Structure and Mechanism of Chymotrypsin
... Our understanding of enzyme catalysis has advanced steadily since x-ray diffraction results gave the first detailed information about the architecture of an enzyme molecule 10 years ago. The mechanism of chymotrypsin is probably understood in more detail than any other enzyme a t the present time. A ...
... Our understanding of enzyme catalysis has advanced steadily since x-ray diffraction results gave the first detailed information about the architecture of an enzyme molecule 10 years ago. The mechanism of chymotrypsin is probably understood in more detail than any other enzyme a t the present time. A ...
Lecture 2 * The Kinetics of Enzyme Catalyzed
... presents a very specific site to the substrate. • The reactive groups encountered in enzymes include the R group of Asp, Cys, Glu, His, Lys, Met, Ser, Thr, and the end amino and carboxyl functions. • Since the number of such groups near the substrate is typically 20, only a small fraction of the enz ...
... presents a very specific site to the substrate. • The reactive groups encountered in enzymes include the R group of Asp, Cys, Glu, His, Lys, Met, Ser, Thr, and the end amino and carboxyl functions. • Since the number of such groups near the substrate is typically 20, only a small fraction of the enz ...
Characterization of α-galactosidase belonging to family-4 glycoside hidrolases Bacillus halodurans
... expressed in Escherichia coli. The melA gene consists of 1305 nucleotides encoding a protein of 434 amino acids with a predicted molecular weight of 49,761. It was assigned to family 4 of glycoside hidrolases. Almost all of the enzyme was produced as inclusion bodies at 37oC. In order to reduce the ...
... expressed in Escherichia coli. The melA gene consists of 1305 nucleotides encoding a protein of 434 amino acids with a predicted molecular weight of 49,761. It was assigned to family 4 of glycoside hidrolases. Almost all of the enzyme was produced as inclusion bodies at 37oC. In order to reduce the ...
Fluorination with an Enzyme and Applications towards Positron
... The lecture will highlight the discovery and isolation of the only known fluorination enzyme so far in Nature. The structure and mechanism of the enzyme will be described and then our recent work in using the enzyme as a catalyst to form C-F bonds with the fluorine-18 isotope will be described. The ...
... The lecture will highlight the discovery and isolation of the only known fluorination enzyme so far in Nature. The structure and mechanism of the enzyme will be described and then our recent work in using the enzyme as a catalyst to form C-F bonds with the fluorine-18 isotope will be described. The ...
3 - IBperiod5
... 3.6.3 Explain the effects of temperature, pH and substrate concentration on enzyme activity. [Enzyme activity could be measured using data loggers such as pressure sensors, pH sensors, or coloromiters. The effects of environmental acid rain could be discussed.] Temperature and pH can change the shap ...
... 3.6.3 Explain the effects of temperature, pH and substrate concentration on enzyme activity. [Enzyme activity could be measured using data loggers such as pressure sensors, pH sensors, or coloromiters. The effects of environmental acid rain could be discussed.] Temperature and pH can change the shap ...
Enzymology: Catalase and Hydrogen Peroxide - UNCG GK-12
... to a specific protein. • Quaternary Structure: A structural level wherein several proteins interact through non-covalent bonds to form one functional protein complex (complex biological macromolecules, i.e. hemoglobin, DNA polymerases) ...
... to a specific protein. • Quaternary Structure: A structural level wherein several proteins interact through non-covalent bonds to form one functional protein complex (complex biological macromolecules, i.e. hemoglobin, DNA polymerases) ...
Enzymes: Molecules That Speed Up Reactions - juan-roldan
... which is the energy required to break down existing bonds between atoms Enzymes speed up two types of reactions: 1. Exergonic Reactions 2. Endergonic Reactions ...
... which is the energy required to break down existing bonds between atoms Enzymes speed up two types of reactions: 1. Exergonic Reactions 2. Endergonic Reactions ...
