Bio1A Unit 1-5 Metabolism Notes File
... Metabolism Metabolic Pathway: series of steps from reactants to products, usually enzyme catlyzed Enzyme 1 A ...
... Metabolism Metabolic Pathway: series of steps from reactants to products, usually enzyme catlyzed Enzyme 1 A ...
Physiology Lecture Outline: Enzymes
... enzymes are involved) and they are transformed into products. All enzymes are proteins with specific 3-D shapes and they contain small regions where substrates bind to the enzyme called the active site. Enzymes carry out catalysis by binding to substrate molecules and bringing them close together an ...
... enzymes are involved) and they are transformed into products. All enzymes are proteins with specific 3-D shapes and they contain small regions where substrates bind to the enzyme called the active site. Enzymes carry out catalysis by binding to substrate molecules and bringing them close together an ...
Intro metabolism
... b. ATP can in turn donate a phosphate group to another molecule, which then becomes primed and energized for specific reactions. 2. ATP's role is like currency in an economy: earning ATP during exergonic reactions and spending it during endergonic ones. 3. ADP can be recycled to ATP very rapidly in ...
... b. ATP can in turn donate a phosphate group to another molecule, which then becomes primed and energized for specific reactions. 2. ATP's role is like currency in an economy: earning ATP during exergonic reactions and spending it during endergonic ones. 3. ADP can be recycled to ATP very rapidly in ...
Cardiff International School Dhaka (CISD) Lost Class Make Up
... (b) Heavy metals (Ag, Hg, TI), ions react with one or more sulfhydryl groups, replacing the hydrogen atom with a metal ion. Q2. (a) At temperatures between 0o C and about 40 o C the rate of enzyme activity increases with temperature. Enzyme activity decreases markedly above 40 o C. (b) As temperatur ...
... (b) Heavy metals (Ag, Hg, TI), ions react with one or more sulfhydryl groups, replacing the hydrogen atom with a metal ion. Q2. (a) At temperatures between 0o C and about 40 o C the rate of enzyme activity increases with temperature. Enzyme activity decreases markedly above 40 o C. (b) As temperatur ...
Enzyme Review Sheet
... Activation energy is often supplied in the form of heat that the reactants absorb from their environment. The chemical bonds will only break if they absorb enough heat to become unstable. Each reaction requires a specific amount of activation energy. Sometimes just the room temperature or body tempe ...
... Activation energy is often supplied in the form of heat that the reactants absorb from their environment. The chemical bonds will only break if they absorb enough heat to become unstable. Each reaction requires a specific amount of activation energy. Sometimes just the room temperature or body tempe ...
digestion - Manhasset Schools
... A catalyst is any substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction. Enzymes are specialized protein catalysts that control metabolic activities like hydrolysis (digestion), synthesis, cellular respiration and photosynthesis. Enzymes have specific shapes which allow them to bind to the reacta ...
... A catalyst is any substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction. Enzymes are specialized protein catalysts that control metabolic activities like hydrolysis (digestion), synthesis, cellular respiration and photosynthesis. Enzymes have specific shapes which allow them to bind to the reacta ...
File
... • The function of any proteins is dependent upon its overall shape • When a protein is denatured, the intermolecular bonds are broken, compromising the shape of the protein, and thereby losing its function. ...
... • The function of any proteins is dependent upon its overall shape • When a protein is denatured, the intermolecular bonds are broken, compromising the shape of the protein, and thereby losing its function. ...
Here - Sycamore
... glucose-6-phosphate -> fructose-6-phosphate 1. You are querying for the Km value of the substrate of the glucose-6phosphate isomerase from Homo sapiens. 2. Insert the SwissProt identifier for that enzyme (P06744). 3. In Structural Information, 30 homologuous protein structures are found in the PDB w ...
... glucose-6-phosphate -> fructose-6-phosphate 1. You are querying for the Km value of the substrate of the glucose-6phosphate isomerase from Homo sapiens. 2. Insert the SwissProt identifier for that enzyme (P06744). 3. In Structural Information, 30 homologuous protein structures are found in the PDB w ...
Enzymes
... speed of a chemical reaction by lowering the energy requirement • Although a catalyst influences a chemical reaction, it is not itself permanently changed, nor does it cause the reaction to occur. • A catalyst can increase the rate of a chemical reaction but cannot cause the reaction . ...
... speed of a chemical reaction by lowering the energy requirement • Although a catalyst influences a chemical reaction, it is not itself permanently changed, nor does it cause the reaction to occur. • A catalyst can increase the rate of a chemical reaction but cannot cause the reaction . ...
Proteins
... -enzymes have a specific pocket or site where the substrate can fit and interact -the specificity of the enzyme is dependent upon its active site ...
... -enzymes have a specific pocket or site where the substrate can fit and interact -the specificity of the enzyme is dependent upon its active site ...
unit 2c File - Uddingston Grammar School
... Hydrolysis is the breaking down of a large molecule into smaller molecules using water. ...
... Hydrolysis is the breaking down of a large molecule into smaller molecules using water. ...
6.3 Enzymes and Nucleic Acids ~ powerpoint
... papain – derived from raw papaya, broad range of substrates and pH, works well breaking down small and large proteins ...
... papain – derived from raw papaya, broad range of substrates and pH, works well breaking down small and large proteins ...
1. What are enzymes? Be able to describe the chemical nature of
... requires a chemical reaction that splits off part of the molecule. Genetic (enzyme) control: Regulation of enzyme activity by hormonal control of the synthesis of enzymes is especially useful for enzymes needed only at certain times. ...
