26 slides
... Include sweat and oil glands, liver, and pancreas Includes both internal and external glands ...
... Include sweat and oil glands, liver, and pancreas Includes both internal and external glands ...
Human Anatomy Lab #4: Human Anatomy in Perspective
... The skull is part of the axial skeleton. It is the most complex region of the skeleton because it is associated with numerous, diverse functions. It is shaped by growth and development, as you can see when you compare the infant and adult skulls. The skull consists of at least 25 separate bones that ...
... The skull is part of the axial skeleton. It is the most complex region of the skeleton because it is associated with numerous, diverse functions. It is shaped by growth and development, as you can see when you compare the infant and adult skulls. The skull consists of at least 25 separate bones that ...
Taking a Brief Look to the Phylum Cnidaria
... more complex than sponges as they have: cells bound by inter-cell connections and carpet-like basement membranes; muscles; nervous systems; and some have sensory organs. Cnidarians are distinguished from all other animals by having cnidocytes that fire like harpoons and are used mainly to capture pr ...
... more complex than sponges as they have: cells bound by inter-cell connections and carpet-like basement membranes; muscles; nervous systems; and some have sensory organs. Cnidarians are distinguished from all other animals by having cnidocytes that fire like harpoons and are used mainly to capture pr ...
Ch1HomeostasisNotes
... Protects and supports body organs; provides a framework the muscles use to cause movement; blood cells are formed within bones; stores minerals. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Protects and supports body organs; provides a framework the muscles use to cause movement; blood cells are formed within bones; stores minerals. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
presence of triple gantzer`s muscle - a rare
... muscle has clinical importance as it may compress both the median nerve1, ...
... muscle has clinical importance as it may compress both the median nerve1, ...
BCH 450 CAT 1 lectures
... fibers, scattered cells of various types; abundant ground substance; numerous blood vessels. In the skin and mucous membranes, it is more compact and sometimes difficult to distinguish from dense irregular connective tissue. ...
... fibers, scattered cells of various types; abundant ground substance; numerous blood vessels. In the skin and mucous membranes, it is more compact and sometimes difficult to distinguish from dense irregular connective tissue. ...
iv splanchnology
... liberation of the oocyte. It is stimulated by LH hormones released from the anterior pituitary gland in response to high amounts of circulating estrogen. Blood increase to the site as well as local release of histamine, prostaglandins, vasopressin and collagenase. Granular cells become loose and fol ...
... liberation of the oocyte. It is stimulated by LH hormones released from the anterior pituitary gland in response to high amounts of circulating estrogen. Blood increase to the site as well as local release of histamine, prostaglandins, vasopressin and collagenase. Granular cells become loose and fol ...
6. Body Wall and Coelomic Cavity.
... At this stage we are going to focus on the paraxial mesoderm and the lateral plate mesoderm. We shall study the intermediate mesoderm with the urogenital systems. Paraxial mesoderm is like a column by the side of the notochord and the neural groove/plate. This column of paraxial mesoderm splits into ...
... At this stage we are going to focus on the paraxial mesoderm and the lateral plate mesoderm. We shall study the intermediate mesoderm with the urogenital systems. Paraxial mesoderm is like a column by the side of the notochord and the neural groove/plate. This column of paraxial mesoderm splits into ...
review questions
... lies in the median plane of the perineum. consists of two symmetrical parts that are united by a median tendinous raphe. arises in part from the conjoint tendon. functions during micturition and erection. is supplied by the perineal nerve. ...
... lies in the median plane of the perineum. consists of two symmetrical parts that are united by a median tendinous raphe. arises in part from the conjoint tendon. functions during micturition and erection. is supplied by the perineal nerve. ...
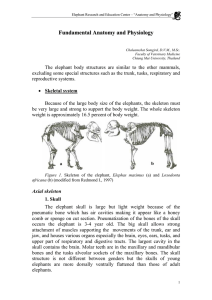
Fundamental Anatomy and Physiology
... The dental formula of adult elephants for both species is I 1/0 C0/0 PM 3/3 M 3/3, with a total number of 26 teeth, the two upper incisors are the tusks. The average weight of the teeth of elephants is approximately 5 kilograms. New born elephants have 2-3 teeth in each jaw quadrant; these teeth dev ...
... The dental formula of adult elephants for both species is I 1/0 C0/0 PM 3/3 M 3/3, with a total number of 26 teeth, the two upper incisors are the tusks. The average weight of the teeth of elephants is approximately 5 kilograms. New born elephants have 2-3 teeth in each jaw quadrant; these teeth dev ...
Anatomy of female genital organs
... 1-The Broad Ligament This is a fold of peritoneum with mesothelium on its anterior and posterior surfaces. It extends from the sides of the uterus to the lateral walls and floor of the pelvis. The broad ligament holds the uterus in its normal position. ...
... 1-The Broad Ligament This is a fold of peritoneum with mesothelium on its anterior and posterior surfaces. It extends from the sides of the uterus to the lateral walls and floor of the pelvis. The broad ligament holds the uterus in its normal position. ...
Spleen - HIMSK
... they are occasionally united, so as to form a single mass; and sometimes separated by an intermediate lobe. The thymus is of a pinkish-gray color, soft, and lobulated on its surfaces. It is about 5 cm. in length, 4 cm. in breadth below, and about 6 mm. in ...
... they are occasionally united, so as to form a single mass; and sometimes separated by an intermediate lobe. The thymus is of a pinkish-gray color, soft, and lobulated on its surfaces. It is about 5 cm. in length, 4 cm. in breadth below, and about 6 mm. in ...
Variation in the Insertion of Brachialis Muscle
... Brachioradialis muscle is a flexor of forearm and arises from upper two third of supracondylar ridge of humerus and lateral intermuscular septum normally. In this case its origin receives a well-defined fibro muscular slip from brachialis. The insertion of brachioradialis is on the base of the stylo ...
