ANATOMY – Cranial Nerves
... Type of nerve fibers which originate from the solitary tract nucleus. Salivary gland which receives parasympathetic innervation from the glossopharyngeal nerve. One of the two muscles innervated by the accessory cranial nerve. Type of hemianopia seen with a large space occupying lesion in the sella ...
... Type of nerve fibers which originate from the solitary tract nucleus. Salivary gland which receives parasympathetic innervation from the glossopharyngeal nerve. One of the two muscles innervated by the accessory cranial nerve. Type of hemianopia seen with a large space occupying lesion in the sella ...
Female Reproductive System
... multiple rows are engendered. This is now called the stratum granulosum. In the secondary follicles a glycoprotein layer, the pellucid zone, between the oocyte and follicular epithelium becomes visible. Cytoplasmic processes of the granulosa cells that lie upon it reach the oocyte through the pelluc ...
... multiple rows are engendered. This is now called the stratum granulosum. In the secondary follicles a glycoprotein layer, the pellucid zone, between the oocyte and follicular epithelium becomes visible. Cytoplasmic processes of the granulosa cells that lie upon it reach the oocyte through the pelluc ...
The Larynx
... • Passes between the arytenoid and thyroid cartilages, on the lateral side of the vocal ligament. • It contracts to shorten the vocal chord and/or decrease its tension. • This movement is opposed by the cricothyroid muscle. ...
... • Passes between the arytenoid and thyroid cartilages, on the lateral side of the vocal ligament. • It contracts to shorten the vocal chord and/or decrease its tension. • This movement is opposed by the cricothyroid muscle. ...
Left inferior lobe
... • Structures of alveoli (cont.) – Type II cells scattered among type I cells • Are cuboidal epithelial cells • Secrete surfactant (very important!) – Detergent-like molecule, that reduces surface tension within alveoli (prevents them from collapsing) ...
... • Structures of alveoli (cont.) – Type II cells scattered among type I cells • Are cuboidal epithelial cells • Secrete surfactant (very important!) – Detergent-like molecule, that reduces surface tension within alveoli (prevents them from collapsing) ...
Axial Skeleton 2 Objectives AXIAL SKELETON APPENDICULAR
... • Extends from the spine (supports head) to pelvis where weight of the body supports the lower limbs. • Formed by 26 irregular bones that re connected in such a way that a curved ...
... • Extends from the spine (supports head) to pelvis where weight of the body supports the lower limbs. • Formed by 26 irregular bones that re connected in such a way that a curved ...
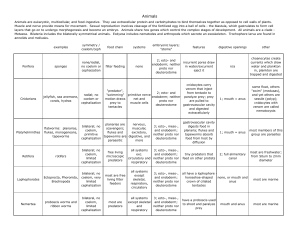
Animals
... have a water 3; ecto-, meso-, vascular and endoderm, system that are deuterostomes operate tube feet ...
... have a water 3; ecto-, meso-, vascular and endoderm, system that are deuterostomes operate tube feet ...
Ch22.Respiratory.System_1
... • Structures of alveoli (cont.) – Type II cells scattered among type I cells • Are cuboidal epithelial cells • Secrete surfactant (very important!) – Detergent-like molecule, that reduces surface tension within alveoli (prevents them from collapsing) ...
... • Structures of alveoli (cont.) – Type II cells scattered among type I cells • Are cuboidal epithelial cells • Secrete surfactant (very important!) – Detergent-like molecule, that reduces surface tension within alveoli (prevents them from collapsing) ...
Gross Anatomical Features of Ureter, Urinnary Bladder and
... Topic : Gross Anatomical Features of Ureter, Urinnary Bladder and Urethera Learning Objectives: At the end of the lecture student will able : To define the collecting parts of excretory system. To describe the gross anatomical feature and relation of the Ureter, urinary bladder, and urethra. To clin ...
... Topic : Gross Anatomical Features of Ureter, Urinnary Bladder and Urethera Learning Objectives: At the end of the lecture student will able : To define the collecting parts of excretory system. To describe the gross anatomical feature and relation of the Ureter, urinary bladder, and urethra. To clin ...
