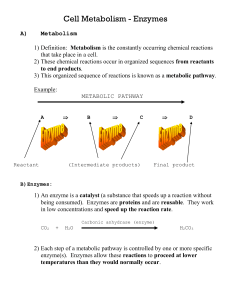
Enzymes Notes
... ENZYMES' ! Enzymes'are'PROTEINS"' ! Enzymes'are'biological' CATALYSTS'that'speed%up% chemical%reac.ons'and' decrease/lower'the' acAvaAon'energy'while' releasing'energy.' ! Enzymes'affect'the'reacAons'in' living'cells'by'changing'the' speed'of'the'reacAon' ...
... ENZYMES' ! Enzymes'are'PROTEINS"' ! Enzymes'are'biological' CATALYSTS'that'speed%up% chemical%reac.ons'and' decrease/lower'the' acAvaAon'energy'while' releasing'energy.' ! Enzymes'affect'the'reacAons'in' living'cells'by'changing'the' speed'of'the'reacAon' ...
CHAPTER-II ENZYMES
... heme). Organic cofactors can be either prosthetic groups, which are tightly bound to an enzyme, or coenzymes, which are released from the enzyme's active site during the reaction. Coenzymes include NADH, NADPH and adenosine triphosphate. These molecules transfer chemical groups between enzymes. An e ...
... heme). Organic cofactors can be either prosthetic groups, which are tightly bound to an enzyme, or coenzymes, which are released from the enzyme's active site during the reaction. Coenzymes include NADH, NADPH and adenosine triphosphate. These molecules transfer chemical groups between enzymes. An e ...
Review Problems #2 (Enzyme Review, Phosphatases
... activity and through regulation of the amount of enzyme that is present. List two general methods of control that affect enzyme activity rather than enzyme amounts. Which of these two methods is employed to control cholesterol biosynthesis? List the control elements that can affect the amount of an ...
... activity and through regulation of the amount of enzyme that is present. List two general methods of control that affect enzyme activity rather than enzyme amounts. Which of these two methods is employed to control cholesterol biosynthesis? List the control elements that can affect the amount of an ...
Chp 4 Carbon and Diversity of Life
... formula but with different structures and different properties. 1. Structural isomers -Isomers that differ in the covalent arrangement of their atoms. Number of possible isomers increases as the carbon skeleton size ...
... formula but with different structures and different properties. 1. Structural isomers -Isomers that differ in the covalent arrangement of their atoms. Number of possible isomers increases as the carbon skeleton size ...
Running Head: EFFECT OF PH ON AMYLASE ACTIVITY 1 Lab
... Chemically, enzymes are protein in nature and act as catalysts for the chemical reactions that occur in living organisms (Adams, 2003). They attach themselves to slots on the substrates called active sites to speed up a particular chemical reaction. There are different types of enzymes each with a p ...
... Chemically, enzymes are protein in nature and act as catalysts for the chemical reactions that occur in living organisms (Adams, 2003). They attach themselves to slots on the substrates called active sites to speed up a particular chemical reaction. There are different types of enzymes each with a p ...
Rate of enzymatic reactions
... of temperature, due to the denaturation of the enzyme protein leading to it losing its catalytic activity. ...
... of temperature, due to the denaturation of the enzyme protein leading to it losing its catalytic activity. ...
Enzymes
... then they use the so-called “activity” of the enzyme, as a unit of effectiveness. This actually means reaction velocity, under precisely known and controlled conditions. It tells us how much S can be converted (or P be generated) by the actual amount of E present in solution, (generally) at the satu ...
... then they use the so-called “activity” of the enzyme, as a unit of effectiveness. This actually means reaction velocity, under precisely known and controlled conditions. It tells us how much S can be converted (or P be generated) by the actual amount of E present in solution, (generally) at the satu ...
27-36
... of the antibiotic. The molecular mass of penicillase is 30,000g/mol. The turnover number of the enzyme at 28°C is 2,000 s-1. If 6.4μg of penicillase catalyzes the destruction of 3.11mg of amoxicillin, an antibiotic with a molecular mass of 364 g/mol, in 20s at 28°C, how many active sites does the en ...
