* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organogenesis Mesoderm - Relative Positions of Different Types
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
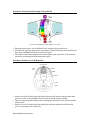
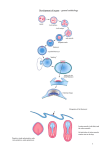
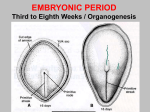
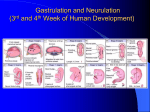
Organogenesis Mesoderm - Relative Positions of Different Types dorsal mesoderm chordamesoderm intermediate mesoderm dorsal mesoderm intermediate mesoderm lateral plate mesoderm lateral plate mesoderm endoderm mesoderm ectoderm • The relative positions of the mesoderm types are shown. The relative sizes are not accurate for the stage shown. Mesoderm - Frog Embryo Mesoderm - Chick Embryo neural plate somite notochord somatic mesoderm neural tube somite somatic mesoderm splanchnic mesoderm intermediate mesoderm gut cavity yolk gut cavity lateral plate mesoderm • The embryo shown is midway through neurulation. • The chordamesoderm has formed the notochord. The dorsal mesoderm has begun somite formation. • The lateral plate mesoderm has begun to split into the somatic and splanchnic mesoderms Developmental Biology Handout 06.1 splanchnic mesoderm notochord • The embryo shown has completed neurulation. • The chordamesoderm has formed the notochord. • The dorsal mesoderm has begun somite formation. • The intermediate mesoderm is clearly visible. • The lateral plate mesoderm has begun to split into the somatic and splanchnic mesoderms Mesoderm - Somite Development Ectoderm - Neurulation neural tube somite neural plate neural fold notochord dermamyotome sclerotome neural crest dermatome migratory cells epidermis myotome sclerotome neural tube • The sclerotome will form the axial skeleton. • The “migratory cells” will form the muscle of the body wall and limbs. • The dermatome will form the dorsal dermis. • The myotome will form the vertebral muscle. Developmental Biology Handout 06.2 • The neural tube will form the brain and spinal cord. • The neural crest cells migrate and form pigment cells of the skin, peripheral nerves, and the adrenal medulla. Ectoderm - Dorsoventral Patterning of Neural Tube From Ulloa and Marti, Dev Dyn 239, 69--76 (2010) • Different neuron types arise at different levels along the dorsoventral axis. • The different types are specified by two groups of signals: Shh from the notochord and floor plate, and BMPs and Wnts from the roof plate. • The signals control transcription factors that regulate gene expression in the neuronal precursors, generating the different neuronal types. Ectoderm - Neural Crest Cell Migration neural crest cells neural tube ectoderm somite notochord coelom gut tube • Neural crest cells following the path leading between the somites and the neural tube give rise to cells of the peripheral nervous system and the adrenal medulla. • The deep migration path actually passes through the sclerotome of the anterior portion of the somite. • Neural crest cells following the path leading between the epidermis and the somite give rise to pigment cells in the skin. Developmental Biology Handout 06.3