Portland Community College, Sylvania Campus BI 232 Lab
... 10. Keep all liquids away from the edge of the lab bench to avoid spills. Immediately notify your instructor of any spills. Keep test tubes in racks provided, except when necessary to transfer to water baths or hot plate. You will be advised of the proper clean-up procedures for any spill. 11. Repor ...
... 10. Keep all liquids away from the edge of the lab bench to avoid spills. Immediately notify your instructor of any spills. Keep test tubes in racks provided, except when necessary to transfer to water baths or hot plate. You will be advised of the proper clean-up procedures for any spill. 11. Repor ...
Roundworms - Advanced
... Roundworms have a thick substance called a cuticle on the surface of their bodies that is secreted by the outer epidermal cells. The cuticle is fairly rigid and limits the volume of the worm. This allows the build up of hydrostatic pressure from fluid accumulated in the worm and contributes to what ...
... Roundworms have a thick substance called a cuticle on the surface of their bodies that is secreted by the outer epidermal cells. The cuticle is fairly rigid and limits the volume of the worm. This allows the build up of hydrostatic pressure from fluid accumulated in the worm and contributes to what ...
Organogenesis Mesoderm - Relative Positions of Different Types
... • The sclerotome will form the axial skeleton. • The “migratory cells” will form the muscle of the body wall and limbs. • The dermatome will form the dorsal dermis. • The myotome will form the vertebral muscle. ...
... • The sclerotome will form the axial skeleton. • The “migratory cells” will form the muscle of the body wall and limbs. • The dermatome will form the dorsal dermis. • The myotome will form the vertebral muscle. ...
The functional anatomy of hip abductors
... The gluteal region was dissected in 18 adult cadavers. The attachments, directions, and orientations of the fibres of the tensor fasciae latae, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus muscles were noted. The gluteus medius was found to be formed of three distinct parts, while the gluteus minimus was for ...
... The gluteal region was dissected in 18 adult cadavers. The attachments, directions, and orientations of the fibres of the tensor fasciae latae, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus muscles were noted. The gluteus medius was found to be formed of three distinct parts, while the gluteus minimus was for ...
Earthworm Dissection – Ch 15
... a) Move aside the organs of the digestive and circulatory systems to locate the parts of the nervous system. b) The brain is a white mass of tissue found in the third segment, just beneath the pharynx. Gently move aside the pharynx and esophagus to expose the brain. c) Also look for the ventral nerv ...
... a) Move aside the organs of the digestive and circulatory systems to locate the parts of the nervous system. b) The brain is a white mass of tissue found in the third segment, just beneath the pharynx. Gently move aside the pharynx and esophagus to expose the brain. c) Also look for the ventral nerv ...
V Platyhelminthes and Nematoda PPT
... • Flatworms with middle tissue layer- mesoderm • Tissues organized into organs • Bilaterally symmetrical and flat • Cells lie close to exterior enabling efficient diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide • Highly branched gastrovascular cavity runs close to all tissues giving cells ready access to foo ...
... • Flatworms with middle tissue layer- mesoderm • Tissues organized into organs • Bilaterally symmetrical and flat • Cells lie close to exterior enabling efficient diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide • Highly branched gastrovascular cavity runs close to all tissues giving cells ready access to foo ...
- Veterinary Research Forum
... have been performed based on dissection of ten guinea pigs. The results showed that, in guinea pig temporal bone was similar to other animals and had three parts; squamous, tympanic and petrous .The tympanic part was much better developed and consisted of oval shaped tympanic bulla with many recesse ...
... have been performed based on dissection of ten guinea pigs. The results showed that, in guinea pig temporal bone was similar to other animals and had three parts; squamous, tympanic and petrous .The tympanic part was much better developed and consisted of oval shaped tympanic bulla with many recesse ...
Anatomical study of the superior orbital fissure as seen during a
... nineteenth century, and Yaşargil refined and popularized the approach in the microneurosurgical era. 5 The SOF is a complex anatomical structure at the junction of two areas of surgical complexity, the anterior cavernous sinus and orbital apex. Consistent with all skull base anatomical junctions, t ...