... requires a chemical reaction that splits off part of the molecule. Genetic (enzyme) control: Regulation of enzyme activity by hormonal control of the synthesis of enzymes is especially useful for enzymes needed only at certain times. ...
Enzyme Reading - BizierDiemHonorsBiology
... A substrate binds to an enzyme at an active site. The enzyme-substrate interaction lowers the activation energy required for the reaction to proceed. In this example, water is added to the weakened bond in sucrose, breaking sucrose into glucose and fructose. ...
... A substrate binds to an enzyme at an active site. The enzyme-substrate interaction lowers the activation energy required for the reaction to proceed. In this example, water is added to the weakened bond in sucrose, breaking sucrose into glucose and fructose. ...
Biological Molecules: What are the building blocks of life?1
... Carboxylic group, Amine group and a Variable R side chain 10. There are 20 naturally-occurring amino acids, and each one only varies in the structure of the R side chain. Two amino acids are shown in Model 1. What are the R side chains in each? ...
... Carboxylic group, Amine group and a Variable R side chain 10. There are 20 naturally-occurring amino acids, and each one only varies in the structure of the R side chain. Two amino acids are shown in Model 1. What are the R side chains in each? ...
* Proteins, or polypeptides, are polymers made of monomers called
... * Proteins, or polypeptides, are polymers made of monomers called amino acids *There are 20 different amino acids, so there are many varieties of proteins. * They are found hair, nails, muscle, bone and in foods like meats, cheeses, and peanuts. ...
... * Proteins, or polypeptides, are polymers made of monomers called amino acids *There are 20 different amino acids, so there are many varieties of proteins. * They are found hair, nails, muscle, bone and in foods like meats, cheeses, and peanuts. ...
Enzyme Kinetics Lab
... Enzymes are a class of proteins that greatly speed up (catalyze) reactions between specific substances, usually at their functional groups. The substances that each type of enzyme acts upon are called its substrates. Enzymes have four common features: 1. They don’t make anything happen that couldn’t ...
... Enzymes are a class of proteins that greatly speed up (catalyze) reactions between specific substances, usually at their functional groups. The substances that each type of enzyme acts upon are called its substrates. Enzymes have four common features: 1. They don’t make anything happen that couldn’t ...
Macromolecules Lab 1
... enzymes! Enzymes are made from amino acids, and they are proteins. When an enzyme is formed, it is made by stringing together between 100 and 1,000 amino acids in a very specific and unique order. The chain of amino acids then folds into a unique shape. That shape allows the enzyme to carry out spec ...
... enzymes! Enzymes are made from amino acids, and they are proteins. When an enzyme is formed, it is made by stringing together between 100 and 1,000 amino acids in a very specific and unique order. The chain of amino acids then folds into a unique shape. That shape allows the enzyme to carry out spec ...
what are enzymes
... our muscles, nerves, and bones would not work properly. Essentially, we would not be living! ...
... our muscles, nerves, and bones would not work properly. Essentially, we would not be living! ...
CHAPTER 4: Enzyme Structure
... Up to the optimum temperature the rate increases geometrically with temperature (i.e. it's a curve, not a straight line). The rate increases because the enzyme and substrate molecules both have more kinetic energy and so collide more often, and also because more molecules have sufficient energy to o ...
... Up to the optimum temperature the rate increases geometrically with temperature (i.e. it's a curve, not a straight line). The rate increases because the enzyme and substrate molecules both have more kinetic energy and so collide more often, and also because more molecules have sufficient energy to o ...
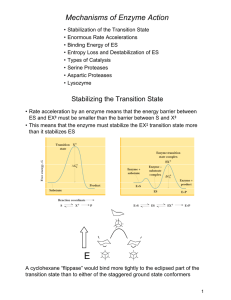
Mechanisms of Enzyme Action - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... • Lysozyme hydrolyzes polysaccharide chains and ruptures certain bacterial cells by breaking down the cell wall • Hen egg white enzyme has 129 residues with four disulfide bonds • The first enzyme whose structure was solved by X-ray crystallography (by David Phillips in 1965) ...
... • Lysozyme hydrolyzes polysaccharide chains and ruptures certain bacterial cells by breaking down the cell wall • Hen egg white enzyme has 129 residues with four disulfide bonds • The first enzyme whose structure was solved by X-ray crystallography (by David Phillips in 1965) ...
Reading GuideMetabolismchapter6
... be made by bacterial cells in one of three ways, substrate level phosphorylation, oxidative phosophorylation, or photophosphorylation. Which of these three methods is how cells make ATP within a metabolic pathway such as glycolysis by the transfer of a phosphate group from an organic compound to ADP ...
... be made by bacterial cells in one of three ways, substrate level phosphorylation, oxidative phosophorylation, or photophosphorylation. Which of these three methods is how cells make ATP within a metabolic pathway such as glycolysis by the transfer of a phosphate group from an organic compound to ADP ...
Today: Membrane Structure continued Membrane Transport Exam
... The Chemistry of Life is driven by more than Thermodynamics! ...
... The Chemistry of Life is driven by more than Thermodynamics! ...
Isomerase

Isomerases are a general class of enzymes which convert a molecule from one isomer to another. Isomerases can either facilitate intramolecular rearrangements in which bonds are broken and formed or they can catalyze conformational changes. The general form of such a reaction is as follows:A–B → B–AThere is only one substrate yielding one product. This product has the same molecular formula as the substrate but differs in bond connectivity or spatial arrangements. Isomerases catalyze reactions across many biological processes, such as in glycolysis and carbohydrate metabolism.