Slide - Journal of Vision
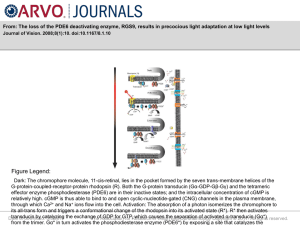
... G-protein-coupled-receptor-protein rhodopsin (R). Both the G-protein transducin (Gα-GDP-Gβ-Gγ) and the tetrameric effector enzyme phosphodiesterase (PDE6) are in their inactive states; and the intracellular concentration of cGMP is relatively high. cGMP is thus able to bind to and open cyclic-nucleo ...
... G-protein-coupled-receptor-protein rhodopsin (R). Both the G-protein transducin (Gα-GDP-Gβ-Gγ) and the tetrameric effector enzyme phosphodiesterase (PDE6) are in their inactive states; and the intracellular concentration of cGMP is relatively high. cGMP is thus able to bind to and open cyclic-nucleo ...
Enzyme Lab - Lessons-Worksheets-and-Such
... What would happen to your cells if they made a poisonous chemical? You might think that they would die. In fact, your cells are always making poisonous chemicals. They do not die because your cells use enzymes to break down these poisonous chemicals into harmless substances. Enzymes are proteins tha ...
... What would happen to your cells if they made a poisonous chemical? You might think that they would die. In fact, your cells are always making poisonous chemicals. They do not die because your cells use enzymes to break down these poisonous chemicals into harmless substances. Enzymes are proteins tha ...
UNIT 2: The Chemistry of Life
... Substances with a pH below 7 are called Acids. Substances with a pH above 7 are called Bases. Substances with a pH of 7 are called Neutral. We need to add one more detail to this scenario: The pH scale actually measures the amount of HYDROGEN IONS (H+) that are present in a solution. The lower the p ...
... Substances with a pH below 7 are called Acids. Substances with a pH above 7 are called Bases. Substances with a pH of 7 are called Neutral. We need to add one more detail to this scenario: The pH scale actually measures the amount of HYDROGEN IONS (H+) that are present in a solution. The lower the p ...
Enzyme Lab
... reaction as well. But what else might impact the rate of reaction? In this activity, you are the enzyme “Toothpickase.” The active sites are your hands and your function is to break any non-colored toothpick (the substrate) in half. Your goal is to break all non-colored toothpicks quickly and effici ...
... reaction as well. But what else might impact the rate of reaction? In this activity, you are the enzyme “Toothpickase.” The active sites are your hands and your function is to break any non-colored toothpick (the substrate) in half. Your goal is to break all non-colored toothpicks quickly and effici ...
amino acid
... polypeptide below? (Hint: count the R groups) How many peptide bonds are shown in the polypeptide below? (Hint: peptide bonds are between which two atoms?) How many water molecules were released as this polypeptide was formed? (Hint: one for each bond made!) ...
... polypeptide below? (Hint: count the R groups) How many peptide bonds are shown in the polypeptide below? (Hint: peptide bonds are between which two atoms?) How many water molecules were released as this polypeptide was formed? (Hint: one for each bond made!) ...
3+7 – HL Enzymes Page 1 1. Structure of Enzymes Like all proteins
... substrate can take part in the reaction, it has to gain energy = activation energy of the reaction. It is needed to break bonds within the substrate. During the progress of the reaction, energy is given out as new bonds are made. Enzymes reduce the activation energy of the reaction that they catalys ...
... substrate can take part in the reaction, it has to gain energy = activation energy of the reaction. It is needed to break bonds within the substrate. During the progress of the reaction, energy is given out as new bonds are made. Enzymes reduce the activation energy of the reaction that they catalys ...
enzymes 2016
... Reactions would still occur, but they would be too slow to support life 3. Fill in the table below describing the difference between pepsin and amylase. Enzyme ...
... Reactions would still occur, but they would be too slow to support life 3. Fill in the table below describing the difference between pepsin and amylase. Enzyme ...
N .B. Aschengreen PROTEOLYTIC ENZYMES USED FOR
... seen from figure 5 After this brief survey of factors, which are of importance, I suggest that we have a look at some useful enzymes. I have listed here in figure 6 a number of amylases, that is enzymes that break down starch, potato flour, corn starch, dextrins etc. I have in this table also includ ...
... seen from figure 5 After this brief survey of factors, which are of importance, I suggest that we have a look at some useful enzymes. I have listed here in figure 6 a number of amylases, that is enzymes that break down starch, potato flour, corn starch, dextrins etc. I have in this table also includ ...
