDOMEN. An example of a TAGMA is the CEPHALOTHORAX in a crayfish. The head and middle body sections (thorax) are joined together to make one piece. You can see the fused dividing line between them. This coverin ...
... TAGMATA). The body of a crayfish is divided into 2 major sections: the CEPHALOTHORAX and ABDOMEN. An example of a TAGMA is the CEPHALOTHORAX in a crayfish. The head and middle body sections (thorax) are joined together to make one piece. You can see the fused dividing line between them. This coverin ...
HO#3 - Teachers TryScience
... TAGMATA). The body of a crayfish is divided into 2 major sections: the CEPHALOTHORAX and ABDOMEN. An example of a TAGMA is the CEPHALOTHORAX in a crayfish. The head and middle body sections (thorax) are joined together to make one piece. You can see the fused dividing line between them. This coverin ...
... TAGMATA). The body of a crayfish is divided into 2 major sections: the CEPHALOTHORAX and ABDOMEN. An example of a TAGMA is the CEPHALOTHORAX in a crayfish. The head and middle body sections (thorax) are joined together to make one piece. You can see the fused dividing line between them. This coverin ...
L05 and L06 - Superficial Back Muscles and Posterior Shoulder with
... – Deep muscles: intrinsic and move the head and the trunk, acting on the spine as principle extensors in lateral flexion and rotation spanning from the pelvis to the skull base Epaxial differentiation Innervated by dorsal sensory root which split into dorsal rami – Movements rarely involve a sin ...
... – Deep muscles: intrinsic and move the head and the trunk, acting on the spine as principle extensors in lateral flexion and rotation spanning from the pelvis to the skull base Epaxial differentiation Innervated by dorsal sensory root which split into dorsal rami – Movements rarely involve a sin ...
Mollusks Worms Arthropods, Echinoderms 1ote
... A. Mollusks—soft-bodied invertebrates with bilateral symmetry and usually one or two shells with organs in a fluid-filled cavity 1. Thin layer of tissue called the mantle covers the body organs and secretes shell. 2. Mantle cavity (between soft body and mantle) contains giiI. 3. For most mollusks, a ...
... A. Mollusks—soft-bodied invertebrates with bilateral symmetry and usually one or two shells with organs in a fluid-filled cavity 1. Thin layer of tissue called the mantle covers the body organs and secretes shell. 2. Mantle cavity (between soft body and mantle) contains giiI. 3. For most mollusks, a ...
Entrapment of the Median Nerves and Brachial Arteries
... SUMMARY: Neuro-vascular entrapments associated with variations observed in the origins of muscles in the arm are not uncommon. Though additional heads of biceps brachii muscle and extra fibres of brachialis muscles have been demonstrated earlier, bilateral additional heads of the biceps are rarely s ...
... SUMMARY: Neuro-vascular entrapments associated with variations observed in the origins of muscles in the arm are not uncommon. Though additional heads of biceps brachii muscle and extra fibres of brachialis muscles have been demonstrated earlier, bilateral additional heads of the biceps are rarely s ...
CHAPTER 8
... Chapter 8 is going to tell us about our vessel selection options. Chapter 9 is closely related in that we will learn the process in selecting the vessels we will be using. So learn chapter 8 well. ...
... Chapter 8 is going to tell us about our vessel selection options. Chapter 9 is closely related in that we will learn the process in selecting the vessels we will be using. So learn chapter 8 well. ...
Gluteal Region, Posterior Thigh and Popliteal Fossa
... What might happen to a person who has this variation and hypertrophies his/her piriformis because of repeated lateral rotation? Say, for example, from playing a lot of racketball. ...
... What might happen to a person who has this variation and hypertrophies his/her piriformis because of repeated lateral rotation? Say, for example, from playing a lot of racketball. ...
tissues
... functions an organism performs • The comparative study of animals reveals that form and function are closely correlated ...
... functions an organism performs • The comparative study of animals reveals that form and function are closely correlated ...
glands
... lymphatics drained by submandibular lymph nodes blood supply by branches of the facial and lingual arteries submandibular or Wharton’s duct duct has a very tortuous path over the anterior floor of the mouth ...
... lymphatics drained by submandibular lymph nodes blood supply by branches of the facial and lingual arteries submandibular or Wharton’s duct duct has a very tortuous path over the anterior floor of the mouth ...
Lecture 10: OMT for GI Disorders and Post
... Primary sympathetic fibers for innervation of all organs below the diaphragm (except descending colon and pelvic organs) pass from cells in the thoracic spinal cord *through the thoracoabdominal diaphragm* Descending colon receives sympathetics from lumbar splanchnic nerves via inferior mesenter ...