... of the antibiotic. The molecular mass of penicillase is 30,000g/mol. The turnover number of the enzyme at 28°C is 2,000 s-1. If 6.4μg of penicillase catalyzes the destruction of 3.11mg of amoxicillin, an antibiotic with a molecular mass of 364 g/mol, in 20s at 28°C, how many active sites does the en ...
Chapter 5: Enzymes
... 3. Oxidation of Glucose Release of Energy to do work Involves a series of enzyme catalysed reactions 4. Breakdown of toxic materials Hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen catalysed by catalase. Enzymes catalyse almost all reactions in body. There are many different types of enzymes and each is ...
... 3. Oxidation of Glucose Release of Energy to do work Involves a series of enzyme catalysed reactions 4. Breakdown of toxic materials Hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen catalysed by catalase. Enzymes catalyse almost all reactions in body. There are many different types of enzymes and each is ...
Rubisco large subunit antibody
... by the abbreviation RuBisCO, is an enzyme involved in the first major step of carbon fixation, a process by which atmospheric carbon dioxide is converted by plants to energy-rich molecules such as glucose. In chemical terms, it catalyzes the carboxylation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (also known as ...
... by the abbreviation RuBisCO, is an enzyme involved in the first major step of carbon fixation, a process by which atmospheric carbon dioxide is converted by plants to energy-rich molecules such as glucose. In chemical terms, it catalyzes the carboxylation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (also known as ...
2 NADH + H + 4 ATPs
... Proteins that function as biological catalysts by lowering the energy of activation and speeding up chemical processes Enzymes are substrate specific, much like a lock and key Enzymes catalyze reactions without being changed ...
... Proteins that function as biological catalysts by lowering the energy of activation and speeding up chemical processes Enzymes are substrate specific, much like a lock and key Enzymes catalyze reactions without being changed ...
Enzyme Notes
... chemical reaction, atoms are not created or destroyed – just rearranged. Therefore, chemical equations must be balanced so there is the same number of atoms on both sides of the equation. ...
... chemical reaction, atoms are not created or destroyed – just rearranged. Therefore, chemical equations must be balanced so there is the same number of atoms on both sides of the equation. ...
AP Biology Photosynthesis – Part 3 Text reading 10.3 Important
... (3 + 1 +1 =5)So we end up with 3 five Carbon molecules of RuBP again. Thus, we have started and ended at the same point… a cycle. a. 1 G3P used to make glucose (So the cycle must go around TWICE to make 1 glucose molecule. So repeat steps 1-3 to make the second half.) C. Total Numbers needed: For ea ...
... (3 + 1 +1 =5)So we end up with 3 five Carbon molecules of RuBP again. Thus, we have started and ended at the same point… a cycle. a. 1 G3P used to make glucose (So the cycle must go around TWICE to make 1 glucose molecule. So repeat steps 1-3 to make the second half.) C. Total Numbers needed: For ea ...
Enzymes - Images
... lower the energy level (activation energy) needed to start the reaction o Enzymes are not reactants and not used up in the reaction ...
... lower the energy level (activation energy) needed to start the reaction o Enzymes are not reactants and not used up in the reaction ...
Enzymes Worksheet - Ms. Perez`s Science
... i) Enzymes are biological ………………… that speed up chemical reactions in living organisms. ii) Enzymes are protein molecules, which are made up of long chains of ………...………. iii) The sequence and type of amino acids are ………………… in each protein, so they produce enzymes with many different shapes and func ...
... i) Enzymes are biological ………………… that speed up chemical reactions in living organisms. ii) Enzymes are protein molecules, which are made up of long chains of ………...………. iii) The sequence and type of amino acids are ………………… in each protein, so they produce enzymes with many different shapes and func ...
Extra Notes on Enzymes (Overview)
... Therefore, starch is the substrate for amylase Active sites - Specific places where substrates temporarily bind to Lock and Key model o Like a key fitting into a lock, substrates exactly fit the active sites of enzymes o This is why if an enzyme’s structure changes, it may not work at all. o L ...
... Therefore, starch is the substrate for amylase Active sites - Specific places where substrates temporarily bind to Lock and Key model o Like a key fitting into a lock, substrates exactly fit the active sites of enzymes o This is why if an enzyme’s structure changes, it may not work at all. o L ...
