Erector spinae muscles - Kettlebell Training Education
... of the thoracic vertebrae. The erector spinae arises from the anterior surface of a broad and thick tendon. It is attached to the medial • longissimus cervicis originates from the transverse crest of the sacrum, to the spinous processes of the lumprocesses of T6-T1 and inserts in the transverse prob ...
... of the thoracic vertebrae. The erector spinae arises from the anterior surface of a broad and thick tendon. It is attached to the medial • longissimus cervicis originates from the transverse crest of the sacrum, to the spinous processes of the lumprocesses of T6-T1 and inserts in the transverse prob ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The endocrine glands
... 3. Note that the body of the crayfish is divided into three parts, the head, the cephalothorax and the abdomen. 4. Head - Identify the compound eyes on the rostrum portion of the head. 5. Cephalothorax - Find the Carapace, the covering of the cephalothorax region. 6. Note the larger antennae and sma ...
... 3. Note that the body of the crayfish is divided into three parts, the head, the cephalothorax and the abdomen. 4. Head - Identify the compound eyes on the rostrum portion of the head. 5. Cephalothorax - Find the Carapace, the covering of the cephalothorax region. 6. Note the larger antennae and sma ...
PDF sample
... The right of the author to be identified as the author of this work has been asserted in accordance with the UK Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, elec ...
... The right of the author to be identified as the author of this work has been asserted in accordance with the UK Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, elec ...
Surgical Anatomy and Approaches to the Anterior Thoracolumbar
... spine, the most significantly manipulated region during anterior thoracolumbar junction surgeries). The lumbar portion has two origins: one from the medial and lateral arcuate ligaments (two fibrous arches over the psoas and quadrates muscles) and another from the crura2,12. The crura are musculoten ...
... spine, the most significantly manipulated region during anterior thoracolumbar junction surgeries). The lumbar portion has two origins: one from the medial and lateral arcuate ligaments (two fibrous arches over the psoas and quadrates muscles) and another from the crura2,12. The crura are musculoten ...
Dissection Instructions of the Superficial Nerves of the Neck, Arm
... c. The accessory is blocked by placing the needle and giving local into the upper part (junction of the upper and middle third) of the SCM. This helps to disallow the patient from strongly turning their head towards the surgical field and helps prevent the patient from lifting their shoulder. Bot of ...
... c. The accessory is blocked by placing the needle and giving local into the upper part (junction of the upper and middle third) of the SCM. This helps to disallow the patient from strongly turning their head towards the surgical field and helps prevent the patient from lifting their shoulder. Bot of ...
AP Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Evolution of Animal Diversity
... Arthropods are segmented, have jointed appendages, and have an exoskeleton composed of chitin. D. Incorrect! Echinoderms possess a well-developed skeleton with numerous spines that extend outward to give the animal a spiny appearance. A unique feature is their water vascular system. E. Incorrect! Ch ...
... Arthropods are segmented, have jointed appendages, and have an exoskeleton composed of chitin. D. Incorrect! Echinoderms possess a well-developed skeleton with numerous spines that extend outward to give the animal a spiny appearance. A unique feature is their water vascular system. E. Incorrect! Ch ...
College Biology - Problem Drill 15: The Evolution of Animal Diversity
... Arthropods are segmented, have jointed appendages, and have an exoskeleton composed of chitin. D. Incorrect! Echinoderms possess a well-developed skeleton with numerous spines that extend outward to give the animal a spiny appearance. A unique feature is their water vascular system. E. Incorrect! Ch ...
... Arthropods are segmented, have jointed appendages, and have an exoskeleton composed of chitin. D. Incorrect! Echinoderms possess a well-developed skeleton with numerous spines that extend outward to give the animal a spiny appearance. A unique feature is their water vascular system. E. Incorrect! Ch ...
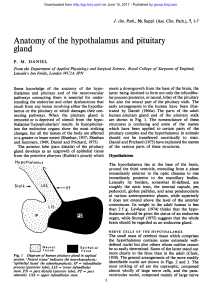
Anatomy of the hypothalamus and pituitary
... morphological studies of the human hypothalamus, forming the anterior lobe of the gland, or pars especially from brains in which lesions have occurred distalis, secrete their hormones directly into the blood which might be termed 'experiments of nature' flowing through the sinusoids that run between ...