... Primary sympathetic fibers for innervation of all organs below the diaphragm (except descending colon and pelvic organs) pass from cells in the thoracic spinal cord *through the thoracoabdominal diaphragm* Descending colon receives sympathetics from lumbar splanchnic nerves via inferior mesenter ...
1 - Unit 3 Upper Limb Objectives
... 1. Identify and describe the boundaries and contents of the cubital fossa. How can this information assist in competent venipuncture in this region? 2. Identify the vascular structures that cross the roof of the cubital fossa. How could an aberrant superficial ulnar artery in this region complicate ...
... 1. Identify and describe the boundaries and contents of the cubital fossa. How can this information assist in competent venipuncture in this region? 2. Identify the vascular structures that cross the roof of the cubital fossa. How could an aberrant superficial ulnar artery in this region complicate ...
Introduction Shoulder girdle is a complex structure
... Scapula is a triangular flat bone that lies on the posterior – lateral surface of the thorax between second and seventh rib. It is important to remember that it is not parallel to frontal plane. The scapular body forms 30–45 degree angle with frontal plane. Anatomically it has three borders – medial ...
... Scapula is a triangular flat bone that lies on the posterior – lateral surface of the thorax between second and seventh rib. It is important to remember that it is not parallel to frontal plane. The scapular body forms 30–45 degree angle with frontal plane. Anatomically it has three borders – medial ...
the neurovascular compression due to the third head of biceps
... in situ, opposite the lower six cervical and upper two thoracic segments, from the limb bud mesenchyme of the lateral plate mesoderm. The formation of muscular elements in the limbs takes place shortly after the skeletal elements begin to take shape. At a certain stage of development, the muscle pri ...
... in situ, opposite the lower six cervical and upper two thoracic segments, from the limb bud mesenchyme of the lateral plate mesoderm. The formation of muscular elements in the limbs takes place shortly after the skeletal elements begin to take shape. At a certain stage of development, the muscle pri ...
Unit 17.2: Overview of Invertebrates
... beetle in Figure above. With concentrated nerve tissue at the head but not at the tail end, the two ends of the body are distinct from each other. The animal can be divided down the middle to form identical right and left halves. It allows the animal to tell front from back and left from right. This ...
... beetle in Figure above. With concentrated nerve tissue at the head but not at the tail end, the two ends of the body are distinct from each other. The animal can be divided down the middle to form identical right and left halves. It allows the animal to tell front from back and left from right. This ...
40_lecture_presentation
... • Organisms exchange heat by four physical processes: conduction, convection, radiation, and evaporation. ...
... • Organisms exchange heat by four physical processes: conduction, convection, radiation, and evaporation. ...
Chapter. 40(Animal Form and Function)
... • Organisms exchange heat by four physical processes: conduction, convection, radiation, and evaporation. ...
... • Organisms exchange heat by four physical processes: conduction, convection, radiation, and evaporation. ...
chapter 4 lecture with my notes
... through the mitotic division of underlying stem cells. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... through the mitotic division of underlying stem cells. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
QUESTION
... • Injury to the common bile duct during laparoscopic cholecystectomy is most likely to occur as a result of ...
... • Injury to the common bile duct during laparoscopic cholecystectomy is most likely to occur as a result of ...
English
... The sternocleidomastoid muscle is a muscle that divides the side of the neck into anterior and posterior triangles. It is an important surgical landmark as it is related to many neurovascular structures in the neck. It originates from two heads. The sternal head is rounded and tendinous. It originat ...
... The sternocleidomastoid muscle is a muscle that divides the side of the neck into anterior and posterior triangles. It is an important surgical landmark as it is related to many neurovascular structures in the neck. It originates from two heads. The sternal head is rounded and tendinous. It originat ...
23. Chordates
... Pharyngeal Pouches and Slits Pharyngeal slits are openings that lead from the pharyngeal cavity to the outside. They are formed when pharyngeal grooves and pharyngeal pouches meet to form an opening. In tetrapods, the pharyngeal pouches give rise to the Eustachian tube, middle ear cavity, tonsi ...
... Pharyngeal Pouches and Slits Pharyngeal slits are openings that lead from the pharyngeal cavity to the outside. They are formed when pharyngeal grooves and pharyngeal pouches meet to form an opening. In tetrapods, the pharyngeal pouches give rise to the Eustachian tube, middle ear cavity, tonsi ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.