Extra slides (lecture Wed. 11/4)
... • carbocation stabilized by • oxonium resonance, promoted by binding the sugar ring in a half-chair configuration • then by covalent bond to Asp 52 • 2nd half of the reaction is the reverse of the first • H20 displaces the leaving sugar • Glu 35 now acts as a base to accept proton from H20, which be ...
... • carbocation stabilized by • oxonium resonance, promoted by binding the sugar ring in a half-chair configuration • then by covalent bond to Asp 52 • 2nd half of the reaction is the reverse of the first • H20 displaces the leaving sugar • Glu 35 now acts as a base to accept proton from H20, which be ...
Enzyme Kinetics - NC State: WWW4 Server
... where W is the number of degrees of freedom available to a molecule. ...
... where W is the number of degrees of freedom available to a molecule. ...
Enzymes - Mr. hawkins
... The enzyme remains unchanged at the end of reaction and is free to interact again with more substrate. ...
... The enzyme remains unchanged at the end of reaction and is free to interact again with more substrate. ...
Basic Enzyme Kinetics
... of regulated enzymes. Thus when a substrate binds to one of the subunits, a conformational change occurs which increases the binding affinity for the remaining vacant bindings on the other subunits. There are a number of mechanistic models which can account for cooperative behavior but for the purpo ...
... of regulated enzymes. Thus when a substrate binds to one of the subunits, a conformational change occurs which increases the binding affinity for the remaining vacant bindings on the other subunits. There are a number of mechanistic models which can account for cooperative behavior but for the purpo ...
Enzymes Review Packet
... i) Enzymes are biological ………………… that speed up chemical reactions in living organisms. ii) Enzymes are protein molecules, which are made up of long chains of ………...………. iii) The sequence and type of amino acids are ………………… in each protein, so they produce enzymes with many different shapes and func ...
... i) Enzymes are biological ………………… that speed up chemical reactions in living organisms. ii) Enzymes are protein molecules, which are made up of long chains of ………...………. iii) The sequence and type of amino acids are ………………… in each protein, so they produce enzymes with many different shapes and func ...
File - need help with revision notes?
... substrate molecules is greater than the number of inhibitor molecules, the level of inhibition decreases, because the enzyme is more likely to collide with a substrate molecule than with an inhibitor molecule. The rate of reaction with a non competitive inhibitor present is reduced; there are fewer ...
... substrate molecules is greater than the number of inhibitor molecules, the level of inhibition decreases, because the enzyme is more likely to collide with a substrate molecule than with an inhibitor molecule. The rate of reaction with a non competitive inhibitor present is reduced; there are fewer ...
CATALASE ENZYME PRE
... process that often requires several chemical steps, and may involve covalent bonds. Finally, the products are released into solution and the enzyme is ready to form another enzyme-substrate complex. As is true of any catalyst, the enzyme is not used up as it carries out the reaction but is recycled ...
... process that often requires several chemical steps, and may involve covalent bonds. Finally, the products are released into solution and the enzyme is ready to form another enzyme-substrate complex. As is true of any catalyst, the enzyme is not used up as it carries out the reaction but is recycled ...
Enzymes
... then they use the so-called “activity” of the enzyme, as a unit of effectiveness. This actually means reaction velocity, under precisely known and controlled conditions. It tells us how much S can be converted (or P be generated) by the actual amount of E present in solution, (generally) at the satu ...
... then they use the so-called “activity” of the enzyme, as a unit of effectiveness. This actually means reaction velocity, under precisely known and controlled conditions. It tells us how much S can be converted (or P be generated) by the actual amount of E present in solution, (generally) at the satu ...
Isomerase

Isomerases are a general class of enzymes which convert a molecule from one isomer to another. Isomerases can either facilitate intramolecular rearrangements in which bonds are broken and formed or they can catalyze conformational changes. The general form of such a reaction is as follows:A–B → B–AThere is only one substrate yielding one product. This product has the same molecular formula as the substrate but differs in bond connectivity or spatial arrangements. Isomerases catalyze reactions across many biological processes, such as in glycolysis and carbohydrate metabolism.