* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Extra Notes on Enzymes (Overview)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
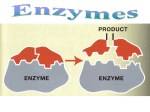
Enzymes: How can we break down a piece of pizza? It happens through the action of proteins called enzymes. Enzymes help start and run chemical reactions in living things. Example: Enzymes are needed to break down food into smaller molecules that cells can use. Without enzymes, a Venus flytrap couldn’t break down its food, and neither could you. Activation energy The amount of energy needed to start a chemical reaction Once a chemical reaction starts, it can be continued by itself and it will continue at a certain rate Often, the activation energy for a chemical reaction comes from an increase in temperature o After a reaction starts, it may happen very slowly o The reactants may not interact enough, or they may not be at a high enough concentration, to quickly form the products of the reaction o The activation energy and rate of a chemical reaction can be changed by a chemical catalyst. Catalyst – a substance that decreases the activation energy needed to start a chemical reaction and, as a result, also increases the rate of the chemical reaction. o Normal conditions – reactions require a certain amount of activation energy, and it occurs at a certain rate o Catalyst present – less energy is needed and the products form faster. Catalysts are not considered to be reactants or products even though they take part in the reaction. The reason is that catalysts are not changed or used up during a reaction! Enzymes allow chemical reactions to occur under tightly controlled conditions Reactants usually found in low concentrations Because reactions must take place quickly, they usually need a catalyst Enzymes o Are catalysts for chemical reactions in living things o Lower the activation energy and increase the rate of chmical reactions o Involved in almost every process in organisms From breaking down food to building proteins, enzymes are needed Example: Amylase is an enzyme in saliva that breaks down starch into simple sugars This reaction occurs up to a million times faster with amylase than without it o Enzymes are proteins Long chains of amino acids Every enzyme depends on its structure to function properly o Factors that affect enzyme function and activity Temperature and pH Enzymes work best in a small temperature range around the organism’s normal body temperature Only at slightly higher temperatures, the bonds inside an enzyme may begin to break apart and the enzyme’s structure will start to change o Once the enzyme shape changes, it will lose its ability to function properly o This is one reason why a very high fever is so dangerous to a person A change in pH can also effect the bond in enzymes o Many enzymes in humans work best at nearly neutral pH that is maintained within cells of the human body o Enzyme structure is important Because each enzyme shape allows only certain reactants to bind to the enzyme Substrate – the specific reactants that an enzyme acts on Example: Amylase only breaks down starch Therefore, starch is the substrate for amylase Active sites - Specific places where substrates temporarily bind to Lock and Key model o Like a key fitting into a lock, substrates exactly fit the active sites of enzymes o This is why if an enzyme’s structure changes, it may not work at all. o Lock and Key Enzymes bring substrate molecules close together Because of the low concentration of reactants in cells, many reactions would be unlikely to take place without enzymes bringing substrates together Next, enzymes decrease the activation energy When substrates bind to the enzymes active site, the bonds inside the substrates become strained If bonds are strained or stretched slightly out of position, they become weaker. Less activation energy is needed for these slightly weakened bonds to be broken Critical thinking questions 1. Infer: Some organisms live in very hot or very acidic environments. Would their enzyms function in a person’s cells? Why or why not? 2. Predict: Suppose that the amino acids that make up an enzyme’s active site are changed. How might this change affect the enzyme? 3. Connecting concepts: Organisms need to maintain homeostasis, or stable internal conditions. Why is homeostasis important for the function of enzymes? Key questions (Aims) How does the structure of an enzyme affect its function? Main ideas: A catalyst lowers activation energy Enzymes allow chemical reactions to occur under tightly controlled conditions Acids and Bases: Acid – compound that releases a hydrogen ion (H+) when it dissolves in water o An acid increases the concentration of H+ ions in a solution Bases – are compounds that remove H+ ions form solution o When a base dissolves in water, the solution has a low H+ concentration A solutions H+ ion concentration, or acidity, is measured by the pH scale. pH scale – measures how acidic a solution is o pH is usually between 0 and 14 o Solution with a pH of 0 = very acidic, with a high H+ concentration o Solution with a pH of 14 is very basic, with a low H+ concentration o Solutions with pH of 7 are neutral – neither acidic or basic Humans need to keep their pH within a very narrow range around neutral (pH 7.0). o Some organisms need different pH ranges The azalea plant thrives in acidic (4.5) soil and has a microorganism called Picrophilus that survives best at an extremely acidic pH of 0.7. o For all organisms, pH must be tightly controlled If your blood (pH between 7.35 and 7.45) has just a small change greater than 7.8 or less than 6.8, for even a short time, can be deadly.