... morphological studies of the human hypothalamus, forming the anterior lobe of the gland, or pars especially from brains in which lesions have occurred distalis, secrete their hormones directly into the blood which might be termed 'experiments of nature' flowing through the sinusoids that run between ...
Medical Science Variant attachment of bicipital aponeurosis and
... It was reported that BA in its proximal part is contributed by the short head and distally it was derived from the fascial sheath over the tendon of long head of biceps12 The bicipital aponeurosis may either be derived from long and short heads respectively in two distinct parts or may arise singly ...
... It was reported that BA in its proximal part is contributed by the short head and distally it was derived from the fascial sheath over the tendon of long head of biceps12 The bicipital aponeurosis may either be derived from long and short heads respectively in two distinct parts or may arise singly ...
Name Marine Biology--Mr. Nelson LAB: SPONGES AND
... polyp (vase shaped). The oral end of the polyp, bearing the mouth and tentacles, is directed upward. But in the medusa, the mouth and tentacles are oriented downward. Between the inner and outer layers of the body wall is a gelatinous mesoglea. The mesoglea of most medusae is thick and well develope ...
... polyp (vase shaped). The oral end of the polyp, bearing the mouth and tentacles, is directed upward. But in the medusa, the mouth and tentacles are oriented downward. Between the inner and outer layers of the body wall is a gelatinous mesoglea. The mesoglea of most medusae is thick and well develope ...
Skeletal System
... The spinal cord exits the braincase at the foramen magnum and the bulbous occipital condyles (near the foramen magnum) articulate with the first vertebrae. Locate the visceral arches near the rear of the chondrocranium. Ancestral vertebrates were filter feeders and Figure 2: Chondrocranium with jaws ...
... The spinal cord exits the braincase at the foramen magnum and the bulbous occipital condyles (near the foramen magnum) articulate with the first vertebrae. Locate the visceral arches near the rear of the chondrocranium. Ancestral vertebrates were filter feeders and Figure 2: Chondrocranium with jaws ...
BSC I ZOOLOGY PRACTICAL
... 6. As the trophozoite grows in size, a central vacuole is developed. 7. As a result of this the nucleus is pushed to one side into peripheral cytoplasm. 8. This stage is clinically referred to as signet – ring sage. 9. Signet- ring trophozoite secretes digestive enzymes which bring lyses of haemoglo ...
... 6. As the trophozoite grows in size, a central vacuole is developed. 7. As a result of this the nucleus is pushed to one side into peripheral cytoplasm. 8. This stage is clinically referred to as signet – ring sage. 9. Signet- ring trophozoite secretes digestive enzymes which bring lyses of haemoglo ...
Think of it as a fluid- filled sac floating in a fluid
... The ORGAN OR CORTI is the sensory receptor in the organ of hearing, and is located in the COCHLEAR. It rests on the basilar membrane. The supporting cells surround cochlear hair cells that include one row of inner hair cells and three rows of outer hair cells. Both types of hair have the typical ste ...
... The ORGAN OR CORTI is the sensory receptor in the organ of hearing, and is located in the COCHLEAR. It rests on the basilar membrane. The supporting cells surround cochlear hair cells that include one row of inner hair cells and three rows of outer hair cells. Both types of hair have the typical ste ...
Ch. 7 Dermatology
... Characteristics of the Epidermis: -epithelial tissue -covers the external surface of the body and mucous membranes. -outer epidermis is the corneal layer. -lower epidermis is the basal layer. -external cells contain keratin, protein that gives skin a waterproofing ability. -cells also contain melan ...
... Characteristics of the Epidermis: -epithelial tissue -covers the external surface of the body and mucous membranes. -outer epidermis is the corneal layer. -lower epidermis is the basal layer. -external cells contain keratin, protein that gives skin a waterproofing ability. -cells also contain melan ...
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM (I)
... About ¾ of the uterus is covered by a flat mesothelial lining. The remaining is the adventitia that connects the uterus to the surrounding organs. FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM (I) LABORATORY SLIDE 22, VAGINA: The vagina is lined by a non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. The superficial ...
... About ¾ of the uterus is covered by a flat mesothelial lining. The remaining is the adventitia that connects the uterus to the surrounding organs. FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM (I) LABORATORY SLIDE 22, VAGINA: The vagina is lined by a non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. The superficial ...