... Brachioradialis muscle is a flexor of forearm and arises from upper two third of supracondylar ridge of humerus and lateral intermuscular septum normally. In this case its origin receives a well-defined fibro muscular slip from brachialis. The insertion of brachioradialis is on the base of the stylo ...
The Dissection of a Fetal Pig
... dissection will give you a sense of how internal systems are arranged within your own body. Dissection involves the careful and systematic examination of the internal structures of an organism. A good dissection will reveal not only the location and structure of individual organs, but also how diffe ...
... dissection will give you a sense of how internal systems are arranged within your own body. Dissection involves the careful and systematic examination of the internal structures of an organism. A good dissection will reveal not only the location and structure of individual organs, but also how diffe ...
Chapter 11 Muscles of the body
... Name based on the number of origins - triceps Name based on the location of attachments brachioradialis Name based on its action – adductor longus ...
... Name based on the number of origins - triceps Name based on the location of attachments brachioradialis Name based on its action – adductor longus ...
Laboratory Manual for Human Anatomy and Physiology I
... Materials: Disarticulated human skeletons or skeleton models, textbooks and skeleton atlases, blunt probes. Students will work in groups. Before you begin Your instructor will allow several weeks for the study of the skeleton and preparation for the laboratory practical exam. It is important that yo ...
... Materials: Disarticulated human skeletons or skeleton models, textbooks and skeleton atlases, blunt probes. Students will work in groups. Before you begin Your instructor will allow several weeks for the study of the skeleton and preparation for the laboratory practical exam. It is important that yo ...
Structure Function/Use Brow Spot Nictitating Membrane Cloacal
... The opening between the two posterior/hind legs that allows reproductive cells to be excreted into the water ...
... The opening between the two posterior/hind legs that allows reproductive cells to be excreted into the water ...
5th international symposion of clinical and applied anatomy and 1st
... Medical and Dental Sciences, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, Japan Background: It is well known that the coracohumeral ligament spreads along the supraspinatus to infraspinatus muscles in order to stabilize the glenohumeral joint. However, only a few reports had mentioned about its extension to ...
... Medical and Dental Sciences, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, Japan Background: It is well known that the coracohumeral ligament spreads along the supraspinatus to infraspinatus muscles in order to stabilize the glenohumeral joint. However, only a few reports had mentioned about its extension to ...
PDF English - International Journal of Morphology
... layered arrangement of its fibers. However, the variation in its insertion is very rare. The origin of the clavicular head may be as broad as 7.5 cm and occasionally divided into many slips with narrow intervals when it is broad. During the development, sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles shar ...
... layered arrangement of its fibers. However, the variation in its insertion is very rare. The origin of the clavicular head may be as broad as 7.5 cm and occasionally divided into many slips with narrow intervals when it is broad. During the development, sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles shar ...
It is All About the Foot - Pedorthic Footcare Association
... Thus far, we have covered the bones and articulations of the foot, along with bipedal motion in this series. These are the foundations of what makeups the foot, but this is not enough. We need to ask now, what makes it come all together? It is time to connect all the previous parts we have discussed ...
... Thus far, we have covered the bones and articulations of the foot, along with bipedal motion in this series. These are the foundations of what makeups the foot, but this is not enough. We need to ask now, what makes it come all together? It is time to connect all the previous parts we have discussed ...
The Skeletal System
... The five lumbar vertebrae (L1-L5) are located in the small of the back and have an enhanced weight-bearing function They have short, thick pedicles and laminae, flat hatchet-shaped spinous processes, and a triangular-shaped vertebral foramen Orientation of articular facets locks the lumbar verte ...
... The five lumbar vertebrae (L1-L5) are located in the small of the back and have an enhanced weight-bearing function They have short, thick pedicles and laminae, flat hatchet-shaped spinous processes, and a triangular-shaped vertebral foramen Orientation of articular facets locks the lumbar verte ...
ch 32 animal diversity
... Cell Structure and Specialization • Animals are multicellular eukaryotes • Their cells lack cell walls • Their bodies are held together by structural proteins such as collagen • Nervous tissue and muscle tissue are unique, defining characteristics of animals • Tissues are groups of cells that have ...
... Cell Structure and Specialization • Animals are multicellular eukaryotes • Their cells lack cell walls • Their bodies are held together by structural proteins such as collagen • Nervous tissue and muscle tissue are unique, defining characteristics of animals • Tissues are groups of cells that have ...
TSM33 - Neck and Pharynx
... The pharynx is a muscular semicircular tube that extends from the base of the skull to the oesophagus Three overlapping constrictor muscles with internal mucous linings make up the pharyngeal walls: o Superior constrictor – from the pterygomandibular raphe to the pharyngeal tubercle o Middle constri ...
... The pharynx is a muscular semicircular tube that extends from the base of the skull to the oesophagus Three overlapping constrictor muscles with internal mucous linings make up the pharyngeal walls: o Superior constrictor – from the pterygomandibular raphe to the pharyngeal tubercle o Middle constri ...
Fetal Pig I External and Ventral Body Cavity Anatomy Introduction to
... Procedure: Dissection and Anatomy of the Neck Region 1) The skin includes the epidermis and dermis overlaying the subcutaneous (adipose) layer. Using your blunt probe, gently push the blunt probe through the subcutaneous layer from the midline at the manubrium to the midline of the mandible. 2) Use ...
... Procedure: Dissection and Anatomy of the Neck Region 1) The skin includes the epidermis and dermis overlaying the subcutaneous (adipose) layer. Using your blunt probe, gently push the blunt probe through the subcutaneous layer from the midline at the manubrium to the midline of the mandible. 2) Use ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.