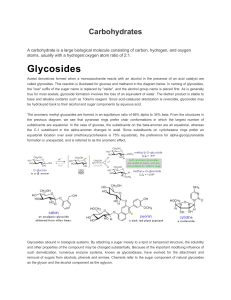
Glycosides
... Cellulose is commonly accompanied by a lower molecular weight, branched, amorphous polymer called hemicellulose. In contrast to cellulose, hemicellulose is structurally weak and is easily hydrolyzed by dilute acid or base. Also, many enzymes catalyze its hydrolysis. Hemicelluloses are composed of ma ...
... Cellulose is commonly accompanied by a lower molecular weight, branched, amorphous polymer called hemicellulose. In contrast to cellulose, hemicellulose is structurally weak and is easily hydrolyzed by dilute acid or base. Also, many enzymes catalyze its hydrolysis. Hemicelluloses are composed of ma ...
Enzyme - CIE Alevel notes!
... The active site of an enzyme is a region, usually a cleft or depression, to which another molecule or molecules can bind. The shape of the active sit allows the substrate to fit perfectly. The idea that the enzyme has a particular shape into which the substrate fit exactly is known as the lock and k ...
... The active site of an enzyme is a region, usually a cleft or depression, to which another molecule or molecules can bind. The shape of the active sit allows the substrate to fit perfectly. The idea that the enzyme has a particular shape into which the substrate fit exactly is known as the lock and k ...
biology lab: enzyme activity
... BACKGROUND INFORMATION: (Summarize the information below in your own words.) "Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts that affect the rate of biochemical reactions. In an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, the substance to be acted upon, the substrate (S), binds to the active site of the enzyme (E). One ...
... BACKGROUND INFORMATION: (Summarize the information below in your own words.) "Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts that affect the rate of biochemical reactions. In an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, the substance to be acted upon, the substrate (S), binds to the active site of the enzyme (E). One ...
2013 Enzymes ppt
... For chemical reactions the Q10 = 2 to 3 (the rate of the reaction doubles or triples with every 10°C rise in temperature) Enzyme-controlled reactions follow this rule as they are chemical reactions BUT at high temperatures proteins denature The optimum temperature for an enzyme controlled reaction w ...
... For chemical reactions the Q10 = 2 to 3 (the rate of the reaction doubles or triples with every 10°C rise in temperature) Enzyme-controlled reactions follow this rule as they are chemical reactions BUT at high temperatures proteins denature The optimum temperature for an enzyme controlled reaction w ...
Unit 2 pH Biomolecules Macromolecules
... 4. This molecule (_____________) is the subunit of this molecule ( ________) that stores information. 5. When a polysaccharide is hydrolyzed, it looks like this: ________. These store energy (circle one): short-term / longterm. 6. This molecule (_______) is hydrophobic and stores energy (circle one) ...
... 4. This molecule (_____________) is the subunit of this molecule ( ________) that stores information. 5. When a polysaccharide is hydrolyzed, it looks like this: ________. These store energy (circle one): short-term / longterm. 6. This molecule (_______) is hydrophobic and stores energy (circle one) ...
Enzymes - Kevan Kruger
... Review of LOCK AND KEY According to this analogy, an enzyme acts like a key by combining with a specific substrate and “unlocking” the substrate for further activity of the cell. This is a useful analogy because the key (enzyme) must have the correct shape to fit the lock (substrate). After the loc ...
... Review of LOCK AND KEY According to this analogy, an enzyme acts like a key by combining with a specific substrate and “unlocking” the substrate for further activity of the cell. This is a useful analogy because the key (enzyme) must have the correct shape to fit the lock (substrate). After the loc ...
Unit-III Enzymes
... • The substrates in nature. • Their structures are altered for subsequent reactions. • Shuttle mobile metabolic groups among different enzyme-catalyzed reactions. ...
... • The substrates in nature. • Their structures are altered for subsequent reactions. • Shuttle mobile metabolic groups among different enzyme-catalyzed reactions. ...
Isomerase

Isomerases are a general class of enzymes which convert a molecule from one isomer to another. Isomerases can either facilitate intramolecular rearrangements in which bonds are broken and formed or they can catalyze conformational changes. The general form of such a reaction is as follows:A–B → B–AThere is only one substrate yielding one product. This product has the same molecular formula as the substrate but differs in bond connectivity or spatial arrangements. Isomerases catalyze reactions across many biological processes, such as in glycolysis and carbohydrate metabolism.