The subanconeus muscle
... The articularis genu (tenseur de la synoviale, capsular muscle of Meckel) is perhaps the most well known muscle with an attachment to the external aspect of a joint capsule [4]. However, other less well described muscles have attachments into joints that they cross. For example, some have depicted f ...
... The articularis genu (tenseur de la synoviale, capsular muscle of Meckel) is perhaps the most well known muscle with an attachment to the external aspect of a joint capsule [4]. However, other less well described muscles have attachments into joints that they cross. For example, some have depicted f ...
Introduction
... function of humans, and serves as the foundation of modern medicine. As a discipline, it connects science, medicine, and health, and creates a framework for understanding how the human body adapts to stresses, physical activity, and disease. Human physiology is closely related to anatomy, in that an ...
... function of humans, and serves as the foundation of modern medicine. As a discipline, it connects science, medicine, and health, and creates a framework for understanding how the human body adapts to stresses, physical activity, and disease. Human physiology is closely related to anatomy, in that an ...
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 9 Face
... Intertragateric notch Concha Helix Antihelix Tubercle Lobule. The Scalp Is composed of 5 layers: the skin, dense connective tissue, and the flat tendon of occipitofrontalis, which can slide forwards and backwards on a loose connective tissue layer over the periosteum of the skull ...
... Intertragateric notch Concha Helix Antihelix Tubercle Lobule. The Scalp Is composed of 5 layers: the skin, dense connective tissue, and the flat tendon of occipitofrontalis, which can slide forwards and backwards on a loose connective tissue layer over the periosteum of the skull ...
Hand
... • Veins from the fingers (dorsal digital vv.) end in the dorsal venous network (arch) opposite the middle of the dorsum of the hand; the superficial palmar arch drains into the basilic v. • Superficial lymphatic vessels - Accompany the superficial veins and enter the cubital lymph nodes - axillary l ...
... • Veins from the fingers (dorsal digital vv.) end in the dorsal venous network (arch) opposite the middle of the dorsum of the hand; the superficial palmar arch drains into the basilic v. • Superficial lymphatic vessels - Accompany the superficial veins and enter the cubital lymph nodes - axillary l ...
Bryozoans and Corals
... calcium carbonate skeleton that serves as a supporting, cup-like base around them. Some corals are solitary, usually forming a horn-like base, while others are colonial, forming a tile-like mosaic of supporting structures that are fused in a single colony. Anatomically corals are one of the simplest ...
... calcium carbonate skeleton that serves as a supporting, cup-like base around them. Some corals are solitary, usually forming a horn-like base, while others are colonial, forming a tile-like mosaic of supporting structures that are fused in a single colony. Anatomically corals are one of the simplest ...
ONE1_02_Postural_Assessment
... Allows joints to move in their mid range to minimize stress on ligaments and articular surfaces. Effective for the individual’s activities of daily living. Allows the individual to avoid injury. ...
... Allows joints to move in their mid range to minimize stress on ligaments and articular surfaces. Effective for the individual’s activities of daily living. Allows the individual to avoid injury. ...
Chapter 14 - Las Positas College
... A. During embryonic development, each spinal nerve grows out between newly formed vertebrae to provide the motor innervation of an adjacent myotome (future trunk muscle) and the sensory innervation of the adjacent skin region (dermatome). (p. 454) ...
... A. During embryonic development, each spinal nerve grows out between newly formed vertebrae to provide the motor innervation of an adjacent myotome (future trunk muscle) and the sensory innervation of the adjacent skin region (dermatome). (p. 454) ...
Student CA2 Essay (A grade)
... pseudostratified columnar epithelium changes to non-ciliated simple cuboidal epithelium in the terminal bronchioles. ...
... pseudostratified columnar epithelium changes to non-ciliated simple cuboidal epithelium in the terminal bronchioles. ...
y. - كلية طب الاسنان
... and orbicularis oculi. They are only important for wrinkling the forehead. (A branch is also termed a frontal branch in some texts.) The zygomatic branches cross the zygomatic arch and zygomatic bone. These branches supply orbicularis oculi. The buccal branches run forwards close to the parotid duct ...
... and orbicularis oculi. They are only important for wrinkling the forehead. (A branch is also termed a frontal branch in some texts.) The zygomatic branches cross the zygomatic arch and zygomatic bone. These branches supply orbicularis oculi. The buccal branches run forwards close to the parotid duct ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.