... nineteenth century, and Yaşargil refined and popularized the approach in the microneurosurgical era. 5 The SOF is a complex anatomical structure at the junction of two areas of surgical complexity, the anterior cavernous sinus and orbital apex. Consistent with all skull base anatomical junctions, t ...
Conodonts, Calcichordates and the Origin of Vertebrates
... upstream collecting system became improved by the invention of pharyngeal slits in primeval deuterostomes, which allowed a more efficient separation of water and food particles before they enter the gut. It is thus clear that there were several parallel attempts to overcome the size limitation of th ...
... upstream collecting system became improved by the invention of pharyngeal slits in primeval deuterostomes, which allowed a more efficient separation of water and food particles before they enter the gut. It is thus clear that there were several parallel attempts to overcome the size limitation of th ...
e983cc6dc44ea1d7381455cdbb55c3f7
... its lateral portion overlying the psoas Ms. The peritoneum can then be incised cephalad lateral and parallel to the ovarian vessels. This is followed by sharp & blunt dissection. The initial dissection should be bounded by the posterior leaflet of the broad ligament & the ureter medially (the ureter ...
... its lateral portion overlying the psoas Ms. The peritoneum can then be incised cephalad lateral and parallel to the ovarian vessels. This is followed by sharp & blunt dissection. The initial dissection should be bounded by the posterior leaflet of the broad ligament & the ureter medially (the ureter ...
Elbow Presentation PTA
... Synovial Membrane- inner layer of loose connective tissue. Lines fibrous layer, covers all internal joint surfaces that are not hyaline cartilage. Functionmakes synovial fluid. Cells in SM secrete hyaluronic acid that lubricates joint. Fibrous layer- external layer of dense connective tissue that is ...
... Synovial Membrane- inner layer of loose connective tissue. Lines fibrous layer, covers all internal joint surfaces that are not hyaline cartilage. Functionmakes synovial fluid. Cells in SM secrete hyaluronic acid that lubricates joint. Fibrous layer- external layer of dense connective tissue that is ...
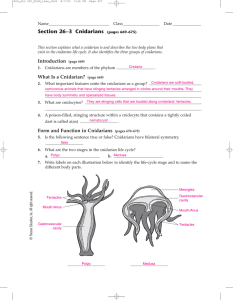
Section 26–3 Cnidarians - Winston Knoll Collegiate
... c. Inner lining of the gastrovascular cavity Nerve net d. Loosely organized network of nerve cells Statocysts e. Layer that lies between gastroderm and epidermis Ocelli f. Eyespots that detect light ...
... c. Inner lining of the gastrovascular cavity Nerve net d. Loosely organized network of nerve cells Statocysts e. Layer that lies between gastroderm and epidermis Ocelli f. Eyespots that detect light ...
Section 26–3 Cnidarians
... c. Inner lining of the gastrovascular cavity Nerve net d. Loosely organized network of nerve cells Statocysts e. Layer that lies between gastroderm and epidermis Ocelli f. Eyespots that detect light ...
... c. Inner lining of the gastrovascular cavity Nerve net d. Loosely organized network of nerve cells Statocysts e. Layer that lies between gastroderm and epidermis Ocelli f. Eyespots that detect light ...
Introduction and Superficial Back
... the body and the relationships of the various planes and sections to one another. Describe the general structural plan of the body and the relationships of the layers, partitions and compartments one encounters when dissecting from superficial to deep in any particular region. Describe a cutaneous n ...
... the body and the relationships of the various planes and sections to one another. Describe the general structural plan of the body and the relationships of the layers, partitions and compartments one encounters when dissecting from superficial to deep in any particular region. Describe a cutaneous n ...
Body Systems - Macmillan/McGraw-Hill
... and capture its energy. The lungs supply oxygen to the blood, and then the blood carries it to cells. The body must keep breathing because cells use oxygen very quickly, and they cannot store it. Water Did you know that water makes up most of the human body? As water is used by cells, it must be rep ...
... and capture its energy. The lungs supply oxygen to the blood, and then the blood carries it to cells. The body must keep breathing because cells use oxygen very quickly, and they cannot store it. Water Did you know that water makes up most of the human body? As water is used by cells, it must be rep ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.